Table of Contents
A competent rivet solution requires not only competent rivet quality, but also proper rivet spacing and edge distance. This is very important to maintain structural stability and reduce costs.
Now, let’s explore this in depth!
Table of Contents
Rivet spacing is an important consideration when installing rivets. Proper rivet spacing can provide a stable connection and also save rivet cost.
Rivet spacing is the straight line distance between two adjacent blind rivets. Why is it important to have spacing between rivets? It is mainly to serve several purposes:
- Ensure that stresses are evenly distributed across the joint material
- Ensure that the rivet’s tightening effect is maximised
- Prevent material tearing in the riveted area

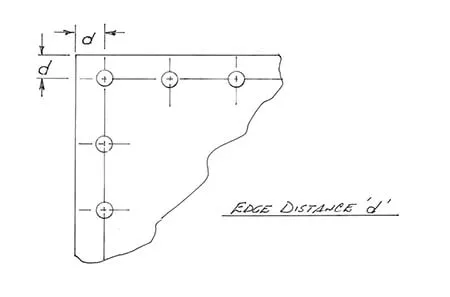
What is Rivet Edge Distance?
Rivet edge distance is the distance from the centre of the rivet to the edge of the material being joined. This is a critical parameter in the design of riveted joints to ensure that rivets are installed in such a way that they do not result in tearing or breaking of the material edge, while ensuring a strong and reliable joint.
Rivets are not installed in just any position. When installing rivets, the rivets should not be too close to the edge of the material, otherwise it will easily lead to edge tearing. Sufficient distance from the edge ensures that the edge is strong enough to withstand the pressure.
What is the Difference Between Rivet Spacing and Edge Distance?
| Comparison Criteria | Rivet Spacing | Edge Distance |
| Common Standards | Typically 3 to 10 times the rivet diameter, with 3 to 5 times being common | Typically 2 to 4 times the rivet diameter, with a minimum of 2 times |
| Function | Distributes stress, ensuring overall connection strength and fastening effectiveness | Prevents edge tearing, protecting the material’s edge integrity |
| Effect of Being Too Small | Too small spacing can cause material tearing or insufficient strength between rivet holes | Too small edge distance can cause material edge tearing or cracking |
| Effect of Being Too Large | Too large spacing can result in loose connections, material separation, or failure | Too large edge distance wastes material and reduces fastening effectiveness |

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
Standard for Rivet Spacing
Rivet spacing is the process of ensuring that rivets are evenly distributed across the material to ensure strength, stability and durability of the connection. The following are common criteria for rivet spacing:
- Minimum Rivet Spacing: Rivet spacing should be 3 times the diameter of the rivet
- Maximum Rivet Spacing: Rivet spacing should normally be no more than 10 times the rivet diameter.
In practice, 3x to 5x rivet diameter is a common rivet spacing design rule for most application scenarios, ensuring strength without wasting material.
What Problems can too Little Rivet Spacing Cause?
If the rivet spacing is too small, the material between the rivets is susceptible to stress concentrations. This may result in tearing of the material or lack of strength around the rivet holes.
What Problems can too Much Rivet Spacing Cause?
If the rivets are spaced too far apart, the strength of the joint between the materials may be insufficient. This can lead to loosening or separation of the structure being joined.
Standard for Rivet Edge Distance
Rivet edge distance is what ensures that the rivet is kept at the proper distance from the edge of the material. This is to avoid tearing or breaking of the edge due to excessive force, and to ensure that the rivet is able to securely fasten the material.

Minimum Rivet Edge Distance
The minimum rivet edge distance is usually two times the rivet diameter.
For example, if the rivet diameter is 6mm, the minimum edge distance should be 12mm, which prevents tearing of the material edge and ensures that the rivet can be fastened to the material.
Maximum Rivet Edge Distance
The maximum edge distance is usually 4 times the rivet diameter.
If the rivet is too far from the edge, the fastening may not be as effective.
What are the Risks of Having too Little Rivet Edge Distance?
A rivet edge distance that is too small can lead to a number of problems, mainly related to stress concentrations at the material edge and material breakage. The following are some of the problems that can be caused by a rivet edge distance that is too small:
- When the rivet is too close to the edge of the material, the stresses generated at the rivet are concentrated at the edge. Since the material at the edge portion is not able to withstand these concentrated stresses effectively, tearing can easily occur.
- Too small a distance from the edge means that the material does not provide sufficient support and the material in the edge section is weaker, resulting in the rivet being destroyed at the edge when a force is applied.
- Increased stress concentration at the edge of the material
- Edge breakage may cause the rivet to lose its fastening effect when the edge distance is too small
What are the Risks of too Much Rivet Edge Distance?
Excessive rivet edge distance can also cause a number of problems, although it does not directly result in material tearing as does a small distance, it can affect joint strength, material utilisation and structural performance. The following are common problems associated with excessive rivet edge distances:
- Reduced joint strength
- Material wastage
- Reduced fastening effect
- Excessive edge distance can cause the material to lose support in the portion of the joint between the point of connection and the edge, especially on thinner materials, and this portion of the material may buckle or deform under stress.
- When the rivet is too far from the edge, the portion of the material at the edge may not participate in the overall distribution of forces, resulting in the rivet being subjected to primarily localised loads.

