Table of Contents
Why does rivet have a tail? Do you know what the purpose of a rivet tail is? By reading this post, you will learn everything you need to know about rivet tails. This includes the types of rivet tails as well as the reasons and types of rivet tails that exist. Let’s explore this together!
Table of Contents
What is the Tail of a Rivet? (Rivet Tail)
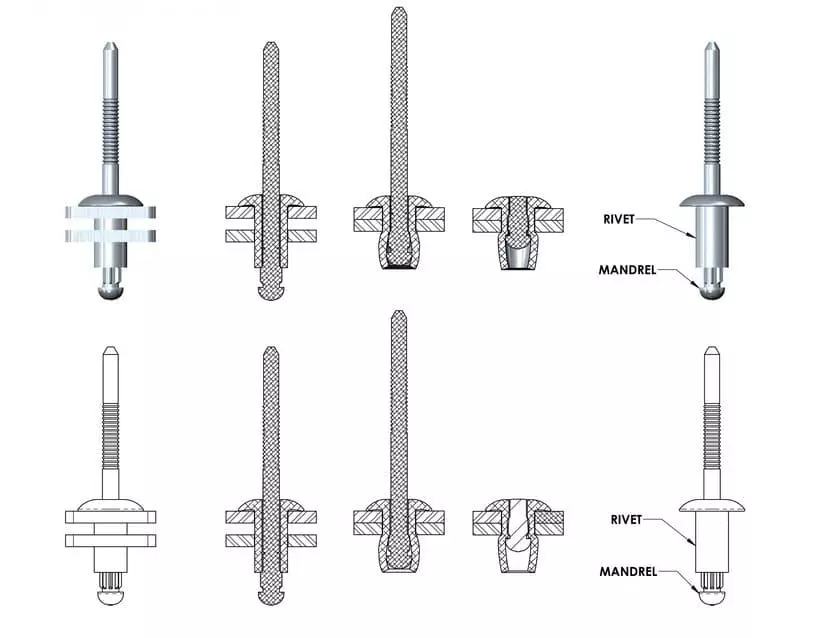
Blind Rivet is composed of two parts: 1. Rivet body (rivet tail) 2. Rivet mandrel. Rivet tail is an important part of the Blind Rivet.Rivet tail is the part of the rivet formed after the deformation of the rivet in the assembly process, its main role is to fix the riveted parts and provide the mechanical strength of the connection.

Blind Rivets are the key part of the riveting process where the rivet tail and rivet head are pressed against each other to secure the materials to be joined. The rivet tail is the key element in the riveting process. It is deformed by expansion or compression to create a stable fastening effect.
Why Does Rivet Have a Tail?
From the above information, I think you already know that rivets are made up of a rivet tail and a rivet mandrel. So why do rivets need to have rivet tails in their design and how does the Rivet tail play a role in the riveting process?The Rivet tail is the key to the rivet’s ability to make a strong connection.Its presence allows the rivet to provide long-lasting mechanical support during the assembly process, spread the load, and ensure vibration resistance and durability of the connection.The Rivet tail is the key to the rivet’s ability to achieve a strong connection. Here’s why and what it does:
1. Provide a Strong Mechanical Connection
Rivets form a locking structure through the deformation of their tails. This structure ensures that the rivet cannot be loosened from the hole, thus holding the joined workpieces firmly together.
- The Rivet Tail presses against the back of the workpiece to create a clamping force for permanent riveting.
- The strength of the joint is supported by the head and tail of the rivet, with additional support provided by the deformation of the tail.

2. Distribute the Load and Protect the Connecting Material
The deformation of the Rivet tail will increase the contact area between the rivet and the workpiece, thus effectively dispersing the concentrated load and avoiding excessive local stresses.
- The ‘cap edge’ or ‘flap’ formed at the end of the rivet tail can reduce the shear or compressive stress on the connected material.
- Particularly suitable for joining thin or soft materials to prevent tearing or damage to the material.
3. Ensure Vibration Resistance of the Connection
The deformation of the Rivet tail will tightly adhere to the surface of the workpiece, which effectively prevents the rivet from loosening or falling out under high vibration or dynamic loads.
- The Rivet tail provides additional tightening force to prevent the connection from loosening due to prolonged use or vibration.
- In high vibration environments (e.g. automotive, aerospace equipment), the deformed tail structure enhances the durability of the connection.
4. Improved Shear and Tensile Resistance

