Table of Contents
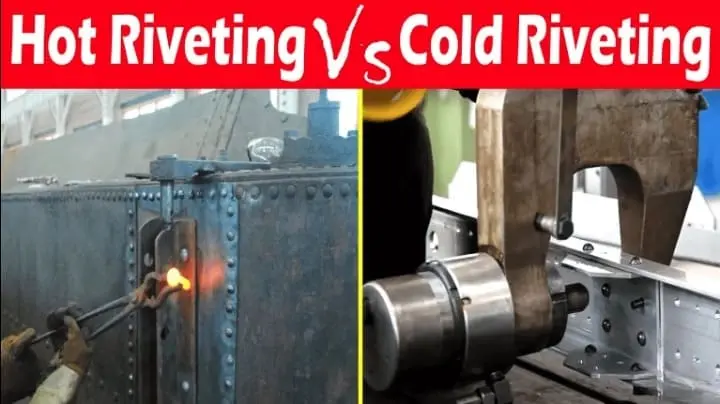
If you want to upgrade your riveting system, you have to know about hot riveting and cold riveting.Understand the difference between hot riveting and cold riveting to make the right choice for your project.
Table of Contents
In this blog post, we will explore the difference between hot riveting and cold riveting. You will also learn about the advantages of hot riveting and cold riveting. So, let’s dive in.
What is Cold Riveting?
Cold Riveting is a common method of joining metals. This joining method utilizes mechanical forces to plastically deform rivets at room temperature to achieve a permanent connection between metal parts. Unlike hot riveting, cold riveting does not require the rivet to be heated, does not damage the surface of the material and does not generate thermal stresses.
Cold riveting is accomplished by applying mechanical force to press the rivet into a pre-drilled hole, which deforms the rivet stem and creates a strong connection. The process involves the following steps:
- Drilling: Drill holes matching the diameter of the rivet in the metal parts to be joined.
- Inserting the rivet: Insert the rivet into the drilled hole, with the stem of the rivet passing through all layers of the metal to be joined.
- Applying Pressure: Pressure is applied using a riveting tool (such as a manual rivet gun, pneumatic rivet gun or hydraulic riveting machine) to deform the rivet stem and form the locking head.
- Fixed Connection: The deformed portion of the rivet stem holds two or more pieces of metal tightly together to form a reliable mechanical connection.
It should be noted that engineers should choose the appropriate riveting tool according to the type and size of rivets, to ensure that the tool performance meets the requirements, regular inspection and maintenance of the tool. Compatibility between materials is also important to avoid problems caused by galvanic corrosion and differences in coefficients of thermal expansion.
Advantages of Cold Riveting
Cold riveting is a high quality and non-polluting joining method. Here are some of its advantages:
1. No Thermal Influence
Cold riveting generates essentially no heat during the installation process. This type of joining maintains material properties. Cold riveting is carried out at room temperature and does not involve heating operations, so it does not affect the metallurgical structure and mechanical properties of the materials being joined. The material maintains its original strength and toughness during the riveting process. Engineers only need a special rivet gun, you can well complete the whole process of cold riveting.
2. Easy and Fast Operation

Traditional hot riveting requires specialized high temperature equipment to complete the riveting process. Cold riveting does not require specialized heating equipment and is relatively simple to operate, making it ideal for on-site and large-scale production.The process of cold riveting is very fast and can effectively increase productivity.
And the tools that can be used are varied. The use of manual rivet gun, pneumatic rivet gun or hydraulic riveting machine and other tools can be completed, the cost of equipment is low.
3. Wide Application
Cold riveting allows for the joining of a wide range of materials due to the lack of thermal influence. These include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper and titanium. It can also be used to join dissimilar materials. Therefore, cold riveting can be used in a wide range of applications. Cold riveting is used in many fields such as aerospace, automotive, construction, household appliances and shipbuilding.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
What is Hot Riveting?
Hot Riveting is a metal joining technique in which rivets are heated to a high temperature and then riveted. This joining technique utilizes the contraction force of the heated rivet as it cools to form a strong mechanical joint. It typically involves heating the rivets to 1000°F – 2000°F.
