The Comprehensive Guide to Blind Rivet Material Selection
Table of Contents
Among all structural fasteners, blind rivets are widely used in critical connections in photovoltaic, electrical, construction, rail and other systems due to their ease of installation and single-sided operation. However, many engineering failures do not originate from rivet structure design problems, but from rivet material selection errors. Different rivet materials have significant differences in strength, corrosion resistance, thermal expansion and galvanic response. Once the wrong choice, the light is to affect the construction efficiency, or lead to corrosion, dislodgement and even structural accidents.
Therefore, the selection of blind rivets is not only the product configuration, but also determines the long-term stability of the connection system and the core elements of engineering quality. This article will focus on the mainstream material performance comparison, typical applications and selection recommendations, systematic explanation of how to select for your project to take into account the performance, cost and environmental adaptability of the ideal blind rivet material.
Why is rivet material selection important? - 4 Core Factors
In the selection process of blind rivets, the choice of material is a key decision that determines whether the connection system can operate stably for a long period of time. Different application environments, structural requirements and construction conditions put forward different performance standards for rivet materials.
1. Adequacy of material strength to carry design loads (shear/tension)
Rivets are subjected to multi-directional loads such as shear and tension in the structure, so the strength level of the material must meet the design requirements of the connection part.
If the choice of insufficient strength rivets (such as aluminum instead of steel), in the long-term wind vibration, heavy loads or thermal expansion and contraction, it is very easy to lead to rivets loose, fracture or structural failure.
In the actual selection process, blind rivets need to be based on its axial tensile force and radial shear force to match the specific conditions, such as the main load-bearing connection of the stent preferred carbon steel or stainless steel.
2. Corrosion resistance to match the use of the environment
Rivets, as exposed connectors, will be frequently exposed to rain, moisture, acid, alkali, salt spray and other environments during use. Therefore, its corrosion resistance will directly affect the system life and safety.
Aluminum has good oxidation resistance and is suitable for general outdoor environments. Stainless steel is suitable for highly corrosive places such as seashores and industrial polluted areas. Carbon steel is strong but must be protected with Dacromet or galvanization. Choosing the wrong material or a low anti-corrosion grade is very likely to rust and expand, fail or even destroy the parent material in a short period of time.
3. Risk of galvanic corrosion with the connecting substrate
Galvanic corrosion is one of the often overlooked pitfalls of structural failure. When two metals with a large potential difference (e.g. aluminum and carbon steel) come into contact in a wet or electrically conductive environment, corrosion of one of the metals (usually aluminum) is accelerated.
The selection of incompatible material rivets can lead to corrosion perforation of the parent material being joined, affecting structural integrity and aesthetics. Therefore, it is especially critical to give preference to aluminum body or aluminum + stainless steel core combination rivets in aluminum profile connections.
4. Whether the riveting equipment is suitable for the processability of the material
Different materials have different requirements for riveting tools, construction techniques and operational stability.
Aluminum and copper and other soft materials are easy to process, suitable for rapid assembly and on-site construction. Stainless steel, high strength, ductility, must be combined with high-power pneumatic or hydraulic rivet gun, in order to break the core thoroughly, riveting stability. If the equipment and materials do not match, it is very easy to false rivets, mandrels can not be pulled or rivet deformation, seriously affecting the installation efficiency and batch consistency.
Commonly used Blind Rivets material introduction and performance comparison
| Material Type | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Workability | Weight | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Medium | Good | Excellent | Light | Solar frames, electronics, lightweight panels |
| Stainless Steel | High | Excellent | Low | Heavy | Marine, electrical enclosures, corrosive areas |
| Carbon Steel | High | Low (requires coating) | Good | Medium | Structural assemblies, machinery frames |
| Copper | Low | Moderate | Excellent | Medium | Electrical contacts, grounding, busbars |
| Monel Alloys | High | Superior | Poor | Heavy | Military, chemical, marine engineering |
| Nylon / Plastic | Very Low | Excellent | Excellent | Very Light | Appliances, electronics, non-structural uses |
Aluminum
Characteristics: Lightweight, naturally corrosion-resistant, good thermal conductivity, excellent workability.
Performance:
- Strength: Medium, suitable for light duty structures
- Performance: Strength: Medium, suitable for light-duty structures Corrosion resistance: Good, suitable for general outdoor environments
- Machinability: excellent for quick installation with hand and pneumatic tools
- Weight: Very light, suitable for weight-sensitive systems.
- Typical applications: photovoltaic module bezels, aerospace housings, electrical equipment, lightweight steel construction.

