Table of Contents

If a blind rivet does not have a rivet body, there is no way for it to form a stable connection. Therefore, the rivet body is the key to providing a permanent connection in a blind rivet.
By reading this ultimate guide, you will learn the basic definition of a rivet body, what it does, what it is made of, and how it is made. Let’s explore the mysteries of rivet body!
Table of Contents
What is Rivet Body?
Rivet body is the main structural part of the rivet, usually refers to the cylindrical shank part (shank), excluding the head (head) or tail deformation formed after riveting. It assumes the core function in the rivet structure.
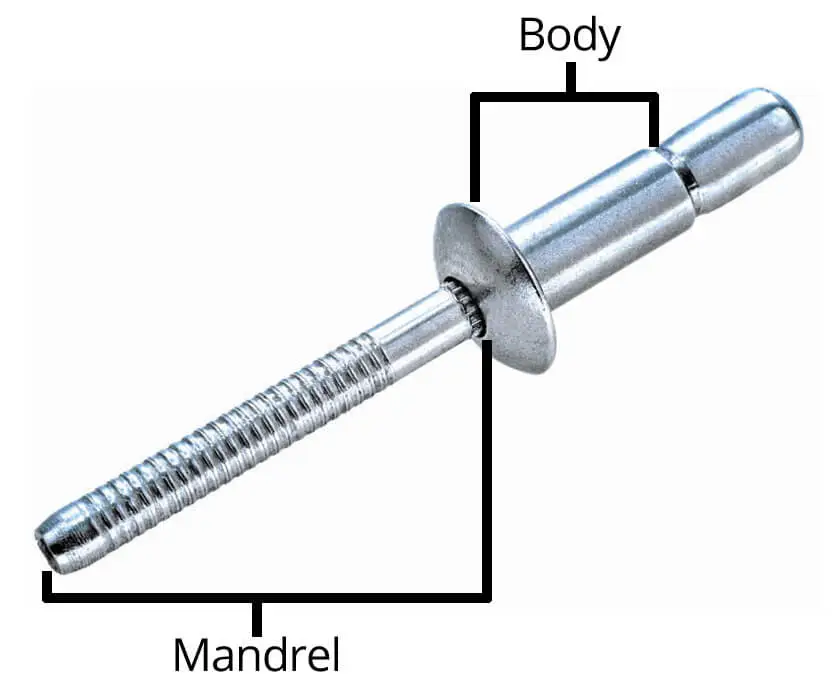
The working principle of the blind rivet is to form a fastening connection through the mechanical deformation of the rivet body. Therefore, the reliability and durability of the rivet body is very important, which is directly related to the overall safety of the riveted joint.
The Role of Rivet Body
1. Fixing and supporting the workpiece
- Expansion to fill the hole: Blind rivet body is usually hollow structure, there is a mandrel inside. During installation, a special tool pulls on the mandrel, causing the end of the rivet body to expand and deform, tightly filling the holes in the workpiece to form a fixed end similar to an “umbrella handle”. This expansion creates radial pressure, clamping the workpiece on both sides and preventing loosening.
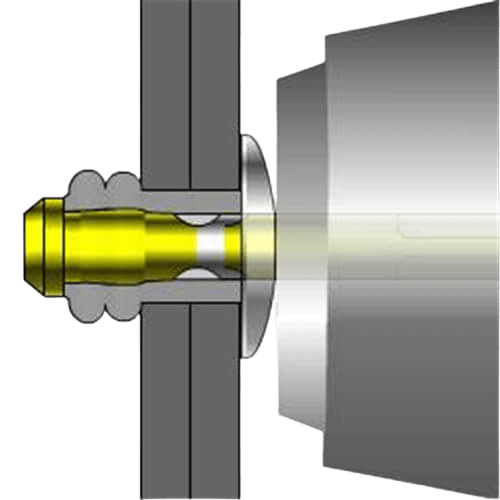
Resistance to mechanical loads:
- Shear force: the expansion of the rivet body through friction and mechanical bite, to prevent the workpiece along the parallel plane of the sliding (such as chassis panels subject to vibration).
- Tensile force: The “tab” formed at the expanding end of the rivet body snaps onto the back of the workpiece, preventing the connection from being pulled apart (e.g. tensile load on billboard frames).
2. Realization of unilateral installation
The design of blind rivet body solves the limitation that traditional rivets need to be operated from both sides. When installing, just pull the mandrel from one side of the workpiece, the tail automatically expands to form a fixed end, without the need to enter the back of the space, suitable for closed or narrow environment (such as pipeline walls, automobile compartments).
3. Applicability and material characteristics
Blind rivet body expands to accommodate different thickness combinations (by adjusting the nail body length). Therefore it is often used in sheet metal, plastic or composite materials.
In addition, the rivet body material is mostly aluminum, stainless steel or nylon, which is lightweight and corrosion resistant. Ideal for aerospace, electronic equipment housings and other scenarios.

