Open End Blind Pop Rivets
Your single source for wholesale open end blind pop rivets, with factory-direct manufacturing and stable supply.
Open End Blind Rivets for Bulk Industrial Use
Open-end blind rivets are mechanical fasteners installed from a single side (blind installation). After riveting, the mandrel breaks at its predetermined fracture point, leaving the rivet tail open.
Open end blind rivets are typically used in non-sealing applications such as sheet metal fabrication, HVAC ductwork systems, electrical enclosures, equipment housings, and automotive interior structures. They significantly enhance assembly speed while maintaining fundamental joint strength, making them ideal for high-frequency, mass-production installations.
- High installation efficiency
- Standardized specifications
- Low overall cost
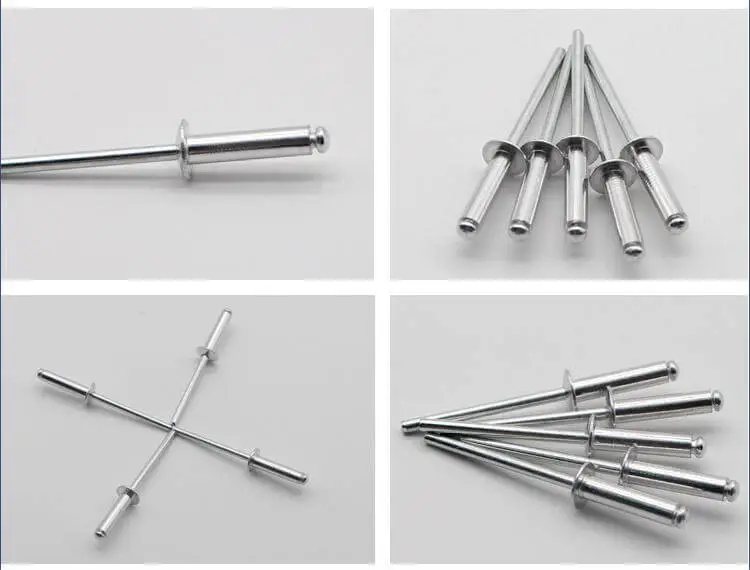


Open End vs Closed End Blind Rivets
Sealing Performance:Open-end blind rivets feature an open structure and do not provide waterproof or airtight capabilities; closed-end blind rivets have sealed ends and are suitable for applications requiring sealing.
Cost and Efficiency:Open-end rivets feature a mature design and lower cost, making them suitable for high-frequency, mass-production installations. Closed-end rivets involve a relatively complex manufacturing process, resulting in higher per-unit costs.
Application Boundaries:In industrial assemblies where sealing is unnecessary, open-end rivets offer superior cost-effectiveness. For applications involving protection ratings or long-term outdoor use, closed-end rivets should be prioritized.
Product Range of Open End Blind Rivets

Full Stainless Steel Open Type CSK Head
Head Styles: CSK Head; Materials: Body: 304 Stainless Steel ; Mandrel: 304/302 Stainless Steel
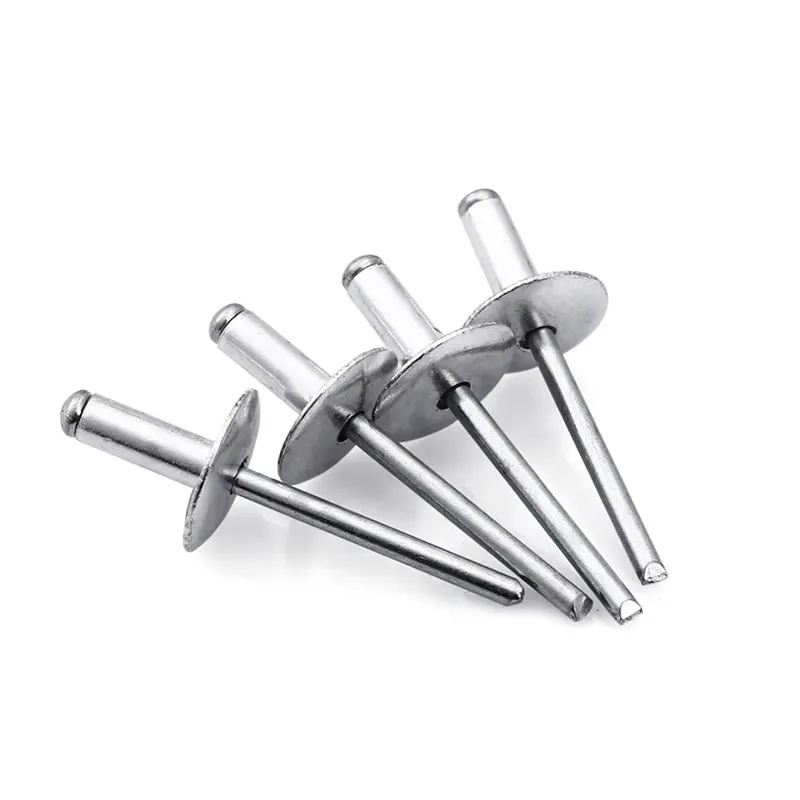

