Lockbolt vs Rivet: Comprehensive Comparison and Usage Guide of Lockbolt
Table of Contents
In the modern manufacturing and assembly industry, Lockbolt and Rivet are two of the most common permanent fasteners. Both can achieve a secure connection, but there are significant differences in structural strength, installation methods, maintenance cycles, and overall costs. This article will conduct a systematic comparison of Lockbolt vs Rivet from the perspective of Rivmate Engineering Fastening Experts.
Lockbolt vs Rivets

Lockbolt rivets and common rivets differ in the way they are joined and the conditions in which they are used; Lockbolt rivets offer greater strength and reliability and are used in situations where high loads are required. The common rivet is a common and widely used connector for general joining needs. The choice of connection depends on the specific application requirements and material properties.
What is a lockbolt ?
Lockbolt is a high-strength, permanent mechanical fastener consisting of a Pin and a Collar. It achieves mechanical interlocking between metals by pressing the locking ring into the groove of the staple using hydraulic or pneumatic tools. This structure offers extremely high shear and tensile strength, and the connection will not loosen or fail due to fatigue. Compared to traditional rivets, Lockbolt is more stable in installation and has a strength approximately 30-40% higher. It is commonly used in high-load scenarios such as railways, aviation, bridges, and heavy machinery.

How do Lockbolt Rivets Work ?
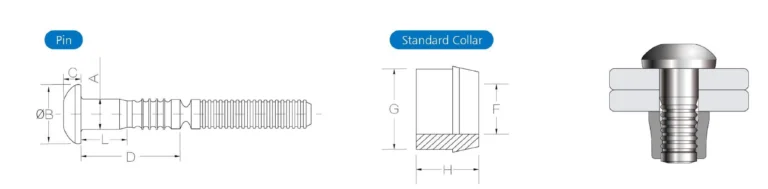
During installation, insert the anchor bolts into the holes, then use a hydraulic tool to press the locking ring into the groove, achieving mechanical locking between the two. The locking ring undergoes plastic deformation under high pressure and bites into the anchor bolt for a secure fixation. After the excess tail is disconnected, a high-strength and permanent connection is formed.
This structure can prevent loosening, and its shear and tensile strength is approximately 30% higher than that of ordinary rivets. Therefore, Lockbolt is often used in high-vibration environments such as railways, aviation, and heavy equipment.
Standard Reference: NAS 1919 / ISO 16120
What is a rivet ?
Rivet is a mechanical fastener that achieves permanent connection by deforming or breaking the core shaft. It is typically composed of a Body and a Mandrel. During installation, the rivet is inserted into a pre-drilled hole, and the core shaft is broken using a rivet gun, causing the dome to expand and lock the workpiece. This connection method does not require threads, and it has the advantages of being lightweight, fast to install, and low in cost.
Rivets are widely used in fields such as automobiles, aviation, home appliances, metal structures and light industry manufacturing. Some structural rivets can withstand high shear and tensile loads.
Standard Reference: ISO 15983 / ASTM F1470
Structural Comparison: Lockbolt vs Rivet

| Category | Rivet | Lockbolt |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Method | Breaks mandrel or deforms the shank to form a permanent joint | Collar is swaged into grooves on the pin to create a permanent mechanical lock |
| Operability | Can be installed from one side (blind type) | Requires access to both sides or a through-hole |
| Strength Performance | Moderate strength, suitable for thin sheet structures | High strength, ideal for heavy-duty structural applications |
| Vibration Resistance | Good, but may loosen over time under vibration | Excellent, collar lock prevents any loosening |
| Maintainability | Non-removable | Non-removable (but longer service life) |
| Common Materials | Aluminum, steel, stainless steel | Alloy steel, stainless steel, titanium |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, appliances, construction | Railways, aerospace, heavy machinery, bridges |
Strength and Durability: Lockbolt vs Rivet Performance Comparison
① Shear and Tensile Strength
From the perspective of structural design, when the lock ring of Lockbolt is combined with the threaded groove, a mechanical lock will be formed on the entire joint surface. This structure can better distribute stress, avoid stress concentration, and enhance the overall connection strength.
The actual measurement data shows that, under the same specification and size, the shear strength of Lockbolt is approximately 25–40% higher than that of ordinary structural rivets. This is why Lockbolt is widely used in high-load environments such as railways, heavy machinery, and bridges.