Stainless Steel
Characteristics: High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for demanding applications
Performance:
- Strength: high, suitable for main load-bearing connections
- Corrosion resistance: excellent, suitable for seashore, chemical and other highly corrosive environments
- Machinability: poor, high hardness, need high power equipment support
- Weight: heavy
- Typical applications: offshore wind power, control boxes, power equipment, heavy industrial assembly
Carbon Steel
Characteristics: High strength and low price for economical connection solutions
Performance:
- Strength: High, suitable for structural connections.
- Corrosion resistance: poor (requires surface protection)
- Machinability: Excellent, easy to form and core break.
- Weight: medium to heavy
- Typical applications: structural steel supports, machine frames, equipment connections, engineering fixtures.
Copper
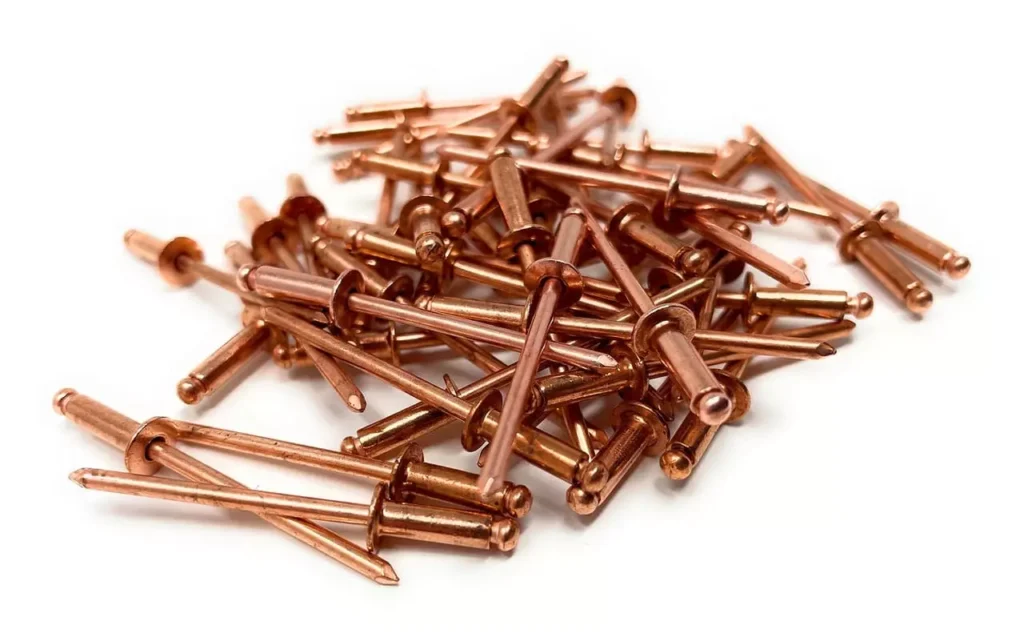