Full Stainless Steel Open Type Large Flange Head
Head Styles: Large Flange; Materials: Body: 304 Stainless Steel ; Mandrel: 304/302 Stainless Steel

Full Stainless Steel Open Type Dome Head
Head Styles: Dome Head; Materials: Body: 304 Stainless Steel ; Mandrel: 304/302 Stainless Steel

Full Steel Open Type CSK Head
Head Styles: CSK Head; Materials: Body: Carbon Steel ; Mandrel: Carbon Steel
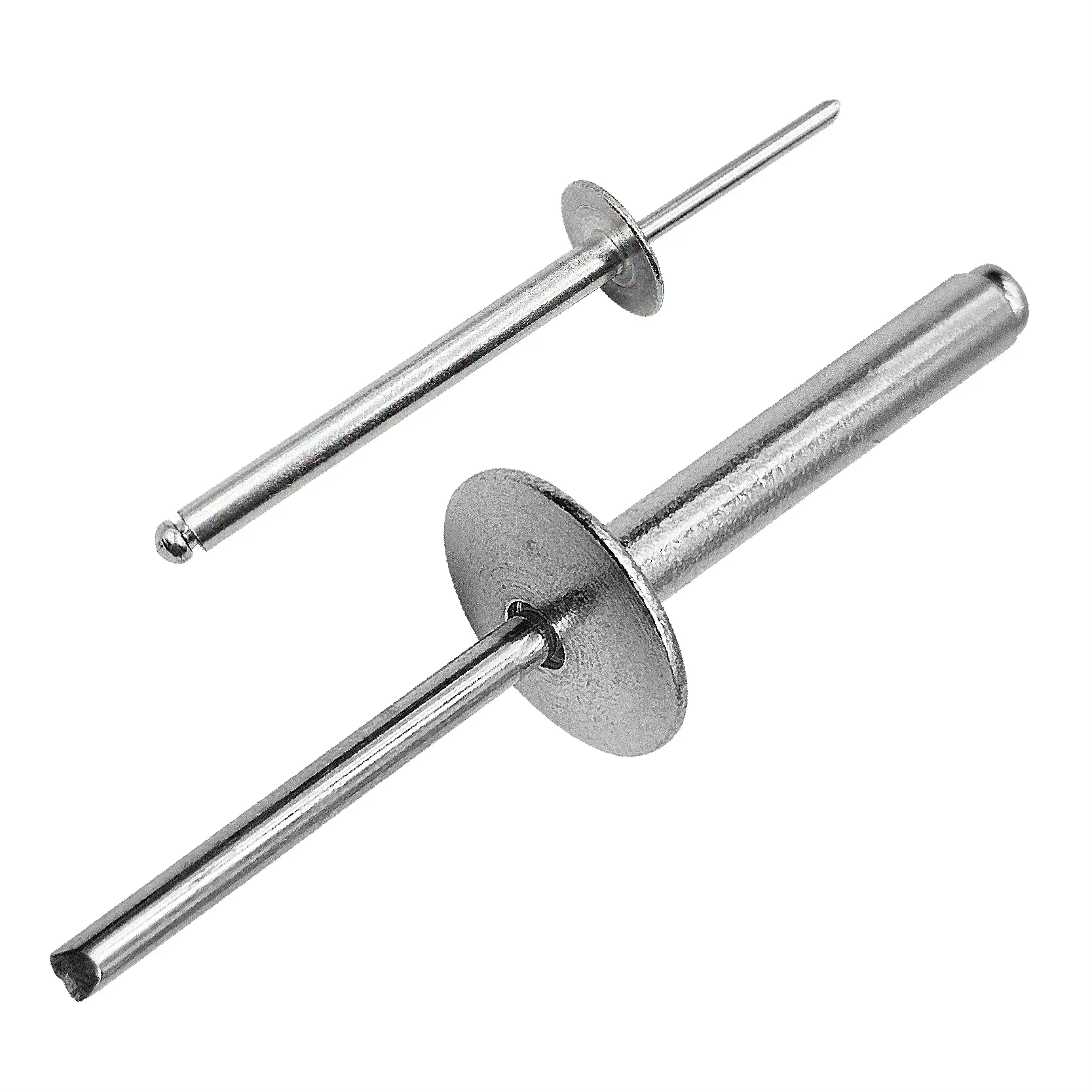

