Table of Contents

I am sure that you are reading this guide and you are confused about “Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet”. Through this article, you will have a clear understanding of the difference between them. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet?
Before you can understand the difference between eyele, grommet and rivet, you need to understand what they are.
What Are Eyelets?
Eyelet is a small metal or plastic ring fitting typically used to reinforce holes in fabric, paper, leather, or other materials to prevent those materials from tearing or fraying during use. When Eyelet is installed, the edges around the holes are usually crimped and used to enhance the durability of the holes while providing a neat appearance.
Eyelets are commonly used for decorating and fixing holes in clothing, stationery and crafts.

What Are Grommets?
A Grommet is a ring-shaped fitting that is typically used to reinforce holes in fabric, leather, metal, or other materials to prevent the material from tearing, fraying, or being damaged. Similar to Eyelet, Grommet is usually made of metal, rubber, or plastic, but is typically larger and stronger than Eyelet, and is used in applications that require more strength and durability.

What Are Rivets?
Rivets are mechanical fasteners used to permanently secure two or more materials together. Installation is accomplished by drilling holes in the material, inserting rivets into the holes, and then compressing or expanding the other end of the rivet to tightly join the materials together. Rivets are commonly used in structures that require a strong, durable connection, such as the fastening of metal, wood or plastic materials.

