How Are Rivets Manufactured? - The Blind Rivet Production Process
Table of Contents
In modern manufacturing, rivets remain one of the most reliable and cost-effective methods for joining metals. From automotive bodies, appliance sheet metal to building curtain wall systems, various assemblies rely on blind rivets and Pop Rivets. For many engineers and purchasers, a key question often arises: How are rivets manufactured? How do they transform from a simple coil of metal wire into structural fasteners capable of withstanding high shear and tensile forces?
As a professional manufacturer of Blind Rivets, Rivmate possesses an ISO 9001 quality system, automated cold heading production lines, and a strict 100% strength testing process. Based on years of production and material research experience, this guide will reveal the manufacturing process and quality control logic of Blind Rivets in a clear and engineering-oriented manner.
Blind Rivet Manufacturing Overview
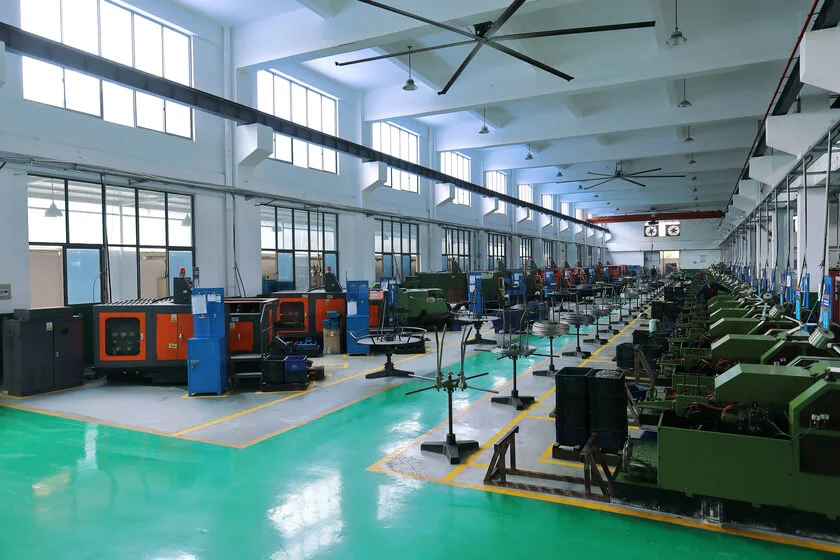
The manufacturing of Rivet is a highly engineered and highly automated process. The entire process starts from raw materials, goes through multiple cold heading, heat treatment, surface treatment and rigorous strength tests, and finally forms a rivet with stable mechanical properties. The following uses the industrial standard process to clearly show you the complete production path:
① Raw Material Preparation
Rivets are typically made from aluminium, steel, stainless steel or copper wire. These wires must have:
- Stable chemical composition
- High purity
- Good cold heading formability
All the wires used by Rivmate are accompanied by material certificates (Mill Certificate), including data on hardness, tensile strength and chemical composition.
② Cold Heading - The Core Process of Rivet Manufacturing
“Cold heading” is the most crucial step in rivet manufacturing. Wire is shaped into the basic form of the rivet body (Rivet Body) through high-speed impact and extrusion at room temperature. The cold heading machine performs multiple actions, including:
- Wire Feeding
- Cutting
- Extrusion
- Heading

This process determines whether the rivet head is round, whether the shank is uniform and whether the strength is stable.
The advantages of cold heading over turning lie in: continuous material fibers → stronger rivets → lower costs → better consistency.
③ Head Forming
After cold heading, the head of the rivet will undergo a secondary heading process to achieve:
- Standardized diameter
- Smooth flange surface
- Uniform meat thickness
The geometric accuracy of the head directly affects the fit and force-bearing performance of the Blind Rivet during assembly.
④ Shank Forming
This step ensures the stability of the shank size, including: the diameter tolerance of the shank, the verticality of the shank, and the basic size of the grip range. Modern rivet production usually corrects mold deviations through an automated detection feedback system, maintaining a tolerance of ±0.02 mm.
