Aluminum vs Steel Rivets: Which is the Best Marterial for Rivets?
Table of Contents
In the application of fasteners, the selection of the rivet material directly affects the structural strength, durability and cost. Among them, aluminum and steel are the two most common blind rivet materials, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Aluminum vs Steel Rivets – Which is the Best Rivet Material? This blog will conduct a systematic comparison from the aspects of strength, corrosion resistance, weight and cost from the professional perspective of the Rivmate engineering team, to help you make a more scientific selection.
Overview of Aluminum and Steel Rivets


| Comparison Item | Aluminum Rivet | Steel Rivet |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 2.7 (Lightweight) | 7.8 (Heavy) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 180–220 | 400–800 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, with natural oxide film protection | Requires galvanizing or surface coating for protection |
| Electrical Conductivity & Thermal Expansion | Good conductivity, higher thermal expansion rate | Low conductivity, better thermal stability |
| Workability | Easy to install, low pulling force required | Requires high pulling force and heavy-duty tools |
| Typical Cost (Relative) | Lower | Medium to higher |
Characteristics of Aluminum Rivets
Aluminum rivets are lightweight and highly processable, making them the preferred material for lightweight design. Their natural oxide film effectively resists corrosion from air and moisture, thus they are widely used in home appliances, car bodies and building curtain walls. They require low tension during installation and can be installed with ordinary electric or manual riveting guns. However, their strength is limited and they are not suitable for long-term load-bearing or high-impact conditions.
Under the condition of 3 mm plate thickness, the average tensile strength of aluminum rivets is approximately 450 N, and the shear strength is about 300 N, which meets the general assembly requirements.
Characteristics of Steel Rivets
Steel rivets have higher mechanical strength and impact resistance. They are suitable for structural connections, high-load areas, or environments with frequent vibrations, such as industrial equipment, steel structures, and vehicle chassis. However, steel is prone to rust and requires anti-corrosion treatment through galvanization, nickel plating, or the use of stainless steel materials. Their installation requires a relatively high tensile force, and pneumatic tools are generally needed.
The average tensile strength of steel rivets reaches 950 N, which is more than double that of aluminum. After 96 hours of salt spray testing, galvanized steel rivets still maintain over 90% of their anti-corrosion integrity.
Performance Comparison: Aluminum vs Steel
The requirements for strength, corrosion resistance, weight and cost vary greatly in different application scenarios. The following compares the performance of aluminum and steel rivets from four dimensions, combined with Rivmate engineering test data, to help users better understand the actual differences between the two.
a. Strength & Load Capacity
The structural strength of rivets is mainly reflected in two aspects: tensile resistance and shear resistance. The mechanical properties of steel rivets are significantly higher than those of aluminum, making them suitable for high-load and structural connections.
- The tensile and shear strength of steel rivets is usually 2 to 3 times that of aluminum.It has high structural stability and can withstand significant mechanical stress and vibration.
- Aluminum rivets, although having relatively low strength, can meet the connection requirements of thin plates and light loads. It is particularly suitable for non-load-bearing components or decorative structures.
The tensile strength of A2 stainless steel rivets is approximately 950 N; that of standard aluminum rivets is about 450 N. It is evident that if the connected parts are subjected to dynamic loads or external impacts, steel rivets will offer a greater safety margin.

The anti-corrosion performance directly determines the service life of the riveting points, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
The surface of aluminum rivets naturally forms a dense oxidation protective film, which can effectively resist oxidation and acid-base corrosion. In neutral or weakly acidic environments, the anti-corrosion performance is stable and maintenance-free. Steel rivets are prone to rust without a protective layer; however, after being treated with galvanization, nickel plating or made of stainless steel, their durability can be significantly enhanced.
When aluminium and steel are used together, galvanic corrosion can occur due to the potential difference. Rivmate suggests adding insulating washers or anti-corrosion isolation coatings at the contact interface of the two metals to prevent accelerated corrosion.
Neutral and dry environment → Aluminum rivets are preferred.
