Pop Rivet Strength Stainless vs. Aluminum
Table of Contents
Pop Rivet is an extremely widely used joining method in structural fastening. With their ease of operation and lack of back support, pop rivets are used in a wide variety of industrial scenarios such as sheet metal assembly, photovoltaic structures, equipment housings, bridge installations and more. However, under the premise of the same size, the materials used for rivets – especially aluminum and stainless steel – can make a several-fold difference to the strength of the connection, which is a key factor often overlooked by many engineers in the selection process.
This blog will focus on the topic of “Pop Rivet Strength: Stainless vs. Aluminum”, in-depth comparison of the actual tensile and shear strength of the two materials in the same size, combined with typical application scenarios. Hopefully, this will help you clarify in which structure you should give priority to the use of high-strength stainless steel rivets, and when you can use lightweight aluminum rivets to achieve cost-effective optimization. Understanding the material differences is the first step in building a safe and efficient connection system.
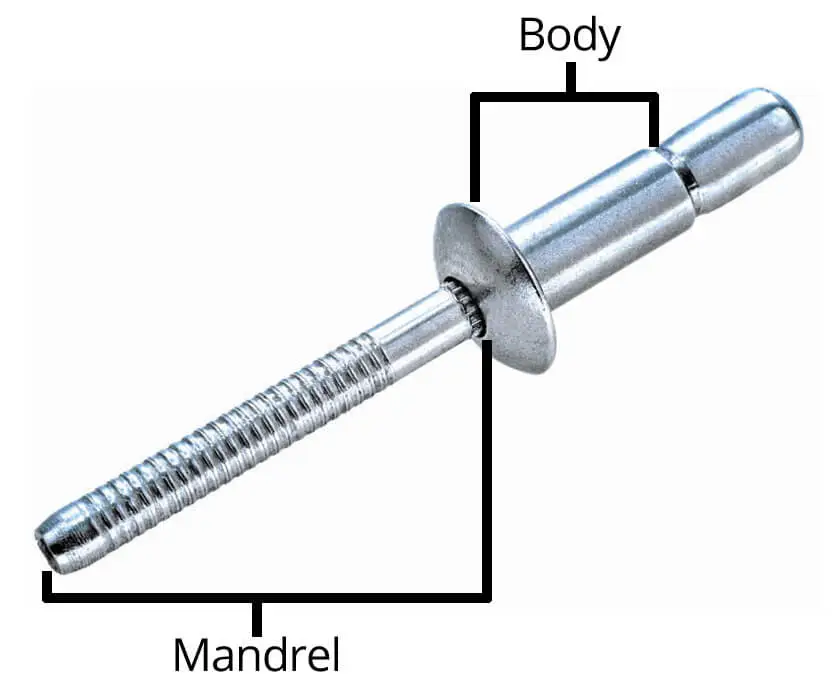
Basic Structure and Force Mechanism of Pop Rivet
Pop Rivet (Blind Rivet) is a permanent mechanical fastener that operates on one side. It consists of the following two major components:
- Rivet Body: Determines the overall mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and material compatibility. It is the main structural part of the connection bearing
- Rivet Mandrel: provides the traction force required for expansion, and its structural design affects the quality of riveting and core stability.
The force mechanism after the riveting is completed:
- Resistance to tension (Rivet Tensile Load): the cap body at both ends respectively clamped to the parent material, in the axial direction to carry the pulling force.
- Rivet Shear Load: The two plates slide on the rivet lateral shear stress.
- Rivet Clamping Force: The compression force created by the expansion of the mandrel ensures that the joint surface does not loosen and does not shift.
Different materials (e.g. aluminum vs. stainless steel) will directly affect the strength level of the cap and mandrel, which in turn determines the ability of the riveted joint to withstand tensile and shear forces. For example, a 4.8mm diameter aluminum rivet will have a shear resistance of 1.2-1.6 kN, while a stainless steel rivet will have a shear resistance of 3.5-5.0 kN, which is a significant difference in performance.
How Strong are Stainless Steel Pop Rivets?
The mechanical strength of stainless steel blind rivets is outstanding. In terms of tensile and shear strength, stainless steel rivets are much stronger than aluminum or carbon steel coated rivets. For example, in the commonly used 4.8mm (3/16 inch) size, stainless steel rivets typically have a tensile strength of 3.5-5.5 kN and a shear strength of 3.0-5.0 kN, which is equivalent to two to three times the strength of an aluminum rivet of the same size.
In addition, stainless steel has excellent fatigue and deformation resistance. Even in extreme environments such as high vibration, alternating heat and cold, moisture and corrosion, the structural stability of the riveted joint can be maintained, preventing loosening or fracture.