⑤ Annealing (Applicable to aluminum or special materials)
Some materials (such as aluminium) need to be annealed to improve plasticity and ensure more uniform expansion during installation. Stainless steel or steel core rivets usually do not undergo this step.
⑥ Cleaning & Degreasing
After the rivets are formed, the cold heading lubricant, metal powder and oil stains should be removed to ensure the adhesion of subsequent surface treatment.
⑦ Heat Treatment - A Crucial Step for Mandrels
The mandrel of a blind rivet must have precisely controlled breaking strength. Heat treatment determines the mandrel’s:
- tensile strength
- fracture groove stability
- reliable breaking load (Break Load)
Insufficient heat treatment → premature fracture of the mandrel
Overheating treatment → Brittle fracture of the mandrel
Rivmate’s heat treatment line can control the hardness of the mandrel within ±2 HRC, ensuring the stability and consistency of each batch of rivets.
⑧ Surface Finishing
To enhance the anti-corrosion performance, various treatments will be carried out, such as:
- Zinc Plating
- Anodizing
- Color Coated
- DACROMET
The surface corrosion resistance can be verified by the ASTM B117 salt spray test. Rivmate’s regular materials can meet the salt spray requirements of 48 to 1000 hours.
⑨ Final Assembly

The Body and Mandrel are combined through automated equipment. Key control points:
- Insertion depth of the mandrel
- Position of the fracture groove
- Matching degree between the body and the mandrel
If the fit is too tight → difficult to install
If the coordination is too loose → the strength will decline.
Rivmate uses CCD cameras for online inspection to ensure that each blind rivet meets the specifications.
⑩ 100% Inspection and Packaging
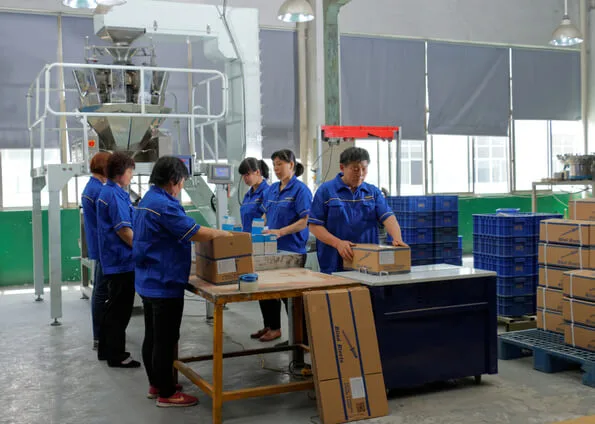

After each batch of rivets is completed, the following should be carried out:
- Breaking force test
- Verification of clamping range
- Random inspection of dimensions
- Appearance inspection
- 100% core shaft residue detection (closed type)
The final packaging uses moisture-proof and shock-proof bags to ensure transportation stability.
Why Are Rivets Heated?
Heat treatment is a special treatment for blind rivets. Please note that not all blind rivets require heat treatment. You will need to judge the need for heat treatment based on your actual application.
There are many benefits to heat treating blind rivets:
- Improve the wear resistance and deformation resistance of blind rivets.
- Improved strength and tensile strength of blind rivets
- Improving the toughness of blind rivets
- Adjustment of material properties
Whether or not you want to heat treat your blind rivets, you can make a judgement in several ways.
If the application scenario of your business requires high strength of the Blind Rivet, which needs to withstand large tensile or shear loads. Then heat treatment is recommended.
In some application environments, the blind rivets will be subject to high friction or abrasion, at this time you need to heat treat them to improve their abrasion resistance and deformation resistance, so as to extend their service life.
If the blind rivets need to work in high temperature environments or extreme temperature conditions, heat treatment can make them have better heat resistance and high temperature resistance.
Of course, heat treatment can reduce the stress and improve the resistance to stress corrosion cracking of the blind rivets.