Hot riveting shrinks rapidly as it cools and simply locks the joining material in place. Hot riveting provides an extremely strong joint compared to cold riveting. It provides a more secure connection for heavy equipment.
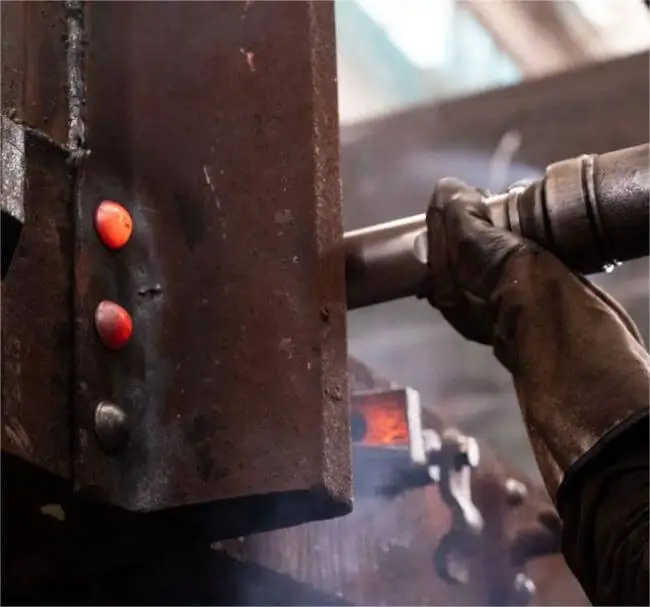

Hot riveting also perfectly fills the gaps between the holes and ensures a tight connection between the materials. Of course, hot riveting is more demanding for engineers, you need to follow the standard operating procedures to complete the process of hot riveting. Otherwise, it is very likely to cause riveting failure.
Advantages of Hot Riveting
Hot Riveting is a riveting technique that utilizes high temperatures to plastically deform the rivet and create a contraction force during cooling to achieve fastening. Hot riveting offers a variety of advantages and is particularly suited to connections that require high strength and durability. The following are the main advantages of hot riveting:
1. High Strength Connections
Hot riveting provides a very strong mechanical connection by shrinking and clamping the rivet tightly to the material being joined during the cooling process. The strength of this connection is great, so Hot riveting is suitable for applications subject to high loads and stresses.
The heated rivets have good plasticity, which allows them to deform uniformly and fill the voids in the holes, creating a tight mechanical lock.
2. Residual Stress Relief

The contraction of the rivet during heating and cooling removes some of the residual stresses, reducing the risk of material fatigue and cracking due to stress concentrations. And through high temperature treatment, some of the internal stresses can be released or redistributed during the riveting process, improving the overall stability of the joint.
3. Reliable Long-term Durability
The high strength connection and tight locking of hot riveting provides stability and durability over a long period of time, making it suitable for structures that need to maintain a strong connection over a long period of time.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
What Scenarios are Each of These Two Types of Riveting Suitable for?
Cold riveting is suitable for joining scenarios where fast, efficient and economical joining is required. Examples include automotive manufacturing, aerospace, household appliances, building and construction, shipbuilding and general metal structures. Its simplicity, lack of thermal impact and environmental friendliness make it particularly suitable for high-volume production and on-site operations.
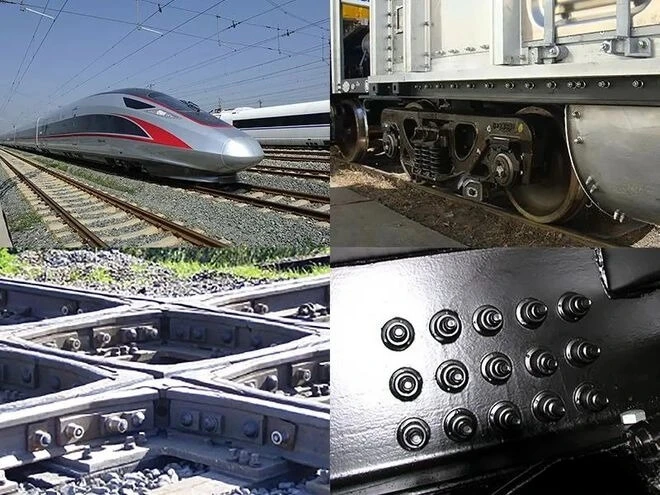
Hot riveting is suitable for joining scenarios where high strength, durability and reliability are required. Examples include bridges and infrastructure, aerospace, shipbuilding, construction, rail and rail transit, and heavy machinery. Its high-strength connections, long-term durability and good filler characteristics make it widely used in heavy structures and highly stressed components.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
Difference Between Hot Riveting and Cold Riveting
While both hot riveting and cold riveting are used to join metals, there are significant differences between them. The differences between the two types of riveting allow them to be used in different scenarios. Here are the difference between hot riveitng and cold riveting.