② Vibration and Fatigue Resistance
Vibration is one of the most common failure causes in metal connections. Traditional rivets tend to experience slight displacement under long-term vibration, which can lead to loosening or cracking of the rivet body. However, Lockbolt achieves high vibration resistance through the permanent interlock between the collar and the groove of the thread. In long-term dynamic load environments, it can effectively prevent micro loosening and the formation of fatigue cracks. This makes Lockbolt the preferred fastener for high-vibration conditions such as railway carriages, engineering machinery chassis, and aviation structures.
③ Corrosion Resistance
The corrosion resistance mainly depends on the material of the fastener. Rivets usually use aluminum, stainless steel or galvanized steel, while Lockbolts typically employ high-strength alloy steel or stainless steel and can enhance the protection level through surface treatments such as galvanizing, nickel coating or Dacromet (a type of electroless nickel coating).
In the ASTM B117, the corrosion resistance lifespan of the coating on Lockbolt can exceed 1000 hours. Therefore, in outdoor, marine or industrial equipment environments with high corrosivity, Lockbolt has a significant advantage.
④ Sealing Capability
In terms of sealing requirements, rivets have a significant advantage. Especially the closed-end rivet, whose tail end is completely sealed, can achieve a waterproof and gas-proof sealing effect. In contrast, Lockbolt focuses more on structural strength and stability rather than anti-seepage performance.
Therefore, in the structural connection application, Lockbolt is recommended; while in waterproof and airtight scenarios (such as aluminum ships and vehicle body shells), Rivet is suggested.
Lockbolt vs Rivet: Applications Comparison
a. Applications of Lockbolt Rivet
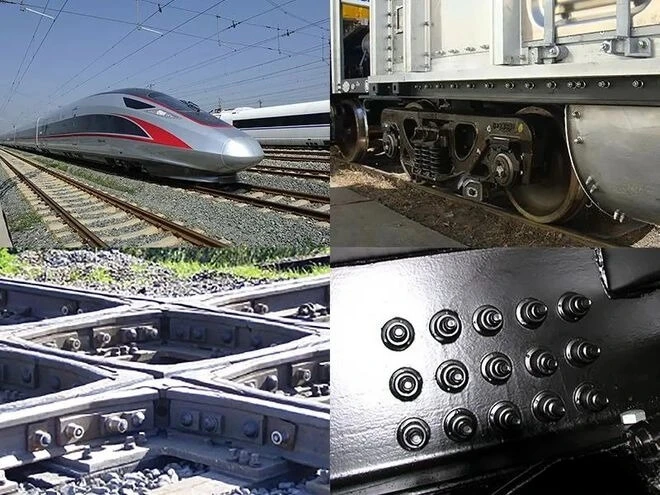
- High-load applications: Lockbolt rivet is used in applications that require high tensile or shear forces, such as aerospace, railroad, automotive, construction and marine applications.
- Requires high strength connections: Because Lockbolt rivet provides high strength connections, it is often used in applications that require reliable and durable connections that can withstand severe service conditions.
- Requirement of anti-loosening: The mechanical locking principle of Lockbolt rivet makes it anti-loosening and suitable for vibration and shock environments.

- General connection needs: Rivet is used in a wide variety of industries including aerospace, automotive manufacturing, construction and electronics. They are primarily used for general joining needs and do not need to be subjected to extremely high loads or harsh working environments.
- Quick Installation: Because Rivet is relatively easy to install, the process can be accomplished quickly using a rivet gun or hand riveting tool, making it suitable for scenarios where efficient installation is required.
- Affordable: Compared to Lockbolt rivet, Rivet is generally less costly, making it suitable for projects with limited budgets.