Full Steel Open Type Large Flange
Head Styles: Large Flange; Materials: Body: Carbon Steel ; Mandrel: Carbon Steel

Full Steel Open Type Dome Head
Head Styles: Dome Head; Materials: Body: Carbon Steel ; Mandrel: Carbon Steel
The Technical Parameters of Open End Blilnd Rivets
| Diameter[d] | Size | Body Length[L] | Grip Range | Drill | Tensile | Shear |
| 2.4(3/32") | 2.4×4.0 | 4.0-5.0 | 0.5-2.0 | 2.5-2.6 | 280N | 180N |
| 2.4×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 2.0-4.0 | ||||
| 2.4×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 4.0-6.0 | ||||
| 2.4×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 6.0-8.0 | ||||
| 2.4×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 7.0-9.5 | ||||
| 2.4×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 8.0-11.5 | ||||
| 2.4×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 10.0-13.0 | ||||
| 3.0(7/61") | 3.0×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 1.0-3.5 | 3.1-3.2 | 400N | 300N |
| 3.0×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 3.5-5.0 | ||||
| 3.0×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 5.0-7.0 | ||||
| 3.0×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 7.0-9.0 | ||||
| 3.0×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 9.0-11.0 | ||||
| 3.0×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 9.0-12.5 | ||||
| 3.0×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 12.0-14.5 | ||||
| 3.0×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 13.0-16.5 | ||||
| 3.2(1/8") | 3.2×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 1.0-3.5 | 3.3-3.4 | 500N | 400N |
| 3.2×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 3.5-5.0 | ||||
| 3.2×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 5.0-7.0 | ||||
| 3.2×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 7.0-9.0 | ||||
| 3.2×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 9.0-11.0 | ||||
| 3.2×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 9.0-12.5 | ||||
| 3.2×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 12.0-14.5 | ||||
| 3.2×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 13.0-16.5 | ||||
| 4.0(5/32") | 4.0×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 1.0-3.0 | 4.4-4.2 | 1000N | 800N |
| 4.0×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 3.0-5.0 | ||||
| 4.0×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 4.0-6.5 | ||||
| 4.0×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 6.0-8.5 | ||||
| 4.0×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 7.0-10.5 | ||||
| 4.0×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 8.0-12.5 | ||||
| 4.0×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 10.0-14.5 | ||||
| 4.0×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 12.0-16.0 | ||||
| 4.0×25.0 | 25.0-26.0 | 16.0-21.0 | ||||
| 4.0×30.0 | 30.0-31.0 | 21.0-26.0 | ||||
| 4.8(3/16") | 4.8×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 1.0-2.5 | 4.9-5.0 | 1500N | 1300N |
| 4.8×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 2.5-4.0 | ||||
| 4.8×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 4.0-6.0 | ||||
| 4.8×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 6.0-8.0 | ||||
| 4.8×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 8.0-10.0 | ||||
| 4.8×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 9.0-12.0 | ||||
| 4.8×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 10.0-14.0 | ||||
| 4.8×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 12.0-16.0 | ||||
| 4.8×25.0 | 25.0-26.0 | 16.0-21.0 | ||||
| 4.8×30.0 | 30.0-31.0 | 21.0-25.0 | ||||
| 4.8×35.0 | 35.0-36.0 | 25.0-30.0 | ||||
| 4.8×40.0 | 40.0-41.0 | 30.0-35.0 | ||||
| 5.0(6/31") | 5.0×6.0 | 6.0-7.0 | 1.0-2.5 | 5.1-5.2 | 1700N | 1500N |
| 5.0×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 2.5-4.0 | ||||
| 5.0×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 4.0-6.0 | ||||
