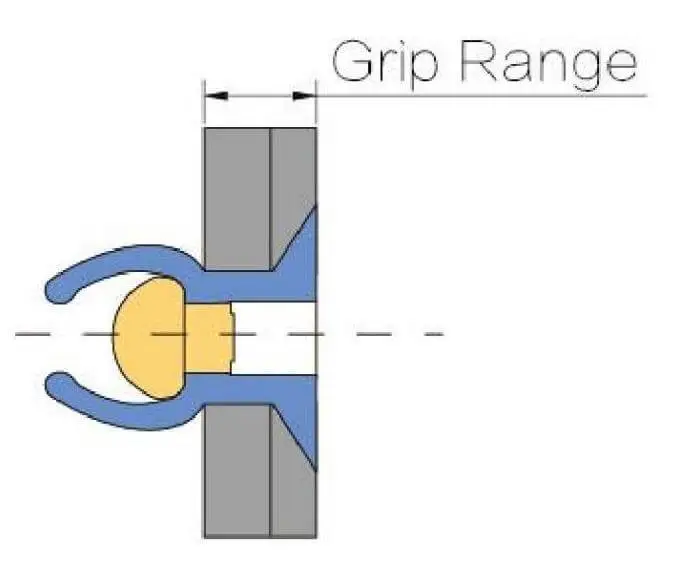
What is the Grip Length of a Rivet?
Table of Contents
One of the common problems when choosing or installing rivets is “what is the grip length of a rivet”. The grip length refers to the total thickness of the material that the rivet can firmly grip when fixed. It directly determines whether the rivet can be formed correctly and whether the connection point has sufficient strength. If the grip length is too short, the rivet cannot fully expand, which may lead to loosening; if it is too long, the rivet may deform unevenly, reducing the structural reliability. Therefore, correctly understanding the grip length is a crucial step in ensuring the quality of riveting.
However, many users often confuse grip length with the total length of the rivets, resulting in incorrect selection or installation. This is a parameter that is frequently misunderstood but is of crucial importance. This article will deeply analyze the concept of grip length, explain its relationship with the material thickness and the diameter of the rivets, and provide practical selection methods.
Definition of Grip Length
In the application of rivets, Grip Length (the thickness range of the material that the rivet can secure) refers to the range of material stacking that the rivet can firmly hold. In other words, it represents the total thickness of the material that the rivet can effectively grip and keep firmly in place after installation. For example, if the combined thickness of two plates is 5mm, then the selected rivet’s grip length must cover this thickness in order to form a qualified rivet connection.
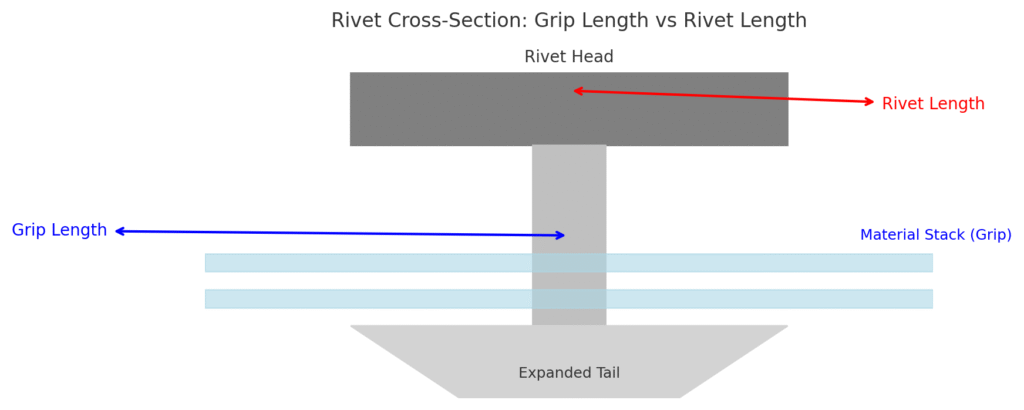
It is particularly important to note that Grip Length ≠ Rivet Length (total length of the rivet).
- Rivet Length refers to the complete length of the rivet from its head to its tail.
- Grip Length is only related to the thickness of the material that can be clamped and does not include the deformed part at the tail after expansion.
Many beginners often mistakenly take the total length of the rivet as the clamping thickness, which leads to incorrect selection and affects the connection strength. The correct approach is: First calculate the thickness of the material stack, then select the type based on the grip length, and finally confirm whether the total length of the rivet matches the installation requirements.
