Table of Contents
Are you in the process of making a decision about purchasing rivets? You need to know about Blind Rivet Strength. What are the components of the strength of a blind rivet? With this guide, you will learn everything you need to know about the strength of a blind rivet.
Table of Contents
Blind Rivet Strength - Basic Overview
Blind rivet strength refers to its ability to withstand external forces under specific conditions without failure.Blind rivet strength mainly includes tensile strength, shear strength, fatigue strength and other key indicators.

Blind Rivet Strength consists of a number of different components. Included:
- Rivet Tensile strength
- Rivet Shear Strength
- Core removal force
- Core retention force
- Nail breakage force
- Clamping force
Components of Blind Rivet Strength
1. Tensile Strength
The tensile strength of a blind rivet is its maximum ability to resist fracture under axial tensile load. This index is the core index to measure the reliability of rivet connection. Tensile force represents the maximum force value (unit: kN or MPa) that a rivet can withstand before failure under axial tensile load, reflecting the comprehensive performance of rivet material strength and structural design.
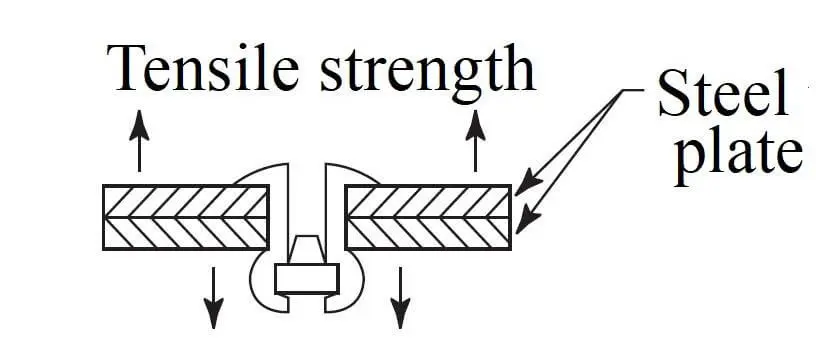
Factors affecting Blind Rivets Tensile Strength
The main factors affecting the tensile strength performance of the blind rivets are two: 1. rivet material 2. rivet head type.
Common metal materials used in the manufacture of blind rivets are aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel and titanium alloy. By their made of blind rivets tensile strength from small to large arrangement for aluminum blind rivets, stainless steel blind rivets, carbon steel blind rivets, titanium alloy blind rivets.

Rivet head types are generally dome head, countersunk head and large flange head. large flange head blind rivets have the highest tensile strength and countersunk head blind rivets have the lowest.
2. Shear Strength
The shear resistance of a blind rivet is its ability to resist fracture or failure under lateral shear. The maximum force value (in kN or MPa) that the rivet can withstand before failure under transverse shear load, reflecting the ability of the rivet to resist material slippage or fracture
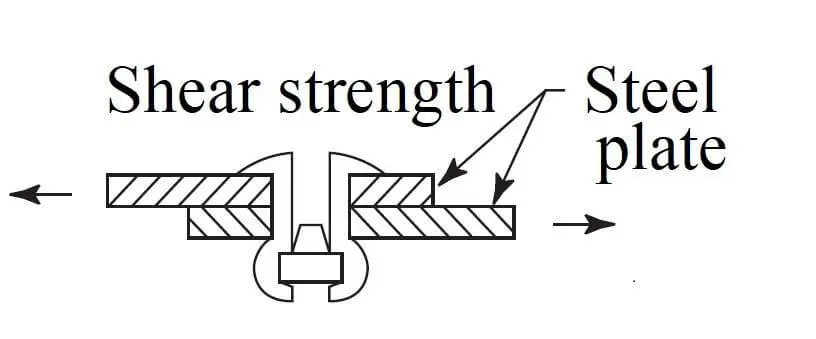
Factors affecting Blind Rivets Tensile Strength
Factors affecting the shear strength of blind rivets include: rivet material and rivet structure.
- Rivet material: aluminum < stainless steel < carbon steel < titanium alloy.
- Rivet construction design: common blind rivets < structural rivets.
3. Core Removal Force
The core ejection force of a blind rivet is the maximum force required when the core is pulled out or ejected during installation. Nail core ejection force is the installation of blind rivets, riveting gun exerted by the axial tension so that the nail core breakage or complete ejection of the force required (unit: kN).
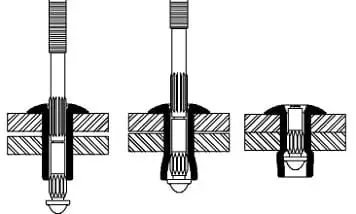
The Role of Nail Core Ejection Force
- Ensure that the nail body expands sufficiently to form a tight joint.
- Controlling material deformation during installation (e.g. avoiding sheet crushing).
- Ensuring that the nail core breaks precisely at the preset break point (Notch Point), preventing excessive length of the residual mandrel.
4. Core Retention Force
The core retention force of a blind rivet refers to the bonding force between the portion of the core remaining in the rivet body and the rivet body after the breakage of the core after the rivet installation is completed. This characteristic ensures that the core of the nail will not be dislodged during vibration, shock or prolonged use. It directly affects the sealing, conductivity (e.g. electrical connection scenarios) and long-term reliability of the connection.
The Role of Nail Core Retention Force
- Maintain connection integrity (avoid loosening or leaking).
- Ensure continuity of electrical connections (e.g. grounded rivets).
- Preventing foreign objects from entering rivet holes (aerospace, outdoor equipment).
nail core retention vs nail core ejection force
| Parameters | Nail Core Retention | Nail Core Ejection Force |
| operative phase | Post-installation use phase | Installation process (moment of nail core breakage) |
| test objective | Assessment of the resistance of the residual part of the nail core to dislodgement | Measurement of the force required to break the nail core |
| typical value | Aluminum rivets: 0.5-2kN, steel rivets: 3-8kN | Aluminum rivets: 1.5-3kN, steel rivets: 5-10kN |
5. Clamping Force
The clamping force of a blind rivet is the squeezing force exerted on 2 loose pieces, after the rivet has been installed. The higher the clamping force, the less likely to loosen the workpiece after riveting, but may cause damage to some soft or brittle workpiece. The role of clamping force is mainly to prevent sliding of the connecting surfaces, to reduce contact resistance (electrical connection), and to improve fatigue life.