| 5.0×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 6.0-8.0 | ||||
| 5.0×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 8.0-10.0 | ||||
| 5.0×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 9.0-12.0 | ||||
| 5.0×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 10.0-14.0 | ||||
| 5.0×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 12.0-16.0 | ||||
| 5.0×25.0 | 25.0-26.0 | 16.0-21.0 | ||||
| 5.0×30.0 | 30.0-31.0 | 21.0-25.0 | ||||
| 5.0×35.0 | 35.0-36.0 | 25.0-30.0 | ||||
| 5.0×40.0 | 40.0-41.0 | 30.0-35.0 | ||||
| 6.0(15/64") | 6.0×8.0 | 8.0-9.0 | 1.5-3.0 | 6.1-6.2 | 2500N | 2000N |
| 6.0×10.0 | 10.0-11.0 | 3.0-5.0 | ||||
| 6.0×12.0 | 12.0-13.0 | 5.0-7.0 | ||||
| 6.0×14.0 | 14.0-15.0 | 7.0-9.0 | ||||
| 6.0×16.0 | 16.0-17.0 | 7.0-11.0 | ||||
| 6.0×18.0 | 18.0-19.0 | 11.0-13.0 | ||||
| 6.0×20.0 | 20.0-21.0 | 11.0-15.0 | ||||
| 6.0×25.0 | 25.0-26.0 | 14.0-19.5 | ||||
| 6.0×30.0 | 30.0-31.0 | 19.5-24.5 | ||||
| 6.0×35.0 | 35.0-36.0 | 24.0-29.0 | ||||
| 6.0×40.0 | 40.0-41.0 | 29.0-34.0 |
WHY USE IT
Open Type Rivet Product Features & Advantages
Blind-Side Installation Efficiency
Supports single-side blind installation without requiring rear access, significantly boosting assembly efficiency while reducing labor and time costs. Ideal for high-frequency, high-volume industrial installation scenarios.
Standardized Specifications for Safer Selection
Multiple diameters, grip ranges, and head configurations simplify engineering selection and future replacements, minimizing rework risks from specification mismatches.
Multiple Material Combinations
Offers aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel, and hybrid options for optimal matching with substrates and environments, balancing strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Consistent Mandrel Break Performance
Stable break-off points and uniform tail expansion ensure installation consistency in batches, minimizing loosening and connection failure rates.
Cost-Effective Solution for High-Volume Use
As a proven universal blind rivet, the open-end design delivers fundamental fastening performance while facilitating bulk procurement and cost control.
Wide Tool Compatibility
Compatible with manual, pneumatic, and electric riveting tools, its universal tooling enables rapid deployment across production lines or job sites, minimizing equipment changeover and training costs.
Reliable Performance in Non-Sealed Applications
Optimized for non-sealed conditions, it delivers stable connection performance in indoor or controlled environments. Suitable for sheet metal, enclosure casings, and structural component assembly.
OEM and Bulk Supply Ready
Supports bulk supply and OEM customization requirements, including specifications, materials, and packaging solutions. Facilitates the establishment of long-term, stable industrial fastener supply systems for customers.
HOW TO CHOOSE
How to Choose the Right Open End Blind Rivet
I. Selection Logic for Grip Range
Grip range refers to the total plate thickness range a rivet can clamp. Ensure the thickness of the materials being joined falls within the midpoint of the recommended range, not at the critical value.
For example: When the total thickness of two sheet metal layers is 3.5 mm, select a rivet with a Grip Range of 3.0–5.0 mm instead of 2.5–3.5 mm to prevent insufficient tail expansion or unstable breakage.
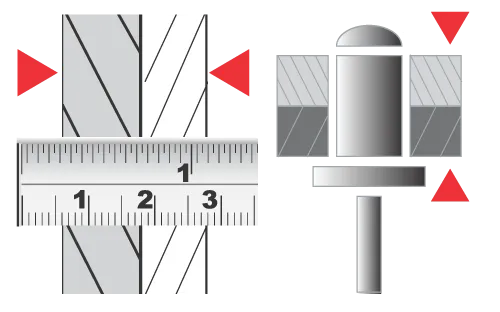
II. Hole Diameter Matching Principle
Hole diameter must precisely match the rivet diameter. Oversized holes cause post-riveting loosening, while undersized holes may damage surface coatings or reduce installation efficiency.
For a Ø4.0 mm rivet, the commonly recommended hole diameter is 4.1–4.2 mm, ensuring smooth installation while achieving stable clamping.
III. Engineering Considerations for Material Combinations