Damp, salt spray or chemical environments → Stainless steel or coated steel rivets are recommended.
c. Weight and Workability
In modern manufacturing, lightweighting and high assembly efficiency are becoming increasingly important.
Aluminum rivets weigh only 1/3 that of steel, significantly reducing the overall structural weight. They are suitable for assembly in automobiles, aviation, home appliances, and electronic devices. Aluminum is soft, requiring less pulling force for installation, and can be installed using either manual or electric riveting guns.
Steel rivets have high strength and require greater tensile force during installation. It is recommended to use pneumatic or hydraulic riveting tools to prevent incomplete core breakage.
For mass production, aluminum rivets can significantly reduce operational load and equipment energy consumption. After replacing carbon steel models with aluminum rivets, the single-line assembly efficiency increased by 18%, and the operational fatigue was reduced by approximately 25%.
d. Cost and Durability
Material cost and service life are the core indicators for evaluating economic efficiency. Aluminum rivets have a low manufacturing cost and high installation efficiency, making them suitable for projects with limited budgets or for medium to short-term use. Steel rivets have a slightly higher initial cost, but their high strength and long service life result in lower maintenance costs.
For high-load or long-running equipment, the total cost of ownership (TCO) is more favorable. In corrosive environments, although stainless steel rivets are the most expensive, they can ensure structural stability for more than 10 years.
Which Material Fits Your Application?
In practical applications, the selection of rivets should always be based on the “usage environment, load requirements and anti-corrosion conditions”. Under different working conditions, there are significant differences in performance and maintenance cycles between aluminum and steel (including stainless steel) rivets.
| Application Environment | Recommended Rivet Material | Main Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Rail Transit | Steel / Stainless Steel | Withstands strong vibration and impact; requires high strength and fatigue resistance. Steel rivets offer structural stability and excellent shear performance. |
| Building & Roofing Systems | Aluminum Cap + Stainless Steel Mandrel (Al + SS Mandrel) | Strong corrosion and rust resistance with lightweight properties; ideal for long-term sealed assemblies in metal roofing and façade systems. |
| Home Appliances & Electronics | All Aluminum | Lightweight, quick installation, non-magnetic; provides a clean appearance and prevents galvanic corrosion, suitable for housings and thin-sheet connections. |
| Outdoor or Coastal Areas | Full Stainless Steel | Excellent salt-spray and moisture resistance; maintains long-term stability in high-humidity environments without rusting or failure. |
| Aerospace & Lightweight Structures | Aluminum | Weighs only one-third of steel, significantly reducing total weight; easy to process and form, ideal for lightweight aerospace and transportation applications. |
Material Selection Essentials
- When structural strength is prioritized — Steel or stainless steel rivets are the preferred choice, especially suitable for supporting components, chassis and welding alternative scenarios.
- When environmental protection is the priority — Aluminum rivets or aluminum + stainless steel core combinations offer greater advantages, effectively resisting moisture, rain and chemical corrosion.
- When lightweight and appearance requirements are high — The all-aluminum series is the best option, with consistent color, aesthetic appeal and low installation load.
- For structures with high risk of electrochemical corrosion — Direct contact between aluminum and carbon steel should be avoided. Insulating gaskets or a mixed rivet structure can be used instead.
Proper Installation and Maintenance of Rivets
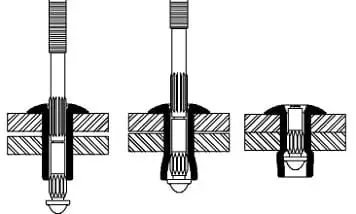
The performance of the rivets is not only dependent on the material selection, but also closely related to the installation method and maintenance procedures. Even if the correct material is chosen, improper installation can still lead to loose connections, unbroken core shafts, or failure of anti-corrosion measures.
① Aluminum Rivets
Aluminum rivets are lightweight and have high ductility, making them suitable for installation using either a manual or electric riveting gun. During installation, it is crucial to carefully control the pulling force and stroke to avoid over-pulling or deformation of the cap body, ensuring that the riveted surfaces are flat and tightly adhered.