Unlike screws, the deformed structure of the Rivet tail allows the rivet to withstand higher shear and tensile forces.
- The rivet tail, by plastic deformation close to the workpiece, can withstand external shear forces, thus enhancing the overall strength of the joint.
- It resists pull-out forces and ensures that the workpiece will not come loose under external forces.
5. Simplifies the Installation Process
Deformation of the Rivet tail allows the rivet to form a tight connection. There is no need to use nuts or washers at all, which greatly simplifies the installation process.
- The connection is made by simple pulling of the rivet and is suitable for one-sided operation.
- This improves installation efficiency, especially in confined spaces or mass production.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
The Process of Rivet tail Formation
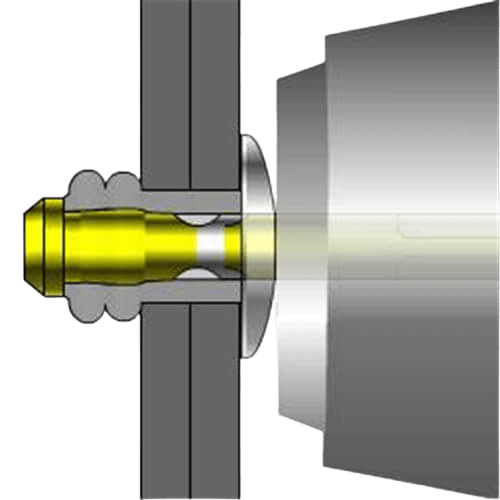
The process of forming the Rivet tail represents the process of forming a complete fastening of the rivet. Below is the process of rivet tail formation.
- Insertion of the rivet: The tail of the rivet is first inserted into the hole of the workpiece to be joined, with the head of the rivet flat against the side of the workpiece.
- Applying Tension: A rivet gun is used to stretch the core of the rivet, causing the tail to expand and compress the workpiece.
- Tail deformation fixation: The tail of the rivet deforms plastically after the application of force to form a mushroom, cone or other shaped structure that is firmly attached to the workpiece.
Types of Rivet Tails
There are several different types of rivet tails when forming a stable connection with a blind rivet.
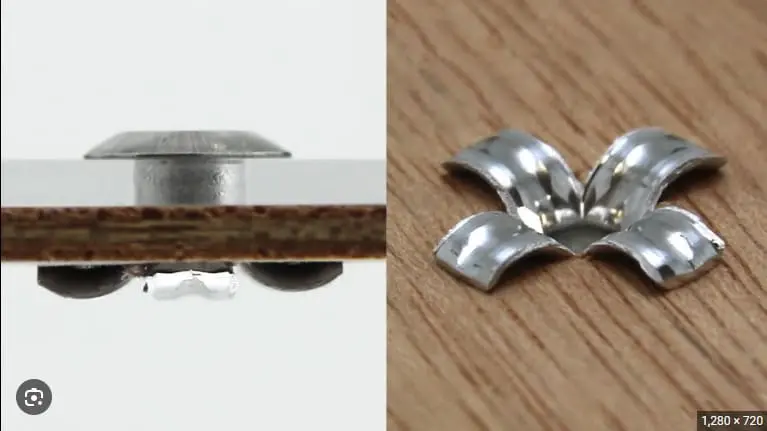
- Mushroom Tail: A round cap-like structure formed by the expansion of the rivet tail. The rivet tail is formed into a round tail when a standard blind rivet is installed. This type of rivet tail provides a larger contact area and distributes pressure.
- Flared Tail: The tail of the rivet expands outward to form a petal-like structure, commonly found in Peel type blind rivets and tri fold rivets.Blind rivets that can form a flared tail are ideal for joining thinner or softer materials, as this structure prevents the material from being damaged by stress.
- Locking Tail: In structural blind rivets, the tail is locked to the rivet core to form a high strength connection. This type of rivet tail provides a fixing that is resistant to vibration and high tensile forces.

Tips of Choosing the Types of Rivet Tails
Which specific rivet tails are right for your project? There are really three main things to consider:
- Material compatibility: rivet tail deformation requires sufficient toughness, the material should be adapted to the hardness of the connected workpiece to avoid inadequate deformation or damage to the workpiece.
- Tail size and shape: the final shape of the rivet tail determines the firmness of its connection and anti-shear performance, need to choose the appropriate tail type according to the application scenario.
- Installation Tools and Methods: Different rivet types require matching tools to form the tail. For example, standard blind rivets and structural rivets use different types of rivet guns.
Wholesale Blind Rvets from Top Rivet Manufacturer
Why does rivet have a tail?
By reading this guide, I’m sure you know the definition and type of rivet tail. If you want to choose the right rivet tail for your project, pleasecontact our engineers.
Get rivet samples to enhance your business now!