Lockbolt vs. Rivet: Comparison of Installation and Maintenance
a. Installation Process Comparison
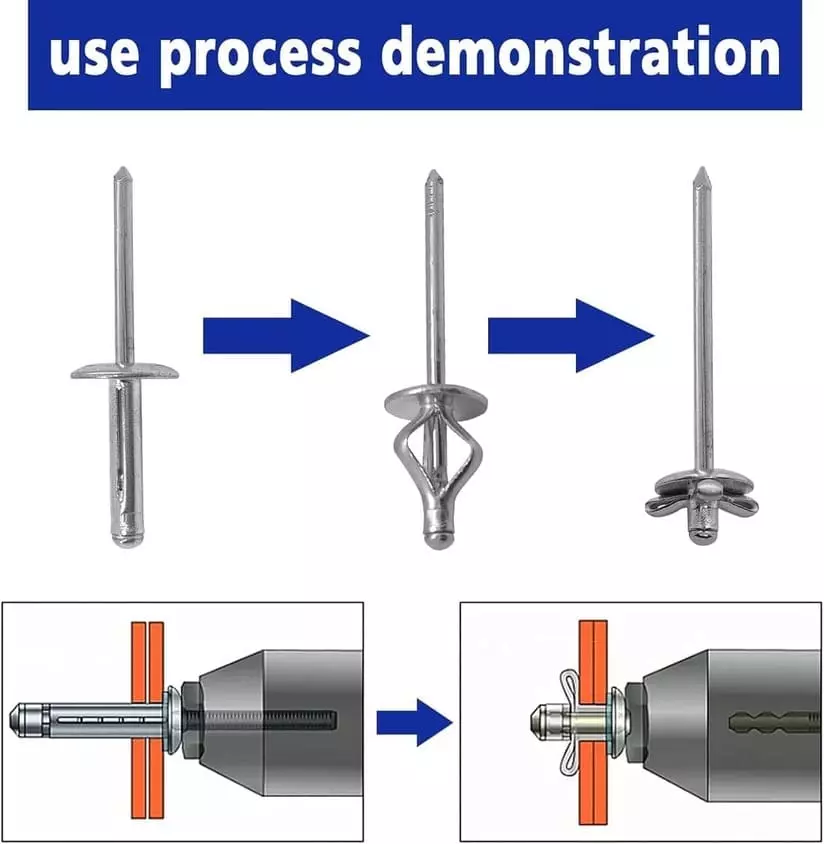
- Pre-drilling
The aperture is usually 0.1–0.2 mm larger than the diameter of the rivet body to ensure the forming space. - Insert Rivet
The rivet body is placed in the hole, and the cap is tightly attached to the surface of the workpiece. - Setting
Use a riveting gun or hydraulic equipment to break the core shaft, thereby forming a locking head at the tail end. - Quality Inspection
Confirm that the cap is flat and the tail is expanded evenly, without any looseness or cracks.
Installation Features:
- The operation is simple and can be completed on one side (Blind Access).
- The tool is lightweight and suitable for assembly line operations.
- Once the rivets are installed, they cannot be removed.
Rivmate Professional Tip:
In applications with high sealing requirements (such as vehicle bodies and ship hulls), the closed-end structural rivet can be selected to enhance water resistance.
Lockbolt Installation Steps:
- Insert Pin
The studs pass through the pre-drilled holes and the tail ends protrude from the connection surface. - Apply Collar
The locking ring slides into the bolt slot area, ready for locking. - Swage the Collar
Use specialized hydraulic tools to press the locking ring into the groove to achieve permanent locking. - Pin Tail Break-Off
The tool automatically cuts off the excess tail section, resulting in a neat appearance.
Installation Features:
- The installation torque is higher, and a bilateral operation space is required.
- It needs to be paired with hydraulic or pneumatic equipment.
- After installation, the structural strength is extremely high and the anti-loosening performance is excellent.
Rivmate Professional Tip:
In high-load scenarios such as railway vehicles, heavy machinery, and bridges, the use of Lockbolt can significantly enhance the reliability and lifespan of the connections.
b. Maintenance and Service Life Comparison
Rivet:
- Usually no regular maintenance is required.
- Under long-term vibration or high stress, slight loosening may occur.
- Once damaged, it needs to be drilled out and reinstalled.
- The general service life is typically 10–15 years (depending on the environment and material).
Lockbolt:
- Almost maintenance-free.
- The locking rings are permanently interlocked and there is no risk of loosening.
- Suitable for long-term high-load conditions (such as railway bridges, lifting equipment).
- The service life can reach more than 25 years, which is longer than that of most riveted structures.
Cost and Efficiency Analysis: Lockbolt vs Rivet
Initial Cost
The single-piece cost of a Rivet is relatively low, and the required tools are simple and lightweight. The price of common aluminum or steel structural rivets is approximately 1/3 to 1/5 of that of a Lockbolt. Therefore, in situations that prioritize cost-effectiveness or require large-scale installation, such as automotive interiors, appliance assembly, and sheet metal connections, rivets are the ideal choice.
Lockbolt:Although its individual price is higher, it possesses greater structural strength and fatigue resistance. In heavy-load structures (such as railway vehicles, wind power equipment, or bridges), its high-strength locking mechanism can significantly extend the service life, thereby reducing the costs of later replacements and downtime.
The test data from Rivmate indicates:
In typical steel structure applications, the initial investment of Lockbolt is approximately 25-40% higher, but it can recover the cost within 3 years by reducing maintenance and downtime.