If the rivet body is of closed design, then it can provide good water and air resistance.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Rivet Body Material : Application Scenarios with Different Materials
The material of the Rivet Body directly affects its mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, weight and cost. In order to adapt to different application scenarios, there are a variety of materials for the rivet body.
- Aluminum Alloy (5056, 2217)
- Carbon steel (low or medium carbon steel)
- Stainless steel (304, 316)
- Monel
- Copper
- Nylon
| Factor | High-priority Materials | Explanation |
| Strength Demand | Steel, Titanium Alloy | Preferred for high shear or tensile loads (e.g., bridges, heavy machinery). |
| Corrosion Resistance | Stainless Steel, Titanium Alloy | Avoid electrochemical corrosion in chemical/offshore environments. |
| Lightweight | Aluminum Alloy, Titanium Alloy | Reduce structural weight in aerospace/automotive applications. |
| Cost Control | Carbon Steel, Aluminum Alloy | Economical choice for mass production or budget-limited projects. |
| Electrical Conductivity/Insulation Requirements | Copper (conductive), Nylon (insulative) | Electrical connections or scenarios requiring current isolation. |
| Temperature Adaptability | Stainless Steel (high temp), Titanium Alloy | Stainless steel for high-temp environments (<800°C); nickel alloys (e.g., Inconel) for extreme temps. |
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Manufacturing Process of Rivet Body
The manufacturing process of the rivet body directly affects its mechanical properties, durability and application scenarios. The following are typical production methods.
Cold Heading
Cold heading is formed by applying high pressure to metal wires in the cold state and extruding them using a die (e.g. cylindrical nail shanks and pre-heads). This step usually involves continuous molding using multiple stations to progressively shape the rivet profile.

The core impact of Cold heading on the rivet body is as follows:
- Increased shear strength (up to 15-20%)
- Suitable for high volume production (hundreds of pieces per minute)
- Material utilization of more than 95 percent
Machining
Machining is the cutting of bars or tubes on CNC lathes, finishing complex features such as outside diameters and head grooves. The tolerance accuracy of this technique can be as high as ±0.01 mm. but it leads to 30-50% material waste and high cost.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is divided into a total of four parts, according to the actual need to choose to use different combinations of parts. In the rivet body, quenching + tempering is often used to increase the hardness and strength of the steel rivet body (tensile strength up to 1000MPa or more). Therefore heat treatment is often used on rivets that require high strength.

The core effects of heat treatment on the rivet body are as follows:
- Strength-toughness balance: Improper quenching is prone to brittle fracture and requires strict control of the cooling rate (e.g. oil quenching or graded quenching).
- Residual stress: Stress relief annealing is required after heat treatment to avoid cracking during installation.
Surface Treatment
On the rivet body, surface treatment is the most commonly used measure to increase the characteristics of the rivet body. The common types of processes are listed below:
- Electroplating (zinc, cadmium): anti-corrosion, with a coating thickness of 5-15 μm.
- Anodizing (Aluminum): Forms an oxide film that is resistant to abrasion and can be colored.
- Dacromet coating: environmental protection against rust, suitable for high temperature environment.

The core impact of the surface finish on the rivet body is as follows:
- Coefficient of Friction: Excessive plating may result in increased resistance to expansion during installation, affecting clamping force.
- Corrosion Resistance Life: Galvanized plating can last up to 500 hours or more in salt spray environments, anodized aluminum is more resistant to chemical corrosion.
Parameter Composition of the Rivet Body
Rivet Body’s dimensional specifications are defined by a number of key parameters, often following international standards (e.g. ISO, ANSI) or industry specifications.
- Rivet diameter: the nominal diameter of the cylindrical part of the rivet body (D), directly affecting the shear and tensile strength.
- Rivet length: the total thickness of the connected parts covered by the nail bar before deformation.
- Rivet head size: rivet head is usually divided into three types: dome head, countersunk head and large flange head. round head diameter is usually 2D-2.5D; countersunk head diameter needs to be matched with workpiece countersunk hole.
- Grip Range: The total thickness of the workpiece to which the blind rivet can be effectively connected (e.g. 0.5mm-8mm).
| Nominal Diameter (D) | Grip Range (T) | Shank Length (L) | Head Type |
| 3mm | 0.5-5mm | 6mm, 8mm, 10mm | Round Head / Countersunk |
| 4mm | 1-8mm | 8mm, 12mm, 16mm | Round Head / Large Flange Head |
| 5mm | 3-12mm | 15mm, 20mm, 25mm | Countersunk / Flat Head |
Requirements for Rivet Body in Different Industries
The design requirements for Rivet Bodies vary significantly from industry to industry. This is mainly due to the working environment, type of load, regulatory standards and special working conditions.
- Aerospace: High requirements for strength and lightweighting. Commonly used 7075 aluminum alloy and titanium alloy rivet body.
- Automobile manufacturing: automobiles have high requirements for shock resistance. Therefore, the rivets with higher strength will be chosen. For example, galvanized steel rivets.
- Construction: the rivets used in construction need to have a high bearing capacity and durability. Commonly used carbon steel and stainless steel rivet body.
Custom Rivet Body for Your Project
The rivet body plays an important role in the riveting process. The thickness of the material that can be riveted is achieved by adjusting the rivet body. If you know how to choose the most suitable rivet body for your project, please contact us. Rivmate is one of the top rivet manufacturers and suppliers in China, which can provide professional riveting solutions for you.
Please get the rivet samples for testing before placing a formal order!