| Point of Difference | Hot Riveting | Cold Riveting |
| Equipment Requirement | Heating equipment (such as flame heaters or induction heaters) and riveting tools are required. | Only ambient riveting tools such as manual rivet guns, pneumatic rivet guns or hydraulic riveting machines are required. |
| Pros | 1. Provides very high connection strength 2. Good pore filling capacity 3. Eliminate some residual stresses | 1. Easy to operate 2. No thermal influence 3. Environmentally friendly 4. Fast and efficient, suitable for mass production |
| Economy and Efficiency | 1. Higher cost 2. Longer operation time | 1. Lower cost 2. Easy and quick to operate |
| Environmental Impact | High-temperature operation may generate exhaust gases and thermal pollution. | No waste gas and heat pollution generated by high temperature, in line with environmental requirements. |
| Residual Stress | Some residual stresses may be removed during high temperature treatment and cooling. | Cold working may produce some residual stresses. |
difference between hot riveting and cold riveting
1. Equipment Requirement
Hot riveting is installed with the aid of heating equipment. For example, flame heaters or induction heaters. In addition to the heating equipment, special riveting tools are required to complete the installation of the heated rivets. cold riveting is different, it only requires the use of riveting tools to complete the entire installation process.
2. Pros
Hot riveting provides very high joint strength, which is not possible with cold riveting. hot riveting has good pore filling and eliminates some residual stresses. cold riveting does not have the same characteristics as hot riveting, but cold riveting does not have a thermal effect, which reduces the risk of material damage. Reduces the risk of material damage. Cold riveting is also a very fast joining method and is suitable for mass production.
3. Economy and Efficiency
The cost of hot riveitng is high compared to cold riveitng.
4. Environmental Impact
Hot riveting requires high temperatures to operate, which results in the generation of exhaust gases and thermal pollution, which is not generated by cold riveting. Cold riveting does not produce these pollutants and meets international environmental standards.
5. Residual Stress
Residual stresses are stresses that remain in a solid material after the original cause of the stress has been removed. Residual stresses are undesirable in metal connections. In the process of hot riveting, some residual stresses are eliminated during high temperature treatment and cooling. While cold riveting may generate some residual stresses.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ 1:Why Does Hot Riveting Provide Higher Joint Strength?
Hot riveting is achieved by heating the rivet to a red-hot state, giving it good plasticity. During the cooling process, the rivet shrinks and clamps tightly to the material being joined, creating a very strong mechanical lock, resulting in a high-strength joint.
FAQ 2:What Effect Does Hot Riveting Have on the Material?
Hot riveting may alter the metallurgical structure of the materials being joined, affecting their mechanical properties and durability. At the same time, high-temperature operation is a safety hazard and requires strict safety measures.
FAQ 3:Is Cold Riveting Suitable for All Metal Materials?
Cold riveting is suitable for a wide range of metal materials, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper and titanium. However, for very hard or thick materials, cold riveting may not be as effective as hot riveting.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
Conclusion
Hot riveting and cold riveting are both commonly used riveting methods. However, there are significant differences between these two methods of joining. As a successful entrepreneur, you need to understand the difference between hot riveting and cold riveting and the scenarios before starting a project. In this way, you can choose the most appropriate riveting method to ensure the quality and performance of the connection.
Get Perfect Blind Rivet from Rivmate Rivet!
Do you want to use high quality blind rivets for your business?Rivmate rivet‘s specialized blind rivet solutions make the difference. Contact us today for the perfect blind rivet or structural rivet to revitalize your project or business.