What Determines Rivet Quality?
To determine the quality of a Rivet, a comprehensive assessment must be conducted from four aspects: material, process, tolerance, and testing. The following indicators directly determine the strength, reliability, and actual assembly performance of the rivet.
a. Material Purity and Tensile Strength
High-quality rivets must be made from high-purity metal wires (aluminum, steel, stainless steel). The tensile strength of the material determines:
- Whether the rivets expand evenly
- Whether the rivets remain stable under shear force and vibration
- Whether cracking occurs during installation
For example: The material strength of Rivmate is all accompanied by the original factory material certificate (Mill Certificate), ensuring the stability of each batch.
b. Precision of Cold Heading Dies
The cold heading die determines the shape and tolerance of the head and shank of the rivet. The more precise the die, the more stable the rivet will be, and the higher the flatness of the head will be.
The concentricity of the rod body will be better, and the force distribution after installation will also be more uniform. If the mold error is too large, it will directly lead to assembly jamming or insufficient clamping force.
c. Mandrel Break-Groove Tolerance
The core shaft fracture groove is the most sensitive position for the Blind Rivet. The stability of the tolerance determines:
- Is the breaking force consistent?
- Will the rivets break prematurely?
- Is the assembly smooth?
The breaking force of high-quality rivets is stable within the range of ±10% of the set value. Rivmate ensures consistency by using CCD cameras to inspect the fracture grooves.
d. Head Geometry Consistency
The shape of the head determines the degree of fit between the rivet and the material, whether the force distribution is balanced, and the appearance (especially for household appliances and sheet metal). An unstable head shape may result in warping, slippage, uneven force distribution, and even failure of the seal.
e. Surface Coating Thickness
Surface treatment affects the anti-corrosion performance, rust prevention ability and salt spray lifespan. Galvanization usually requires 5–12 μm; anodizing is controlled at 7–15 μm depending on the application.
The surface is too thin → It is prone to corrosion
Too thick → Affects tolerance and assembly
f. Mandrel Insertion Depth
If the core shaft is inserted too deeply or too shallowly, it will cause problems such as unstable pull-out, jamming during riveting, and reduced strength. The insertion depth of the core shaft in high-quality products is usually controlled within ±0.05 mm.
g. Salt Spray Resistance Performance
This point must be paid attention to in outdoor projects and in high-humidity environments. Typical reference standards:
- Ordinary galvanizing: 48 – 72 hours
- High zinc coating treatment: 120 – 240 hours
- Sealed stainless steel: 500 – 1000+ hours
Rivmate provides a salt spray test report in accordance with ASTM B117.
h. ISO Quality Control
If the factory manufacturing Blind Rivets does not have ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification, it usually cannot ensure stable quality. This is a mandatory requirement for industries with high standards (such as automotive, rail, and aviation).
Common Defects in Rivet Manufacturing
In the procurement of rivets, identifying manufacturing defects is of utmost importance.
These defects directly affect the tensile strength, clamping force, water resistance, and overall structural reliability of the rivets.
The following are the most common defects in the industrial sector, along with Rivmate’s preventive strategies in quality control.