Material selection must balance substrate properties, strength requirements, and corrosion exposure.
- Aluminum sheet connections: Commonly use aluminum body + steel core to meet basic strength while controlling costs
- Humid or mildly corrosive environments: Opt for aluminum body + stainless steel core
- Strength-critical applications or steel structures: Recommend all-carbon steel or all-stainless steel rivets
Avoid mismatched metal combinations in highly corrosive environments to reduce the risk of galvanic corrosion.
Have More Questions?
Contact our engineers for reliable product data and engineering advice.
OPEN END RIVETS INSTALLATION
Installation Guide for Open End Blind Rivets
Tools for Rivet Installation



Tools for Rivet Installation
Common installation tools include:
- Manual rivet gun: Suitable for small batches or riveting lightweight materials. Simple and easy to use, typically employed for field repairs or prototype assembly.
- Pneumatic riveting tool: Ideal for medium-volume production. Delivers consistent force output, reducing operator fatigue.
- Battery-operated/electric rivet gun: Suitable for high-volume assembly lines, offering high efficiency and low vibration during repetitive, large-scale riveting
Selecting the correct tool helps ensure uniform rivet breakage and consistent clamping force for each rivet; insufficient tool power is a common cause of riveting failure in the field.

Step-by-Step Installation Process
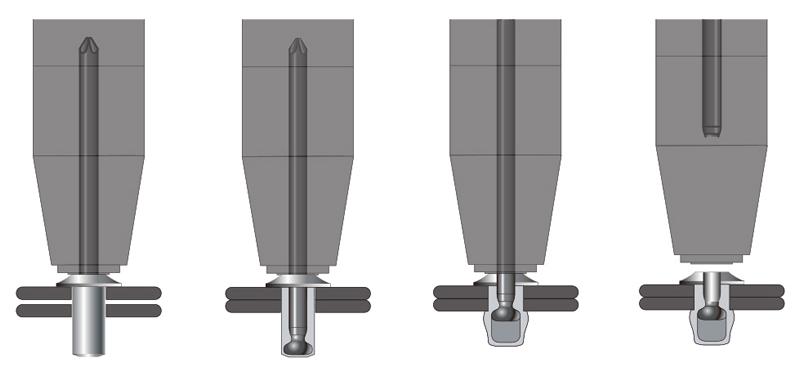
Standard installation procedure is as follows:
- Drill appropriate hole – Drill diameter should be slightly larger than the rivet body diameter (e.g., Ø4.8 mm rivets typically require 4.9–5.0 mm holes).
