How Do I Choose The Right Size Pop Rivet?
Table of Contents
How Do I Choose The Right Size Pop Rivet? Do you know what factors you should base your choice of the most suitable pop rivets on? Are you overwhelmed by all this, don’t worry, this article will solve all your questions about how do i choose the right size pop rivet!
What Determines Rivet Size?
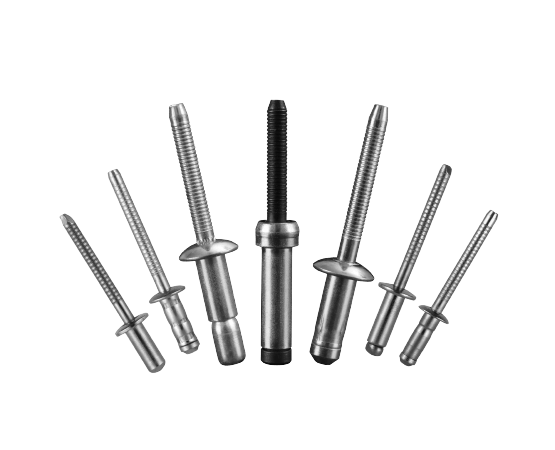

To select the correct size for Pop Rivet, the key lies in understanding four crucial parameters, which directly determine the strength, clamping effect and long-term stability of the riveting.
- Material Thickness
The rivets must be able to penetrate all the workpieces and form sufficient expansion shapes on the backside. Therefore, the total plate thickness is the basic starting point for selection. The greater the total thickness, the longer the required rivets and the larger the diameters usually need to be. - Grip Range
This is the key parameter that determines whether the rivet truly “holds the material”. The Grip Range must cover the total thickness of your plate; otherwise, there will be insufficient clamping or incomplete expansion. Engineering tests by Rivmate show that incorrect selection of the Grip Range can result in a loss of up to 40–70% of strength, which is the most dangerous error. - Rivet Diameter
The larger the diameter, the usually higher the shear strength. Thin plates are generally made of 3.2mm or 4.0mm, while structural components are mostly made of 4.8mm or 6.4mm. The hole diameter must precisely match the diameter; otherwise, there will be loosening, pull-bolting tilt or insufficient expansion. - Rivet Length
The length must be sufficient to cover the thickness of the material and leave the amount of material needed for proper expansion. Industry experience typically uses:
Length = Total plate thickness + 1.2D (D = Diameter of the rivet)
If the length is too short, it cannot form properly. If it is too long, it may cause the rivet to bend or fail to be fully tightened.
Overall, the correct logic for determining the Rivet Size is as follows: First, look at the total plate thickness, then match the Grip Range, and finally confirm whether the diameter and length meet the structural requirements.
The grip range is always the most crucial factor. It cannot be determined by intuition or appearance; otherwise, the rivets will not be able to generate sufficient clamping force, resulting in structural loosening or premature failure.
How to Choose the Right Pop Rivets Diameter?
The selection of the diameter of Pop Rivet is one of the factors that have the greatest impact on the structural strength among all the size parameters. The diameter determines the shear strength, the degree of material deformation, and the adaptability of the rivet in the thin plate. Therefore, in the engineering selection process, we will first assess the thickness of the sheet, the structural load, and the hardness of the material, and then determine the diameter range.
Here are the two core principles that users need to understand most, explained from an engineering perspective:

- When the sheet material is very thin, it is advisable to avoid using rivets with excessively large diameters.
When subjected to force, thin plates are prone to bulging and deformation, and even cause the rivets to fail to adhere tightly to the material surface. An excessively large diameter will also increase the difficulty of hole processing and affect the final clamping quality. Therefore, for household appliances sheet metal, light-load equipment, and DIY projects, using 3.2 mm or 4.0 mm rivets is sufficient to meet the requirements. - When the structure is subjected to a large load, the diameter must be increased to enhance the shear strength.
The shear resistance of the rivets mainly depends on the diameter. The larger the diameter, the larger the force-bearing area, and the higher the overall strength. Therefore, for vehicle sheet metal, mechanical structural components, and heavy-duty connections, 4.8 mm or 6.4 mm are typically used, especially for structural blind rivets (Structural Rivet / Monobolt).
3.2 mm (1/8″): Suitable for thin sheets, light-load structures, household appliances, electronic enclosures, DIY projects; minimum risk of deformation.
4.0 mm (5/32″): Commonly used in sheet metal chassis cabinets and light industrial equipment; it performs well in balancing strength and plate thickness compatibility.
4.8 mm (3/16″): Suitable for load-bearing structures in automotive bodies and mechanical enclosures; the shear strength has been significantly enhanced.
6.4 mm (1/4″): Suitable for heavy-duty applications, structural components, construction machinery, etc.; mostly structural type rivets, with strength comparable to bolt connections.
In summary, the larger the diameter, the higher the strength; however, the thinner the material, the more prone it is to deformation due to an excessively large diameter. The principle for choosing the diameter correctly is to find the optimal balance point between “the material’s bearing capacity” and “the structural strength required”.
How to Choose the Right Grip Range?
Grip Range represents the total material thickness range within which the rivets can effectively grip. As long as the total plate thickness falls within the Grip Range, the rivets can expand correctly and form a stable connection.
To make the correct selection of Grip Range, one must follow three engineering principles:
- The grip range must completely cover the total thickness of the board.
The clamping range refers to the thickness interval within which the rivet can form normally. If the plate thickness exceeds the upper limit of the Grip Range, the rivet cannot fully expand; if the plate thickness is below the lower limit of the Grip Range, the rivet will expand excessively, resulting in loosening. - If the grip range is set too large, it will result in insufficient clamping force.
The wider the clamping range, the more likely the rivet is to “fail to fully expand” when expanding on thinner materials. This can lead to loosening of the connection and a decrease in vibration resistance. In practical engineering, a too large Grip Range is the most common cause of failure. - The grip range is set too small, causing the rivets to fail to form properly.
The rivets are not fully expanded, and the mandrel may have been pulled apart before any clamping force was applied. This results in a “false riveting” phenomenon. The strength of such connections is usually less than 30%.
Example:
When the total thickness of your material is 2.0 mm, you should choose the Grip Range of 1.5–3.0 mm. Never select 0–1.5 mm, as the rivets may become loose due to insufficient clamping, or even fail to expand properly.
Select the Length of the Pop Rivets
We determined the thickness of the material being joined and the diameter of the pop rivet in the first and second steps, respectively. Next we need to determine the length of the pop rivets.
So how do you choose the right rivet length for your project? Based on practical experience, the length of the rivet should be greater than or equal to the total material thickness plus 1.5 times the rivet diameter. Here is the formula:
Rivet Length = Total Material Thickness + 1.5 x Rivet Diameter
Next I will use an example where the thickness being riveted is 6mm and the rivet diameter is 1/8″ (3.2mm).
Total material thickness = 6mm
Rivet diameter = 3.2mm
1.5 times rivet diameter = 3.2mm × 1.5 = 4.8mm
Recommended Rivet Length = Total Material Thickness + 1.5x Rivet Diameter = 6mm + 4.8mm = 10.8mm
Therefore, a rivet with a length of 10.8mm and a diameter of 3.2mm should be selected to join a 6mm sheet. (Usually take a close standard length such as 11mm or 12mm)
| Rivet Diameter | Total Material Thickness | Recommended Rivet Length |
|---|---|---|
| 3/32″ (2.4 mm) | 0.5 – 3 mm | 4.8 mm |
| 1/8″ (3.2 mm) | 3 – 5 mm | 6.4 mm |
| 5/32″ (4.0 mm) | 5 – 7 mm | 8.0 mm |
| 3/16″ (4.8 mm) | 7 – 9 mm | 9.6 mm |
| 1/4″ (6.4 mm) | 9 – 11 mm | 12.7 mm |
Should Rivets be The Same Size as Holes?

In practice, the diameter of the rivet is not the same as the diameter of the hole. Generally speaking, the hole diameter will be slightly larger than the rivet diameter, so as to ensure that the rivet can be inserted smoothly into the hole and correctly expand to form a solid connection. Please follow our recommended hole diameter ranges and tolerances and use the appropriate drill and drilling method to ensure the quality and reliability of the installation of pop rivets.
Rivet Size Chart and Drill Size Chart
Rivet Diameter | Drill |
mm(inch) | mm |
| 2.4(3/32″) | 2.5-2.6 |
| 3.0(7/61″) | 3.1-3.2 |
| 3.2(1/8″) | 3.3-3.4 |
| 4.0(5/32″) | 4.1-4.2 |
| 4.8(3/16″) | 4.9-5.0 |
| 5.0(6/31″) | 5.1-5.2 |
| 6.0(15/64″) | 6.1-6.2 |
| 6.4(1/4″) | 6.5-6.6 |
| 8.0(5/16″) | 8.1-8.2 |
| 9.6(3/8″) | 9.1-9.2 |

FAQ: Common Questions About Choosing Pop Rivet Size
Q1. How do I choose the right size pop rivet?
When selecting dimensions, simply verify that the total plate thickness falls within the Grip Range, then choose the diameter according to strength requirements. Finally, determine the length by applying the formula “plate thickness + 1.3D”. The Grip Range is the most critical parameter and must fully encompass the plate thickness.
Q2. What size pop rivet do I need for sheet metal?
Thin plates are typically selected at 3.2 mm or 4.0 mm, which prevents plate bulging while providing sufficient strength. For applications with higher load-bearing requirements, 4.8 mm should be chosen. Always ensure the Grip Range is matched to the plate thickness.
Q3. What drill bit for 1/8 rivet?
1/8″ (3.2 mm) rivets paired with a #30 drill bit (approximately 3.3 mm bore diameter). The bore diameter must be slightly larger than the rivet body to ensure smooth installation without compromising clamping force.
Q4. How long should a pop rivet be?
The rivet length shall satisfy the formula: Length = Plate thickness + 1.3 × Diameter. Ensure the tail end expands fully to form a stable clamping force.
Request Rivmate Rivet Samples & Engineering Support

If you are choosing the appropriate rivet size, material or structural type for your project, the engineering team at Rivmate can offer you one-on-one professional support. We provide free samples to help you verify strength and compatibility in actual working conditions; at the same time, we offer free selection suggestions, including hole diameter, Grip Range, and thickness matching checks, to ensure that each rivet meets the application requirements.
Rivmate can also issue an ISO strength test report and support OEM brand packaging, which is suitable for production enterprises and long-term supply projects. Please contact us to obtain the fastest 4-hour technical and quotation response.
📧 Product Inquiry: manufacture@world-rivet.com
🌐 Official Website: https://worldrivet.com/
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