Difference with tensile/shear
| Parameters | Clamping Force | Tensile/Shear Strength |
| Define | Maintains static compression force of the connection | Maximum load capacity before failure |
| Test Condition | Non-destructive measurements (e.g. ultrasound) | Destructive testing (tensile/shear to break) |
| Typical Value | Aluminum rivets: 1-5 kN, steel rivets: 5-20 kN | Aluminum rivet shear resistance: 2-10 kN |
Factors affecting Blind Rivets clamping force
The clamping force is not always constant. It will change depending on the following factors.
- Rivet design and material
- Correct installation
- Characteristics of the material being joined
Rivet design and materials: Open end rivets do not have the same clamping force as closed end rivets and structural rivets. Titanium rivets have the highest clamping force and aluminum alloys are relatively low.
Correct installation: Incorrect installation may result in rivet failure.
Characteristics of the material to be joined: The softer the material to be joined, the higher the clamping force required to compensate for plastic deformation.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Comparison of Blind Rivets Strength with Other Fasteners
| Parameter | Blind Rivet | Bolt/Nut | Self-Tapping Screw | Welding | Structural Adhesive |
| Tensile Strength | Medium-High (Al: 3-5kN, Steel: 8-15kN) | High (Grade 8.8 Bolt: ≥800MPa) | Low (M5 Screw: 2-4kN) | Extreme (Matches Base Material) | Medium (Epoxy: 10-30MPa) |
| Shear Strength | Medium-High (Al: 2-5kN, Steel: 6-12kN) | High (Grade 8.8 Bolt: ≥640MPa) | Low (M5 Screw: 1-3kN) | Extreme (Matches Base Material) | Low (Epoxy: 5-15MPa) |
| Fatigue Strength | Medium (Clamping-Dependent) | High (Preload-Controlled) | Low (Prone to Loosening) | Medium (HAZ Weakness) | Low (Aging/Cracking) |
| Dynamic Load Adaptability | Medium (Requires Anti-Loose Design) | High (Elastic Deformation) | Low (Vibration Failure) | Medium (Weld Toughness) | Very Low (Brittle Failure) |
Comprehensive Comparison Table
| Metric | Blind Rivet | Bolt | Self-Tapping Screw | Welding | Structural Adhesive |
| Static Strength | ★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆ |
| Dynamic Strength | ★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★☆ | ★★★☆ | ★☆ |
| Ease of Installation | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆ | ★★★☆ |
| Reusability | ★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆ | ☆ | ☆ |
| Corrosion Resistance | ★★★★ (Stainless/Al) | ★★☆ (Coating Required) | ★★☆ | ★★★ (Weld Treatment) | ★★★☆ |
| Cost | ★★★☆ | ★★★☆ | ★★☆ | ★★☆ | ★★★☆ |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How to Choose the Right Blind Rivet to Meet the Strength Requirements?
1. Clarify intensity requirements
Before choosing the right Blind Rivet, you need to first figure out the type of load for your application scenario. The types of loads that may occur in common application scenarios are as follows:
- Static loads: tensile/shear strength is of concern (e.g. steel connections).
- Dynamic loads: fatigue strength needs to be evaluated (e.g. vehicle chassis, aircraft skins).
- Composite loads: both tensile-shear combinations are considered (e.g. lifting brackets).
2. Key Selection Parameters
Rivet Material
| Rivet Material | Shear Strength Range | Application | Notes |
| Aluminum (5056) | 2-5 kN | Lightweight structures (electronics) | Avoid direct contact with steel (galvanic corrosion) |
| Stainless Steel (316) | 6-12 kN | High-corrosion environments (ships, chemical plants) | Must pair with stainless steel substrates |
| Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) | 15-22 kN | Aerospace high-temperature parts | High cost, requires specialized tools |
| Carbon Steel (Galvanized) | 8-15 kN | Industrial machinery, steel structures | Coating thickness affects corrosion resistance |
Diameter Selection Guidelines
| Total Thickness (mm) | Recommended Diameter (mm) | Typical Shear Strength (Stainless Steel) |
| 1-3 | 3.2 | 4-6 kN |
| 3-6 | 4.0 | 8-12 kN |
| 6-10 | 4.8 | 12-18 kN |
Rivet Type
- Open type: low shear resistance (friction-dependent), suitable for non-load-bearing connections.
- Closed type/multi grip type: 30%-50% higher shear resistance (mechanical interlocking structure).
Custom Blind Rivets for Your Project
There is no one rivet that is the best or the worst. There is only the right rivet for your project. If you don’t know how to go about choosing the right strength of blind rivets for your business, contact us!
Rivmate is leading rivet manufacturer and supplier in china. You can solve all your rivet sourcing problems at once. Get samples for testing immediately.