- Insert rivet into hole – The rivet flange should lie flush against the material surface.
- Engage tool and pull mandrel – The tool pulls the mandrel, causing the rivet tail to expand and lock the material on the blind side through stretching.
- Mandrel breaks at notch – The mandrel fractures as designed, completing the riveting process.
When the standard procedure is executed correctly, the consistency of blind-side expansion height with mandrel breakage is critical for achieving a stable connection.
Common Installation Failures
The following are common failure types encountered during installation (frequently observed at construction sites):
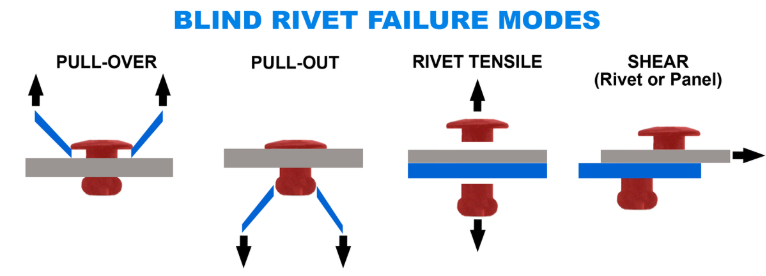
- Hole too large or too small – Mismatched hole sizes can cause rivets to become loose or fail to seat properly.
- Insufficient grip range – Selecting a grip range below the total material thickness results in inadequate blind-side expansion, leading to loose connections.
- Tool misalignment – Failure to position the rivet gun perpendicular to the workpiece surface causes uneven expansion of the rivet head.
These failures often result in dropped parts, loose connections, and inconsistent batch quality on-site, representing the most critical risk points for B2B clients.
APPLICATIONS
Applications of Open End Blind Rivets

Sheet Metal Fabrication
Widely used for connecting thin plates and sheet metal components, enabling stable connections without sealing requirements while significantly improving assembly efficiency.
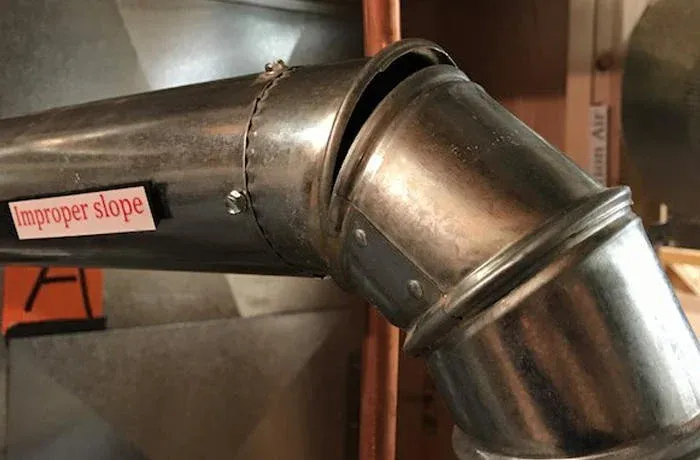