Characteristics: Soft, excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, suitable for electrical connections.
Performance:
- Strength: low
- Corrosion resistance: medium, easy to oxidize and discolor.
- Processability: Excellent, stable riveting
- Weight: Medium
- Typical applications: grounding systems, electrical busbars, cable fixing, copper connections
Monel / Nickel-based alloys
Characteristics: Superior corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, for extreme environments
Performance:
- Strength: High
- Corrosion resistance: very high, suitable for acid, alkali and salt spray environments.
- Machinability: Poor, requires specialized tools and high powered equipment.
- Weight: heavy
- Typical applications: offshore engineering, chemical equipment, nuclear power plants, aerospace high-temperature resistant structures
Nylon / Plastic
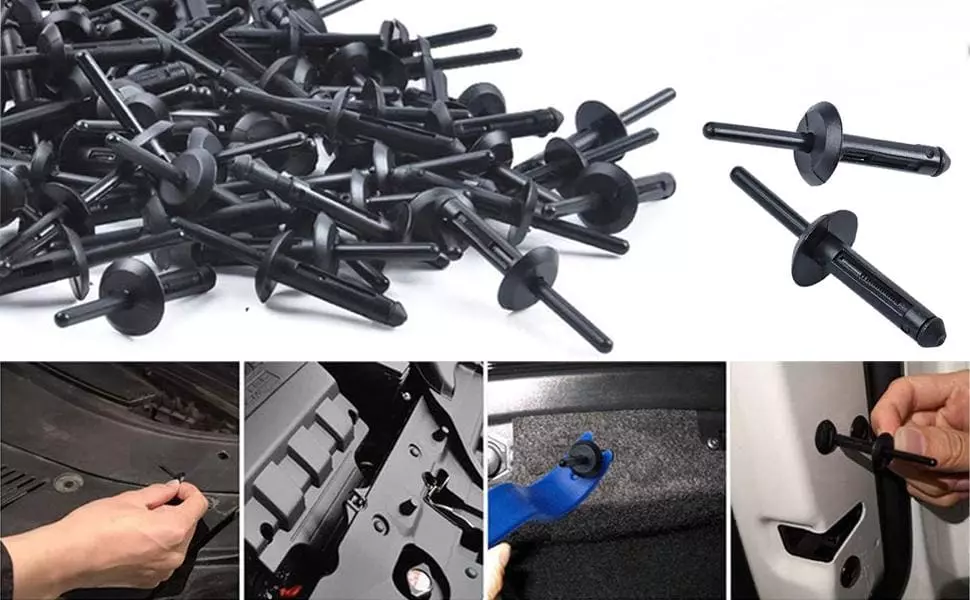

Characteristics: Insulated, waterproof, lightweight, suitable for non-structural light duty connections
Performance:
- Strength: very low, light assembly only
- Corrosion resistance: Excellent, suitable for electronic housings.
- Machinability: excellent, no special tools required
- Weight: Very light
- Typical applications: Appliance housings, weak modules, electronic equipment interiors, instrument assemblies
Recommended rivet materials based on application
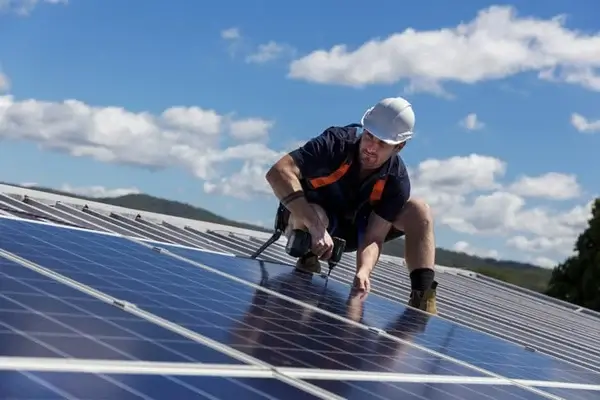

In photovoltaic systems, blind rivets are mainly used for module bezel fixing, rail connection, block positioning and control box assembly. Because the system is exposed to wind and rain for a long time, and the temperature difference between day and night is large, the rivet material must take into account the lightweight, anti-corrosion, thermal expansion matching and convenient construction.
Aluminum rivets are recommended. It is lightweight, naturally oxidation-resistant, and especially suitable for aluminum profile structures. Meanwhile, it is recommended to use aluminum body + stainless steel mandrel structure to enhance the strength of pulling and shearing and at the same time to avoid the corrosion and fall off of the core shaft.
2. Industrial steel connections
Structural steel systems require rivets with high strength, high holding power and reliable structural rigidity, while providing some cost control. For these applications, carbon steel rivets (with zinc or Dacromet finish) are preferred for good shear resistance and stability for high load environments.