8 Differences Between Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet
| Attribute | Rivet | Eyelet | Grommet |
| Primary Purpose | Used for permanent connection of two or more materials. | Used to reinforce holes to prevent tearing of fabric, paper, etc. | Reinforces holes and protects cables or ropes from wear. |
| Material | Metal (aluminum, stainless steel, copper, etc.) | Metal (copper, brass, stainless steel, etc.) or plastic | Metal (stainless steel, aluminum, etc.), plastic, rubber |
| Installation Method | Fixed by mechanical deformation, usually with a rivet gun or hammer. | Typically fixed by rolling edges using a press tool. | Fixed by rolling or pressing, requires a special tool. |
| Structure | Has a head and shank; the shank is deformed or expanded to secure the materials. | A small ring that surrounds a hole and is secured by rolling its edges. | Larger and thicker ring used to surround and protect holes. |
| Suitable Materials | Metal, wood, plastic, or other materials requiring strong connections. | Fabric, paper, leather, and other lightweight materials. | Fabric, rubber, plastic, leather, and heavy-duty materials. |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, automotive, construction, and other fields requiring high-strength connections. | Clothing, shoes, stationery, often for decorative or reinforcing purposes. | Cable management, tents, sails, banners, industrial equipment. |
| Connection Strength | High: Suitable for high-load, high-stress structures. | Low to medium: Used for lightweight material reinforcement. | Medium to high: Used where durability and protection are needed. |
| Removal | Non-removable: Permanent connection, must be destroyed to remove. | Easily removable: Often for temporary or light connections. | Removable, but typically designed as semi-permanent. |
| Visual Effect | After riveting, a head is formed on both sides, generally not aesthetic-focused. | Forms a decorative ring, often for both appearance and function. | Larger ring, used primarily for functional protection. |
1. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Primary Purpose
- Rivets: used for permanent structural connections and suitable for high strength applications. Once completed, these connections are difficult to dismantle and are therefore used in structures that require long-term fixing.
- Eyelets: Used for hole reinforcement in lightweight materials, often also decorative.
- Grommet: used for hole protection in heavy materials, especially when cables or ropes need to be passed through to provide additional protection.
2. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Material
Rivet: Usually made of metal, such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, carbon steel, etc.. Applications using rivets usually have certain requirements for strength and durability, so it is often used for heavy-duty and structural connections.
Eyelet: Materials include metals and plastics, used for reinforcement and decoration of lightweight materials, with a greater focus on aesthetics and lightness.
Gtommet: Diverse range of materials, including metal, rubber and plastic, mainly used for hole reinforcement and protection. Particularly suitable for wear and corrosion resistant scenarios. For example, cable management or waterproof sealing.
3. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Installation Method
| Category | Rivet | Eyelet | Grommet |
| Installation Tools | Rivet gun, hammer | Manual press tool, punch tool, eyelet pliers | Punch tool, press tool |
| Installation Method | Insert into materials, deform rivet tail to form a permanent connection | Press and roll edges to secure, mostly for decorative and light material reinforcement | Press two parts to secure around the hole, primarily for heavy-duty material protection |
| Suitable Materials | Metal, wood, plastic, and other hard materials | Fabric, leather, paper, and other lightweight materials | Fabric, rubber, plastic, and other thick or heavy materials |
| Connection Strength | High strength, non-removable permanent connection | Medium strength, suitable for light decorative applications | Medium to high strength, ideal for cable and rope protection |
- The process of rivet installation requires the use of specialized tools, such as pneumatic rivet guns, manual rivet guns.
- Eyelets are simpler to install and can be done quickly with hand tools.
- Grommet is used to protect the holes and requires the use of punching tools and press fit tools to complete.
4. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Structure
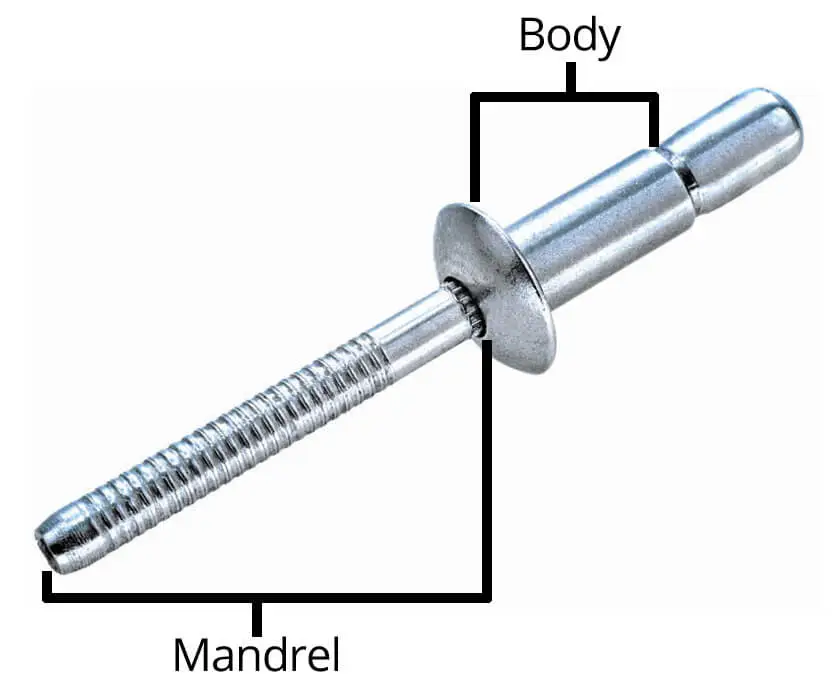
The structure of a rivet consists of two parts: the rivet body and the rivet mandrel. different types of rivets have different structures on the rivet mandrel, for example, some have a lot of rubbing and some have vertical rubbing.
An eyelet consists of a circular hole with a shorter raised edge, usually a simple metal or plastic ring. It has a rolled edge on one side and a smooth ring on the other. Its construction is very simple.
The Grommet also consists of two parts, an inner ring and an outer ring, which are snapped or pressed into each other to encircle the hole. Both the outer and inner rings of the grommet are thicker, providing more strength and protection.
5. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Suitable Materials
- Rivets are very much applicable in industry. It is perfect for linking metal, wood, plastic and other hard materials.
- Eyelet is widely used in lightweight materials such as fabric, leather and paper. It is commonly used in areas such as clothing and footwear.
- Grommet is suitable for thick or industrial materials such as thick canvas, plastics, thick leathers
6. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Common Applications
Eyelet is lightweight and suitable for decorative purposes. Frequently applied eyelet places include the following:
- Clothing and textiles: in shoelace holes, belt holes, handbags, etc.
- Paper products: used in stationery such as folders, cards or labels to enhance the durability of paper holes.
- Lightweight materials: typically applied to thin and soft materials such as leather, canvas or plastic.
Grommet’s primary function is to reinforce holes, prevent pulling and cracking, and provide greater abrasion resistance. It is commonly used in the following scenarios:
- Industrial use: cable management, hose hole protection, preventing wires or cords from abrading the material.
- Outdoor equipment and canvas: holes in tents, sails, flags and tarps for enhanced durability and tensile strength.
- Heavy duty materials: canvas, plastic, leather or rubber.
The use of rivets is very wide, basically all kinds of industrial products or assembly line products can be applied rivets to fix. The following are a few common applications:
- Metal structures: such as aircraft fuselages, bridges, building steel structures, etc.
- Appliances and electronics: used to fix the shell and internal parts, such as home appliances, computers and other consumer electronics.
- Automotive manufacturing: rivets are used in body panels, chassis and other important connection parts.
7. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Connection Strength
The strengths of eyelet, grommet and rivet are in descending order: rivet>grommet>eyelet. according to their different strengths, the application scenarios are also different. For example, eyelet is a lighter material because of its low strength, while rivet has high strength and is ideal for high-strength applications with permanent connections.
8. Eyelet vs Grommet vs Rivet: Removal
| Fastener Type | Removal Difficulty | Removal Method | Reusability |
| Eyelet | Easy | Pry open with pliers or screwdriver, or cut around the material | Typically not reusable |
| Grommet | Moderate | Pry open with screwdriver or pliers, or cut with shearing tools | Typically not reusable |
| Rivet | Difficult | Drill out rivet head or cut with metal snips, then punch out the rivet tail | Not reusable |

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
Finding the right fastener for your project takes a lot of work. eyelet, grommet, rivet all have their own application scenarios. If your project requires the application of rivet to do the connecting work, please contact us!
You can get satisfied with rivet solutions at Rivmate, request a quote to get the best rivet solution for your project and get started on your project.