Common edge distance rules:
- 2x Rivet Diameter: Suitable for hard materials (e.g. steel) and thicker materials for static load environments.
- 3x Rivet Diameter: Common edge distances, suitable for most material types and application scenarios.
- 4x Rivet Diameter: Suitable for soft, brittle materials or high load, high vibration applications to ensure that the edge is not overstressed and broken.
Why Edge Distance Requirements Differ for Different Materials?
Different materials vary in strength, toughness, brittleness and thickness, and these properties determine the ability of the material to withstand stresses during the riveting process. Edge distances are designed to be optimised according to the physical properties of the materials being joined to prevent breakage, ensure a strong connection and enhance structural performance.
For materials with low strength (e.g. aluminium, plastics, soft metals), they are prone to tearing or deformation when subjected to stress, and in particular the edge portion is prone to breakage under stress.
Therefore, in the actual installation process, usually need a larger rivet edge distance (close to 4 times the rivet diameter). This spreads the stress and prevents the edge from breaking near the rivet.
For stronger materials (e.g. steel, stainless steel, titanium), the strength is higher. Their edges are able to withstand greater stresses and are less prone to tearing or deformation.
These materials allow for smaller edge distances (close to 2x the rivet diameter) because they are able to withstand greater stresses without damage.
How are Rivet Spacing and Edge Distances Designed in Multi-row Rivet Applications?
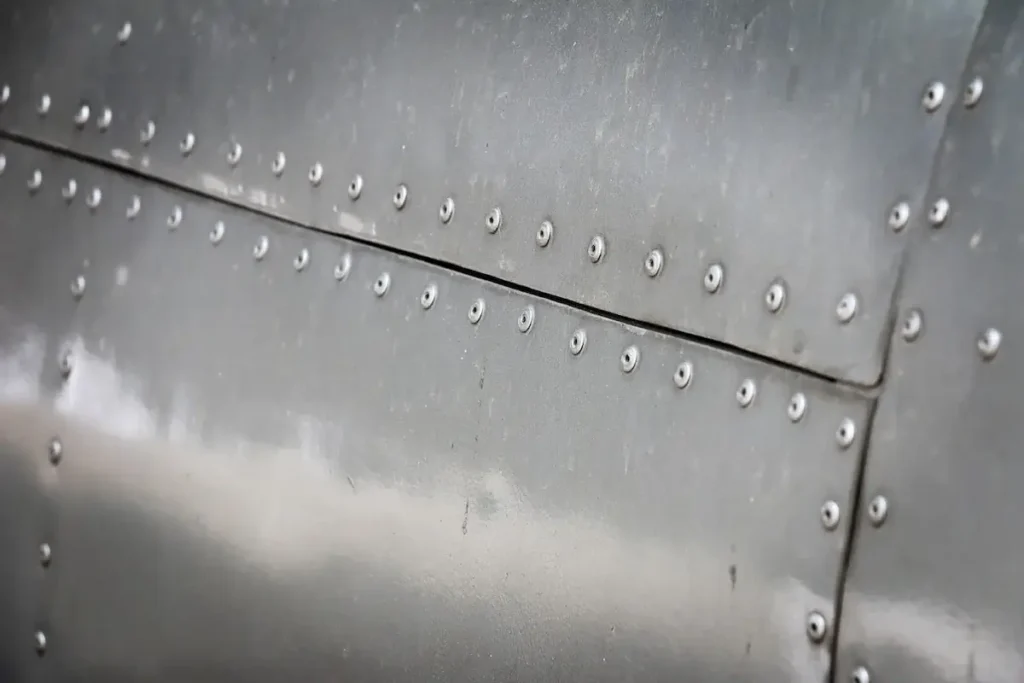

1. Rivet Spacing in Multi-row Applications
- Spacing between rivets in the same row: the minimum spacing shall be at least 3 times the rivet diameter. The maximum spacing should not exceed 10 times the rivet diameter.
- Spacing between different rows of rivets (Row Spacing): the distance between two adjacent rows of rivets should be at least 3 times the diameter of the rivet. However, we recommend that multiple rows of rivets be spaced 4 times the diameter of the rivet to ensure strength and prevent material fatigue.
2. Edge Distance in Multi-row Applications
The distance from the centre of the rivet to the edge of the material should be 2 to 4 times the rivet diameter. For soft or brittle materials, the edge distance should be as close as possible to 4 times the rivet diameter to prevent the edge from tearing under excessive force. For high strength materials such as steel and stainless steel, smaller edge distances (closer to 2 times the rivet diameter) can be used.
What Remedies can be Taken When the Edge Distance is too Small?
If you encounter a situation where it is not possible to increase the distance between the edges, you can consider using a large flange pop rivet. It increases the bearing area of the rivet and can effectively spread the pressure. It can reduce the possibility of material tearing.

Contact Our Engineers Today
We provide you with high quality rivets, including customized services.
Get Riveting Solutions form Rivmate
Finally, I believe that there has been a clear perception of how rivet spacing and rivet edge distance are designed. Proper rivet spacing and rivet edge distance are crucial to the stability of a project.Rivmate has been in the riveting industry for 15 years and has a wealth of riveting experience. If you don’t know how to choose the right rivet solution for your project, please contact our engineers!
Get a professional riveting quote today! Let us help you!