👉 The figure below illustrates the position of Grip Length (a cross-sectional view of the head, shaft, and expansion zone):
- Head of the rivet: Exposed, serving a fixing function.
- Grip Length: The thickness range of the material stack.
- Bulging area at the tail: Deforms during installation and is used for locking the material.
Why Grip Length Matters
In the application of rivets, the Grip Length directly determines the strength and reliability of the connection. If the grip length is too short, the rivet cannot fully grip the material, and the connection point is prone to loosening or even detachment. On the contrary, if the grip length is too long, the tail end may not expand adequately, and there may be situations such as rotation, slippage, or uneven deformation.
Installation stability also depends on the correct grip length. Only when the clamping length matches the thickness of the material can the rivet form uniform and stable deformation during installation. Either too short or too long will increase the difficulty of installation and even result in the failure of the rivet.
From the perspective of cost efficiency, choosing the wrong grip length can lead to rework, material waste, and potential failure costs. In large-scale production or engineering projects, such losses can escalate into significant economic burdens. According to industry data, improper selection of fasteners can increase the rework rate by 10% – 15%, directly increasing manufacturing and maintenance costs.
More importantly, in industries with high reliability such as construction, transportation, and aviation, the standards are extremely strict. For instance, the US aviation standard NAS, the US industrial fastener standard IFI, and the international standard ISO all clearly stipulate that the rivets must be correctly selected based on the grip length. These standards not only ensure the connection strength but also guarantee safety and long-term durability.
How to Measure and Choose the Correct Grip Length
Choosing the correct grip length is the first step in ensuring the quality of rivet connections. Here are the recommended steps:
Use a caliper or grip gauge to measure the thickness of all the materials that need to be tightened. This should include the gap, tolerance, surface coating, and thickness of the gasket. Ignoring these details will result in a shorter grip length, thereby causing installation problems.
Step 2: Refer to the manufacturer's Grip Range chart
Most rivet manufacturers (such as Rivmate) will provide a Grip Range chart. Just compare the total thickness of the material with the chart to find the appropriate grip length range. Rivmate also offers its own Grip Chart, which can be used as a reference tool to quickly confirm the matching model.
Step 3: Recommended Nail Length
Once the grip length is determined, the corresponding total length of the rivet (rivet length) can be recommended by the chart or the selection software. Usually, the total length of the rivet = grip length + an appropriate allowance, which is used for the tail to be expanded and shaped.
Common Errors to Avoid:
- Only the thickness of the bare material was measured, without including the paint, anodized layer or adhesive.
- The additional layers such as gaskets and seals were ignored.
- The selection was made solely based on experience, without referring to the grip chart or industry standards.
Recommended Tools:
- Grip Gauge (Clamping Length Measuring Tool): The most commonly used specialized tool, which can directly display the grip length.
- Digital Caliper: Suitable for quickly measuring the thickness of material stacks.
- Selection Software or Mobile Application: Some manufacturers provide digital tools that can automatically recommend the appropriate nail type based on the input thickness.
By following the above methods, users can not only avoid selection errors but also improve installation efficiency and ensure long-term stability and reliability of the connection.
Grip Length vs. Grip Range

In the selection of rivets, Grip Length and Grip Range are often confused with each other, but they have different meanings.
- Grip Length: This refers to the specific material thickness that the rivet can grip. It is a fixed point value used to determine whether the rivet can match a particular thickness.
- Grip Range: This indicates the thickness range covered by a certain type of rivet. Rivets of the same model can be applicable to various material thicknesses, as long as they fall within this range, installation can ensure reliability.
For example: The Grip Range of a certain type of rivet is marked as 0.062″—0.125″(1.6—3.2mm). This means that this rivet can be used for material combinations with a total thickness ranging from 1.6mm to 3.2mm. Users only need to confirm that the measured total thickness falls within this range, and then they can be assured to use it.
Correct understanding of these two terms can prevent errors in procurement caused by confusion. For instance, if one only focuses on the point value of grip length but ignores the grip range, one might select a model that lacks adaptability and tolerance margin, thereby increasing the risk of assembly.
Remember: Grip Length is a single point, while Grip Range is an interval. In practical applications, Grip Range is more commonly found in selection tables and product catalogs, facilitating users to quickly match the material thickness.
Case Studies
Case 1: Incorrect Choice of Grip Resulted in Re-work
A certain transportation equipment manufacturer selected the components based solely on the total length of the rivets, without taking into account the actual grip length. As a result, some rivets failed to fully expand, causing loosening and rotation problems. Eventually, over 30% of the rivets required rework, directly resulting in delays in work time and material waste. This case clearly demonstrates that ignoring grip length can seriously affect assembly quality and production efficiency.