HVAC Ducting Systems
Suitable for rapid fastening of ductwork, brackets, and related metal parts, meeting bulk installation demands while helping control overall assembly costs.
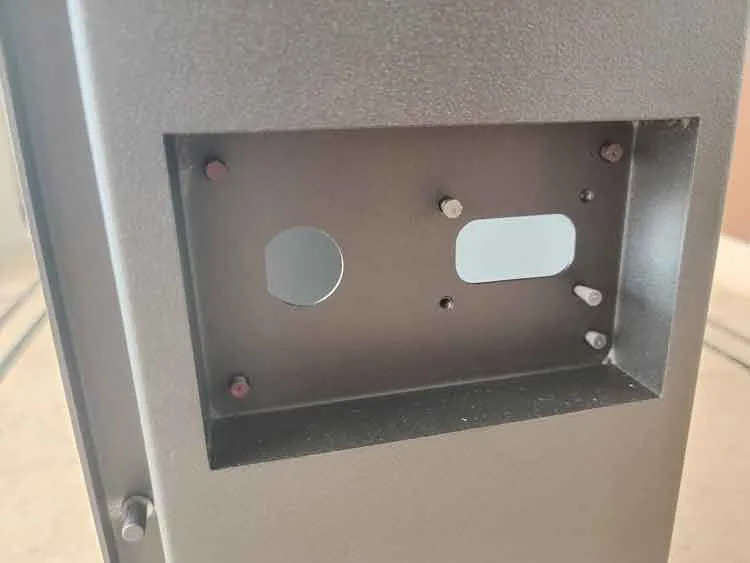

Electrical Enclosures and Cabinets
Commonly used for structural connections in electrical cabinets, control panel housings, and similar applications where moderate aesthetic standards and assembly consistency are prioritized.
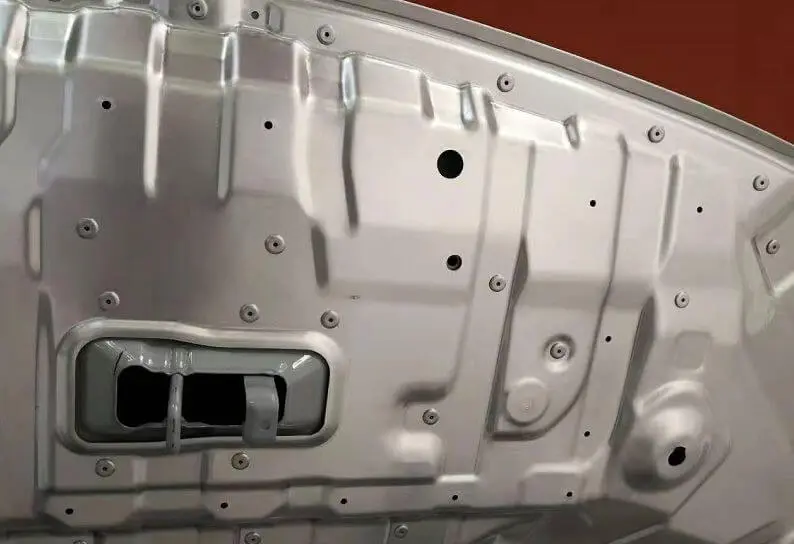

Automotive Interior Components
Suitable for assembling automotive interiors and non-load-bearing structural components, ensuring connection reliability while supporting high-tempo production line operations.
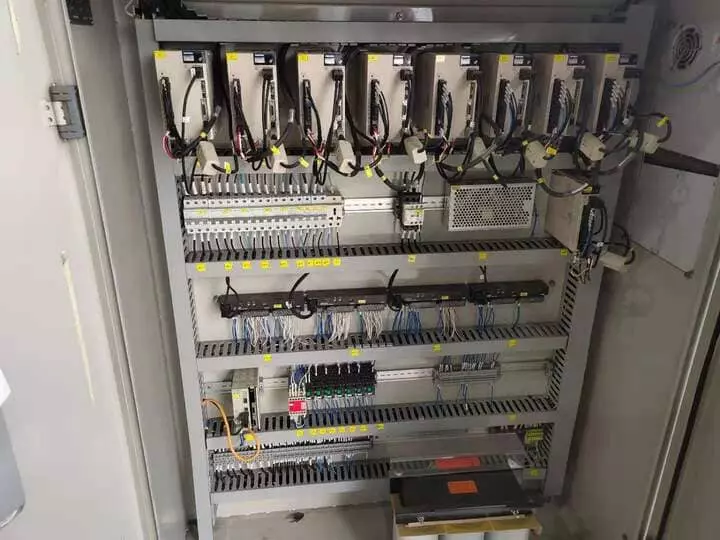