| Defect Type | Description | Technical Cause | Rivmate Prevention Measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premature Mandrel Break | Rivet does not fully expand; joint fails to lock properly | Break groove too deep; unstable mandrel hardness; misaligned mandrel insertion | CCD inspection of break grooves; mandrel hardness controlled at HV110–130; mandrel insertion tolerance ±0.05 mm |
| Off-Center Rivet Head | Poor appearance; uneven loading; reduced shear strength | Worn cold-heading dies; misfeeding during forming | Replace dies every 80,000–120,000 cycles; automatic feed alignment calibration |
| Shank Cracks | Rivet shank cracks during setting, causing joint failure | Material impurities; excessive cold-heading stress; improper heat treatment | Use high-purity wire; multi-station cold heading; batch tensile testing |
| Uneven Coating | Faster corrosion; rough or inconsistent surface finish | Inadequate pre-treatment; inconsistent coating thickness | Fully automated barrel/plating line; ≥72h salt spray resistance; anodizing thickness 7–15 μm |
| Poor Mandrel Fit | Mandrel too loose (slips) or too tight (hard to break) | Incorrect fit tolerance; uncalibrated assembly equipment | Fit controlled under H9/h9 tolerance; daily calibration of assembly machines |
| Unstable Grip Range | Joint may loosen or under-clamp after installation | Inconsistent body wall thickness; unstable expansion ratio; break load variation | Control body wall thickness ±0.03 mm; 100% break-load testing; batch installation validation |
Rivmate Blind Rivet Manufacturing Capabilities
The production capacity of Rivmate is the fundamental source of stable quality. We adopt a fully digitalized process, with strict tracking from raw materials to the factory exit. The following key points directly reflect the factory’s strength and provide reliable basis for purchasing and engineering users.

- ISO9001 Quality System Assurance All Rivmate factories have obtained ISO9001 certification. Each batch of rivets has a traceable batch number, inspection records and process control forms. This ensures consistency in terms of size, strength and surface treatment.
- Multi-Station Cold Heading Process The core rivets are formed in one process by a 4-6 station cold heading machine, with higher precision for the head, shank and fracture groove. The cold heading process can increase the metal density and significantly enhance the tensile and shear resistance properties.
- Fully automatic assembly & 100% online inspection The production line of Blind Rivet adopts: automatic core insertion machine, online CCD appearance inspection, and online break load monitoring (Break Load Monitor). This ensures that the core insertion depth, break groove size and cap shape of each rivet meet the tolerance requirements.
- Global customer coverage for OEM and engineering projects We provide long-term supply for multiple industries:
- Automotive and rail transportation OEM
- Metal roofing and curtain wall systems
- Industrial equipment and cabinets
- HVAC, electrical enclosures
- Home appliance manufacturing
FAQ: How Are Rivets Manufactured
Q1. How are blind rivets made?
The blind rivets are formed from metal wire through a multi-station cold heading machine in a single process. The core shaft and the cap body are produced separately, then automatically inserted and assembled, and undergo strength testing, surface treatment and packaging.
Common materials include aluminium, steel, stainless steel and copper. The choice depends on strength, corrosion resistance and cost requirements.
- Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant
- Steel: High strength
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant, resistant to salt fog
- Copper: Commonly used in electrical equipment
Q3. Are the rivets forged or machined?
Blind rivets are produced by cold forging rather than machining. Cold forging is achieved through high-speed stamping, which is highly efficient, cost-effective, and results in a continuous metal fiber flow, thereby enhancing the strength.
Q4. What is cold heading in rivet manufacturing?
Cold heading is a process where metal wire is shaped by impacting it with a mold at room temperature. This method enables the formation of the head and shank of a rivet without cutting the material. The advantages include:
- High strength (the metal is not damaged)
- Good dimensional consistency
- High efficiency, suitable for mass production
Q5. How strong are pop rivets?
The strength depends on the material and diameter:
- Aluminum Rivet: Tensile strength of 400–700 N
- Steel Rivet: Tensile strength of 800–1,800 N
- Structural Blind Rivet: Can reach up to 2,000–3,500 N

Rivmate Rivet provides high quality sustainable riveting solutions. We are one of the leading blind rivet manufacturers in China, offering a large selection of standard blind rivets and high strength structural rivet solutions.
Our blind rivets are not only affordable but also of consistent quality. We provide our customers and partners with the best riveting solutions within their budget.
We offer a wide range of rivet types. So, if you are looking for the best Blind Rivet solution for any kind of project or business, feel free to contact us. Our engineers will get back to you as soon as possible.
📧 Product Inquiry: manufacture@world-rivet.com
🌐 Official Website: https://worldrivet.com/

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met