Surface treatments are available in electro-galvanized, hot-dip galvanized or zinc-aluminum coating for enhanced corrosion life. Suitable for plant steel frames, support beams, angle reinforcement and other scenarios, especially suitable for high-volume construction projects requiring cost-effective systems.
3. Connection of equipment in coastal or high salt spray areas (e.g., seaside power stations, communication towers)
Such areas have a high concentration of salt in the air and are humid all year round, which requires very high corrosion resistance of fasteners. Improper selection of materials will lead to a short period of time rivets corrosion de-core, cap body expansion, electrochemical corrosion of the parent material and other serious problems.
It is recommended to use stainless steel blind rivets (304 or 316), with strong salt spray resistance. 316 profile is more suitable for coastal systems with chloride ion environment. Commonly used in solar off-grid power stations, meteorological towers, aerial camera poles, inverter shells and other parts.
4. Electrical equipment, electrical control cabinets, grounding copper rows and other conductive parts
In the power system, electronic control equipment, grounding row bus and other connection occasions, rivets not only assume the fixed function, but also need to have good conductivity and flexible adaptability. At this time should avoid the use of stainless steel or carbon steel materials, in order to prevent the impact of contact resistance and conductive path.

Recommended use of copper rivets, or high conductive aluminum rivets by electroplating. Copper is flexible, can evenly cover the conductive surface, suitable for copper rows, bare conductors and other structures, commonly used in ground crimping, cable end fixing, module grounding buckle.
5. BIPV building integrated systems (curtain walls, aluminum tiles, decorative surfaces)
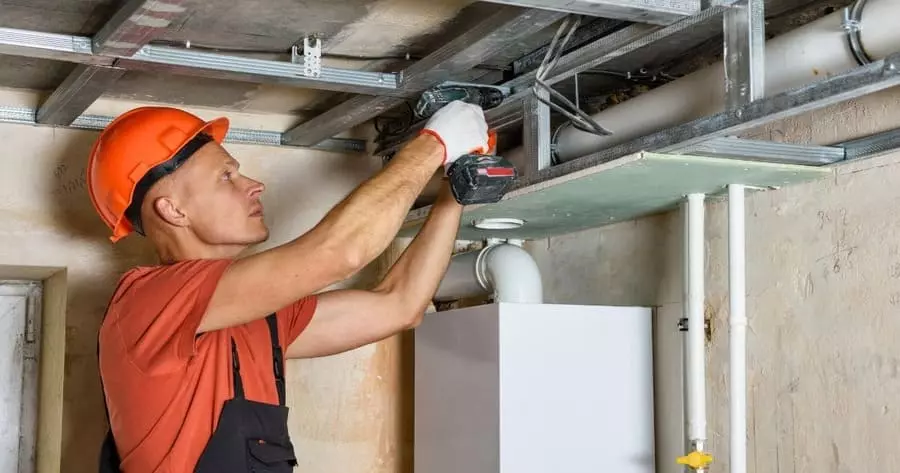