- It is recommended to use an electric riveting gun that complies with ISO standards, with the pulling force set between 3–5 kN.
- The diameter of the hole should be approximately 0.1–0.2 mm larger than the diameter of the rivet to ensure smooth insertion and prevent loosening.
- If used on waterproof or coated surfaces, the oil stains at the hole opening should be cleaned before riveting, and sealing gaskets can be added to enhance the waterproofing effect.
For the assembly of aluminum alloy or plastic parts, the “low shear force” mode or segmented riveting technology should be used to avoid stress cracks on the material surface.
② Steel Rivets
Steel rivets have high strength, but they also require more stringent installation equipment. It is recommended to use a high-torque pneumatic or hydraulic riveting gun to ensure that the mandrel breaks completely and is locked in place under the specified pulling force.
- Recommended tension setting value: 8–12 kN (adjustable according to the diameter of the rivet and the type of structure).
- After the riveting is completed, check the fit of the cap and whether the back expansion is uniform.
- If the tension is insufficient during installation, it may cause the core shaft not to break or the lock core not to be securely engaged, thereby affecting the structural safety.
During the assembly test, using uncalibrated riveting equipment resulted in an incomplete core breakage rate of up to 12% for the steel rivets. Regular equipment calibration can reduce the failure rate to below 1%.
③ Mixed-Material Assembly
When different materials such as aluminium, steel, and stainless steel are used together, the electrochemical corrosion risk must be taken into account. If the potential difference between two metals is significant (for example, between aluminium and steel), electrochemical corrosion is likely to occur in humid or salt spray environments.
Rivmate suggests adding insulating washers or corrosion barrier coatings between the contact surfaces. For areas with high corrosion (such as coastal projects), it is recommended to use composite rivets with aluminum caps and stainless steel cores, which can balance strength and corrosion resistance.
After installation, the joint area can be sealed with neutral preservative or silicone sealant to further extend its service life.
Choose Smart, Build Strong — Rivmate’s Recommendations

In the design of riveting, there is no such thing as the “best” rivet. What really matters is to select the “most suitable material” based on the application environment, structural requirements and the lifespan of the product.
Aluminum and steel rivets each have their own unique advantages: one represents lightness and corrosion resistance, while the other represents strength and durability. Rivmate always advocates making decisions from an engineering perspective, rather than solely pursuing a single performance metric.
- When aiming for lightweight and corrosion resistance → Choose aluminum rivets
Suitable for roof systems, building facades, appliance and lightweight equipment assembly. The aluminum material has an inherent oxide protective layer, with excellent anti-corrosion performance, quick installation and high cost-effectiveness. - When focusing on structural strength and safe load-bearing → Choose steel or stainless steel rivets (Steel / Stainless Steel Rivets)
Suitable for high-load structures, mechanical equipment and transportation fields. The tensile strength can reach more than twice that of aluminum, making it suitable for long-term stressed environments. - When you want to balance both corrosion resistance and strength → Choose the hybrid type rivet (Aluminum Body + Steel Mandrel)
Combining the advantages of both, it is lightweight, has high tensile strength, and is corrosion-resistant. It is particularly suitable for composite structures, outdoor applications, and multi-material connections.
Rivmate's Professional Commitment to Engineering Quality

Each rivet of Rivmate has undergone strict testing and has been certified to international standards, including:
- ISO 14589 (Blind Rivet Mechanical Performance)
- ASTM B117 (Salt Spray Corrosion Test)
- DIN 7337 (Blind Rivet Manufacturing Standard)
In addition, Rivmate offers sample testing, material compatibility assessment and application verification services, ensuring that your project maintains the highest level of reliability throughout the design, production and maintenance stages.
📘 Want to obtain the most suitable rivet solution for your project? Contact the Rivmate engineering team immediately to obtain customized selection guidance and sample test report.
📧 Product Inquiry: manufacture@world-rivet.com
🌐 Official Website: https://worldrivet.com/
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met