Life Cycle Cost
Although the rivets are relatively inexpensive initially, they may become loose, corroded or develop fatigue cracks in high-vibration or corrosive environments. Regular inspections and replacements are necessary. This implies that during the product’s lifespan, maintenance and downtime costs may be higher than anticipated.
The Lockbolt structure is robust and requires no maintenance. Under long-term high-stress conditions (such as in railway or bridge connections), the locking ring maintains almost no attenuation of force.
The fatigue test results of Rivmate show that: The Lockbolt maintains 98% of its clamping force after 1 million cycles of load, while the Rivet drops to 82–85%. From a life-cycle perspective, the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the Lockbolt is approximately 20–30% lower than that of the rivet.
FAQ
Q1. Is a lockbolt stronger than a rivet?
Yes, in terms of structural strength and fatigue resistance, Lockbolt typically has 25% – 40% higher strength than Rivet of the same size. This is mainly due to its unique collar swaging structure, which can achieve permanent mechanical interlocking on the thread groove, thereby evenly distributing stress and preventing loosening.
Lockbolt is particularly suitable for structures that can withstand shear loads and vibrations, such as railway vehicles, wind power equipment, lifting machinery, and bridge connections. Although rivets perform well in thin plates and lightweight structures, their clamping force gradually decreases under heavy loads and high vibration conditions. Therefore, Rivet emphasizes light weight and economy, while Lockbolt emphasizes structural strength and stability.
2. Can lockbolts replace welding?
In many cases, Lockbolt can be an ideal alternative to welding. Its connection strength is comparable to that of welded structures, but it is safer to install and has a more stable process. Unlike welding, Lockbolt does not cause a heat affected zone (HAZ) in the metal, thus avoiding material deformation or strength degradation.
Furthermore, the installation of Lockbolt does not require special welding skills and is not affected by humidity, temperature or metal coatings. In high-strength structures (such as railway bridges, steel beam connections or heavy machinery chassis), Lockbolt has been widely used as an alternative to traditional welding.
For areas subjected to impact loads or requiring complete sealing, Lockbolt can be used in conjunction with structural sealant or waterproof sealing solutions to achieve the best results.
3. Are lockbolts reusable?
No.
The Lockbolt is designed as a permanent fastener. During installation, the lock ring undergoes plastic deformation and is pressed into the threaded groove, forming an irreversible mechanical locking structure. To remove it, only specialized cutting tools or grinding methods can be used. Rivmate does not recommend reusing the removed lock bolts because the deformation of the lock ring after removal will affect the accuracy and strength of re-locking. If the structure requires later disassembly and assembly, it is recommended to choose high-strength bolts.
4. Which is more cost-effective for industrial assembly?
From a short-term cost perspective, Rivet is more economical. It has a lower unit price, fast installation speed, and low tool costs, making it suitable for large-scale lightweight assembly line production. However, when analyzed from the total cost of ownership perspective, Lockbolt actually has a greater cost advantage in long-term applications. Due to its maintenance-free feature and high durability, it can significantly reduce the costs of later maintenance and downtime.
In the heavy machinery assembly project, replacing Rivet with Lockbolt can reduce maintenance costs by approximately 35% and extend the structural lifespan by more than 50%.
Build Stronger Connections with Rivmate Lockbolt and Rivet Solutions
In modern industrial assembly and structural engineering, Lockbolt and Rivet each have their own unique value.
Lockbolt is stronger, more stable and more durable, making it an ideal choice for heavy-load structures and high-vibration conditions.
Rivet is lighter, more flexible and more efficient. It performs exceptionally well in lightweighting, single-side installation and mass production.
From automobile manufacturing to railway bridges, from wind turbine towers to steel structure assembly, choosing the right tightening solution determines the safety and life cycle cost of the product.

Rivmate, as a world-leading expert in fastening systems, has always relied on engineering data and industry standards to provide customers with solutions that are highly strong, highly reliable and highly economical.
Our products cover:
- Rivmate Blind Rivets —— The preferred choice for lightweight assembly;
- Rivmate Lockbolt Systems —— High-strength fastening solutions for industrial structures;
- Rivmate Power Tools —— Installation tools that ensure high efficiency and consistency.
Whether you are designing a new product or upgrading an existing structure, Rivmate can help you achieve higher strength, higher efficiency and longer lifespan in assembly performance.
👉 Contact us immediately: Obtain professional fastening solutions tailored for various working conditions, engineering consultation, and sample trials. Let Rivmate’s expertise serve as the core guarantee for the safety of your structure and the efficiency of your production.
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