BIPV system integrates power generation and building appearance, which requires higher visual consistency of rivets, structural concealment and long-term corrosion resistance. Common structures are aluminum alloy panels, color steel sandwich panels, custom keel and other combinations.
Recommended to use hidden aluminum or stainless steel blind rivets. With Flush-head closed structure, the surface after installation is flat, no mandrel exposed, no cuts, no water seepage, to ensure the building aesthetics and anti-theft level. Suitable for metal curtain wall panels, border strips, photovoltaic tiles and other parts.
How to avoid the wrong type of blind rivet material selection?
In the selection of blind rivets, one of the common misconceptions is to ignore the electrochemical compatibility of the base material and rivet material. For example, the use of carbon steel rivets on aluminum, long-term exposure to moisture or salt spray environment will trigger galvanic coupling corrosion, resulting in rapid corrosion of rivets, connection failure. In order to ensure anti-corrosion performance, priority should be given to the choice of materials similar to the material being connected or small potential difference between the rivet material, such as aluminum to aluminum, stainless steel to stainless steel, etc., while paying attention to the plating process is protective rather than decorative.
Another major misunderstanding is not based on the use of the environment to choose the appropriate structure and strength level. Such as high vibration, high load conditions using low strength aluminum rivets, easy to pull off, loose and other problems. Correct selection should be comprehensive consideration of the thickness of the installation material, load type, environmental conditions and tensile and shear strength requirements, if necessary, reference to ISO or industry standards for calculation and selection. The ideal solution is to work with experienced manufacturers to customize matching rivet structures and material combinations according to actual usage scenarios.
FAQs about Blind Rivet Materials Selections
1. Does the mandrel material of a blind rivet matter?
Yes, the rivet mandrel material directly affects the shear strength during riveting, the pull-off behavior and the structural stability after nail breakage. If the strength of the mandrel material is too low, it may lead to early breakage or insufficient clamping force during the riveting process. Conversely, too high a strength may damage the base material or cause the rivet to be poorly formed. In addition, mismatches between mandrel and housing materials may result in galvanic corrosion or thermal expansion stresses. When selecting the type, the load requirements and the use of the environment should be clearly defined, the manufacturer to provide matching design.
2. Stainless steel rivets must not rust?
Stainless steel rivets have excellent corrosion resistance, but not absolutely “will not rust”. If the choice of low-grade stainless steel (such as 201 or some 430), in high salt, high humidity or acidic and alkaline environment may still produce pitting or rust spots. Even with high grade stainless steel such as 304/316, corrosion may occur if there is processing damage, surface contamination or electrochemical imbalance. Therefore, it is recommended to select the appropriate grade of stainless steel according to the usage environment and ensure that the riveting process is clean and free from contamination.

3. How can I tell if galvanic corrosion is occurring?
Galvanic corrosion usually occurs when two different metals are in contact for a long period of time and exposed to a conductive liquid environment (e.g. water, salt spray).
Initial manifestations are: rusting, blistering, color change at the contact edge or localized corrosion of the substrate around the rivet. Technically can be observed through the combination of potential difference (metal electrochemical sequence) to determine the risk, such as aluminum + stainless steel for high-risk combination. The site can be used to test the corrosion rate of conductive liquid, or confirmed by visual + material analysis.
4. Can special rivet configurations in mixed materials be provided?
Can. High quality rivet manufacturers such as Rivmate can provide a variety of dissimilar material combination structure, such as aluminum body + stainless steel core, steel shell + copper core, aluminum body + nickel core, etc. to balance the strength, corrosion resistance, weight and conductive requirements.
This type of structure is commonly used in automotive, electronic, electrical and other industries for special connection parts. When customized, the thickness of the installation substrate, load conditions, environmental requirements should be provided, and the technical team will carry out selection and matching and structure confirmation.
Rivmate Rivet Material Selection System Solutions
When selecting a material for a blind rivet, the only way to achieve both strength and longevity is to have a thorough understanding of the structural requirements, environmental variables and material compatibility.Rivmate has built a complete material system solution based on many years of experience in the development and manufacture of blind rivets. This solution encompasses aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel, copper and a wide range of plating combinations to meet the challenges of multi-industry, multi-condition applications.
Whether your concern is galvanic corrosion, tensile strength, lightweighting, or environmental compliance such as RoHS/REACH, Rivmate can customize a riveting solution to meet your needs. From structural selection to material optimization, we are committed to becoming your trusted riveting technology partner, helping every connection node stable, efficient and durable.

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met