Industrial Equipment Housing
Used for securing equipment enclosures and auxiliary structural components, facilitating installation under single-side access conditions to reduce assembly complexity.
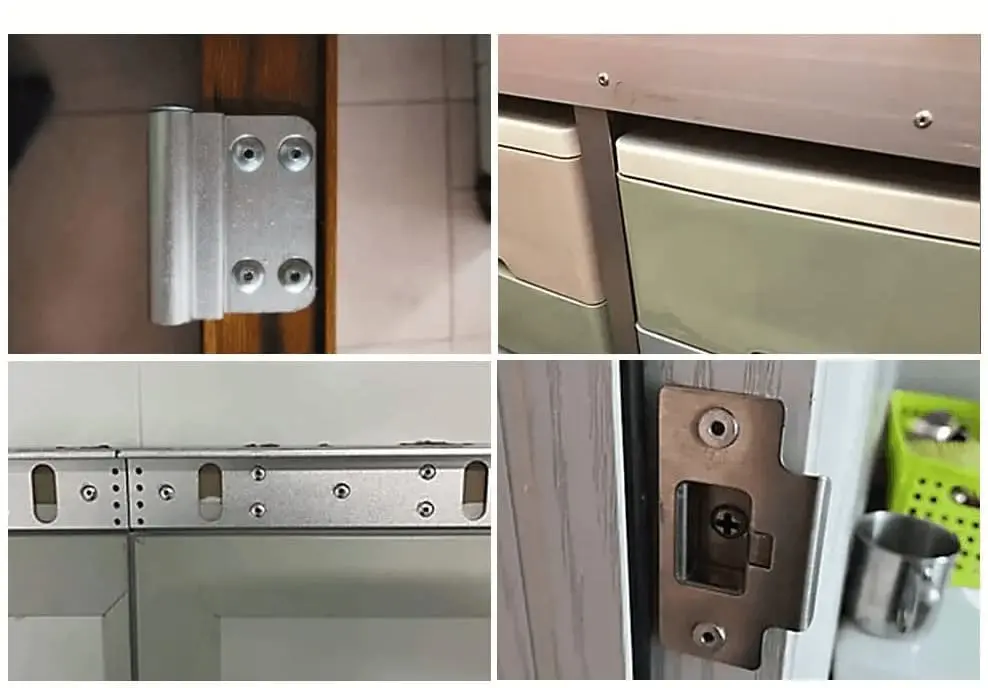

Furniture and Appliance Assembly
Suitable for non-sealed connections in furniture and appliance housings, balancing installation efficiency, structural stability, and mass production costs.
FAQs
Q1: What are open end blind pop rivets used for?
A: Open end blind pop rivets are primarily used for industrial connections that do not require sealing. They are suitable for sheet metal fabrication, HVAC ductwork, electrical enclosures, and equipment housings, emphasizing installation efficiency and cost control.
Q2: What is the difference between open end and closed end blind rivets?
A: Open end blind rivets maintain an open tail after riveting, offering no waterproof or airtight properties but featuring lower cost and broader applicability; closed end blind rivets provide superior sealing performance, suitable for applications demanding higher protection standards.
Q3: How do I choose the correct grip range for an open end blind rivet?
A: Select the appropriate grip range based on the total thickness of the materials being joined. Ensure material thickness falls within the recommended range to prevent issues like insufficient rivet hold or abnormal breakage.
Q4: Can open end blind rivets be used outdoors?
A: In outdoor environments without waterproofing or gas-tight requirements, open end blind rivets made from suitable materials (such as stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys) are viable. However, for prolonged exposure or highly corrosive conditions, careful evaluation is needed, or alternative rivet types should be selected.
Q5: Do you support OEM and bulk supply for open end blind pop rivets?
A: We support bulk supply and OEM customization, including specifications, material combinations, and packaging solutions, suitable for long-term project procurement and industrial-grade stable supply needs.