Case 2: Selecting the Right Model Enhances Efficiency
Another customer used the “Grip Range” chart provided by Rivmate for component assembly in aviation. By accurately measuring the material thickness and selecting the appropriate grip length, the success rate of assembly was increased to 98%. The rework rate significantly decreased, and the overall assembly efficiency improved by approximately 15%. Not only did this save labor costs, but it also reduced inventory pressure.
Case 3: Industry Application Feedback
- Aerospace sector: Customer feedback indicates that the correct selection of grip length can effectively meet the NAS and ISO standards, avoiding potential safety hazards caused by the failure of fasteners.
- Transportation industry: In the manufacturing of railway carriages, Rivmate rivets, due to their high grip length matching degree, have increased assembly efficiency by 12% and significantly reduced maintenance frequency.
- Furniture manufacturing: Customer reports show that after adopting the recommended grip length, the connection between wood and metal parts becomes more stable, reducing the rate of after-sales maintenance.
These cases demonstrate that: The correct selection of Grip Length is not only a technical issue, but also a key aspect of quality and cost management. Through scientific measurement and reasonable selection, enterprises can achieve the best balance among safety, efficiency and economic benefits.
FAQs

Q1: What if the material thickness falls between the two Grip Lengths?
A: Always choose the rivet model whose material thickness falls within the Grip Range. If the thickness is exactly at the critical value, it is preferable to select the one with a grip range that is closer to the actual value rather than relying on a single grip length point value. This ensures that the tail expansion is sufficient and the connection is stable.
Q2: Can we use rivets with a longer Grip Length?
A: It is not recommended. When the Grip Length is too long, the tail end of the rivet cannot fully extend, which may result in rotation, loosening or insufficient connection strength. Industry standards (such as NAS, IFI) clearly stipulate that the rivet must match the material thickness to ensure installation quality.
Q3: Does Grip Length Affect Shear/Compression Strength?
A: Yes. Incorrect grip length will prevent the rivet from achieving the ideal expansion form, thereby reducing the shear strength and tensile strength. For instance, when the grip length is too short, the bearing capacity of the connection point is insufficient; when it is too long, the expansion is incomplete and the strength also decreases. A correct grip length can ensure that the strength is close to the design value of the rivet.
Q4: Does the thickness of the coating need to be calculated separately?
A: Required. Any additional thickness – including coatings, anodizing, sealants or gaskets – should be included in the total material thickness. If this part is ignored, the actual grip length will be shorter, causing the rivets to fail to form correctly. Especially in the aviation and transportation industries, the standard requires that the coating thickness must be precisely considered to ensure long-term reliability.
Rivmate Expert Recommendations
Before the formal riveting process, Rivmate advises users to ensure the following three key parameters:

- Material Thickness: Accurately measure the total thickness, including the coating, gap, and washer.
- Material Type: Different materials (aluminum, steel, stainless steel) have different requirements for the expansion form and strength of the rivets.
- Structural Strength Requirements: Select the appropriate shear and tensile strength based on the application scenario to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Rivmate not only offers products, but also provides technical support and selection assistance to customers. Through the Grip Range chart, selection software and consultation with engineers, customers can quickly find the optimal rivet solution, avoiding rework and cost waste caused by incorrect selection.
Meanwhile, Rivmate has developed bolting solutions for multiple industries, including aviation, transportation, furniture, and construction. We can offer:
- Online Selection Tool: Just input the material thickness and type, and it will automatically recommend the appropriate model.
- One-on-One Technical Support: A team of professional engineers will assist you in resolving installation issues.
- Customer Exclusive Channel: Quick connection for sample application and large-scale procurement demands.
Through scientific measurement and professional support, Rivmate helps customers achieve the optimal balance between safety, efficiency and cost control.
Get the Right Grip, Every Time – Start with Rivmate

In the application of rivets, Grip Length is a key parameter that ensures the strength and reliability of the connection. Incorrect selection can lead to assembly failures, rework, and additional costs, while correct selection can significantly improve installation efficiency and structural durability. Whether in aviation, transportation, furniture, or construction industries, having a correct understanding and application of grip length is a prerequisite for achieving high-quality assembly.
Rivmate invites you to learn more:
- Contact the Rivmate technical team to obtain professional selection support and application solutions.
- Further reading:
Take immediate action to ensure that every riveting operation is precise, reliable and efficient.
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met