How Strong are Aluminum Pop Rivets?
Aluminum blind rivets are not as strong overall as stainless steel rivets, but they perform consistently in low to medium load connections. To the commonly used 4.8mm (3/16 inch) specifications, for example, the tensile strength of aluminum rivets is usually in the 1.5-2.0 kN, shear strength of about 1.2-1.6 kN.
At the same time, aluminum rivets have good corrosion resistance and high ductility, not easy to rupture stress concentration. Its light weight, low cost and strong adaptability make it an economical fastening solution for light manufacturing, appliance assembly, display structures and ventilation equipment.
Stainless vs Aluminum Pop Rivet Material Comparison
| Property | Aluminum Rivet | Stainless Steel Rivet |
|---|---|---|
| Material Density | ≈ 2.7 g/cm³ (Lightweight) | ≈ 7.9 g/cm³ (Heavy) |
| Tensile Strength | 150–250 MPa (Medium) | 450–700 MPa (High) |
| Shear Strength (Typical 4.8mm) | ~1.2–1.6 kN | ~3.5–5.0 kN |
| Hardness | Low to Medium | High – suitable for vibration/structural use |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (oxidation-resistant) | Excellent (especially 304/316) |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | High (matches aluminum structures) | Medium-low (better for steel frameworks) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Workability | Excellent – easy to install | Poor – requires high-power tools |
| Cost | Low to Medium | Medium to High (2–4× aluminum) |
| Recommended Applications | Solar frames, electronics, enclosures | Marine, heavy-load, corrosive environments |
Measured difference in strength between stainless steel and aluminum pop rivet of the same size
There is a significant difference in strength between Stainless Steel and Aluminum Pop Rivets in the same size (e.g. 4.8mm / 3/16″). This difference is mainly in the two key parameters of rivet Tensile Strength and rivet Shear Strength. This difference stems not only from the material’s yield limit and structural rigidity, but also directly affects its reliability under high loads or long-term use.

Tensile and Shear Strength Comparison of 4.8mm Pop Rivets
| Material Type | Tensile Strength (kN) | Shear Strength (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Rivet | approx. 1.2–1.8 | approx. 1.0–1.6 |
| Stainless Steel Rivet | approx. 3.5–5.5 | approx. 3.0–5.0 |
As can be seen from the table above, the tensile and shear strengths of stainless steel rivets are typically 2-3 times or more than those of aluminum rivets for the same diameter. This difference is extremely critical in primary structural connections, high vibration loads, dynamic shock or outdoor fatigue conditions. Stainless steel caps provide greater grip and structural rigidity, and mandrel breaks are more stable and reliable, and less prone to premature failure due to impact or fatigue fracture.
Take a typical photovoltaic rail connection as an example, if you use aluminum rivets, in the strong wind, thermal expansion and contraction of the frequent role of the rivets are prone to loosening, pulling cracks. While the use of stainless steel rivets can maintain long-term structural stability, extend the life of the system, and enhance the anti-dislodgement risk level.
Conclusion
The strength of a Pop Rivet of the same size depends not only on the diameter, but also on the material. Stainless steel rivets are suitable for load and corrosion resistance of the two high requirements of the structure, while aluminum rivets in the lightweight, economic and general corrosion resistance needs of excellent performance. Engineering selection should be strictly based on the load rating and working conditions for material matching.

Preferred scenarios for stainless steel rivets
Highly loaded structural connections
For main connection parts with high force strength. Such as industrial supports, steel beam ends, heavy equipment shells, requiring high shear and tensile properties.
Outdoor or coastal highly corrosive environments
such as seaside power stations, wind turbine foundations, traffic signs, communication equipment, etc., which need to withstand rain, salt spray and chloride ions for a long time.
Long-term maintenance-free or inaccessible structures
including building curtain wall hanging structures, roof anchors, marine facilities fastening points, etc., the service life is required to be ≥20 years or more.
High vibration or shock working condition system
Scenarios such as rail transportation, robotic arms, truck structural components, engine hatch covers, etc., with high requirements for fatigue strength and riveting stability.
Connection parts with high temperature requirements
Industrial exhaust ducts, hot air systems, high temperature control boxes, etc. Stainless steel has superior heat resistance and thermal expansion stability.


Scenarios suitable for the use of aluminum rivets
Lightweight assemblies or non-load bearing structures
such as photovoltaic bezels, medium pressure blocks, electronic control box housings, lighting fixtures, etc., with low tensile and shear requirements, emphasizing lightweight and installation efficiency.
Weight-sensitive application systems
such as aerospace lightweight panels, automotive interior parts, battery tray fixing, low density of aluminum, facilitating the lightweight design of the whole machine.
Aluminum Profile Structural Connections (Thermally Compatible)
In architectural aluminum profiles, door and window keels, and aluminum bracket systems, aluminum rivets are aligned with the thermal expansion of the connected parts to avoid stress buildup.
Low corrosion, dry environment
Indoor electrical equipment, closed cabinets, office structural components and other environmentally stable, not easy to corrode working conditions, aluminum can meet the protection needs.
Projects requiring high construction efficiency and cost
mass installation (such as rapid assembly plant, solar racking construction), aluminum rivets are easy to construct, reduce installation and tool load.
Custom Riveting Solutions from Rivmate
Stainless steel and aluminum have their own advantages and disadvantages, the former provides excellent structural strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments. The latter is characterized by lightweight, economical and efficient construction, and is widely used in the photovoltaic, electrical and light structural industries. Understanding the performance logic behind the materials is the only way to select the truly appropriate riveting solution for your project.
As a professional industrial fastener brand, Rivmate specializes in the development and manufacture of blind rivets, structural rivets and custom connectors. We offer a full range of material combinations including aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, copper and composite structures, and our products are widely used in the fields of new energy, construction, electrical and rail transportation.

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



