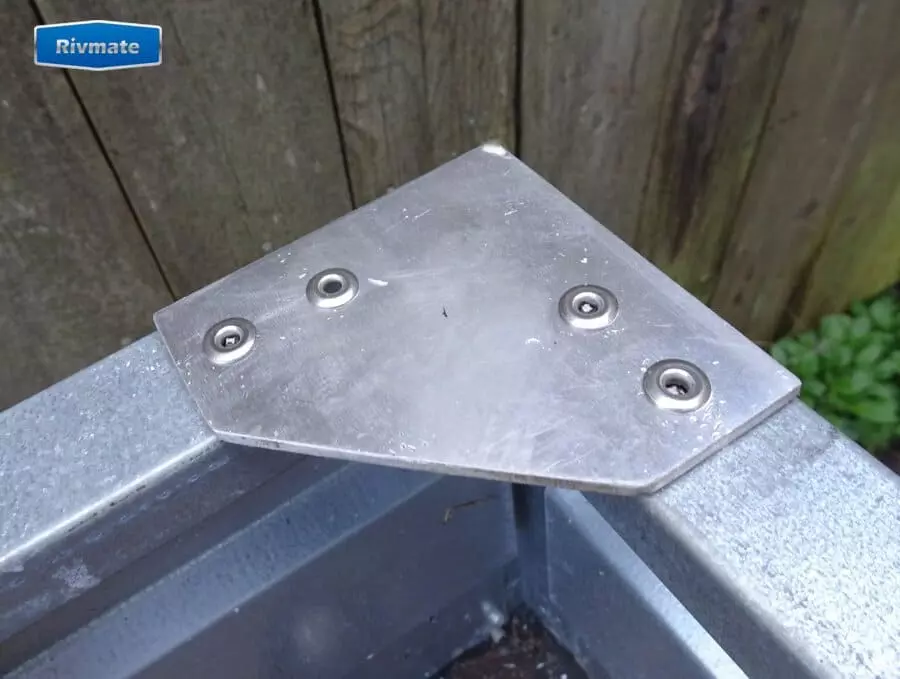
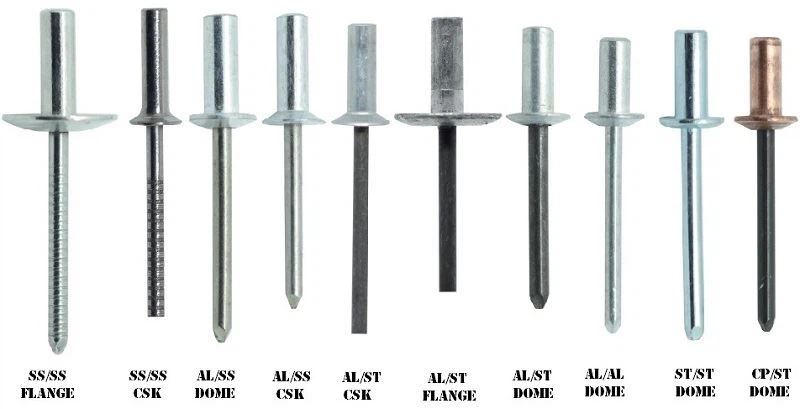
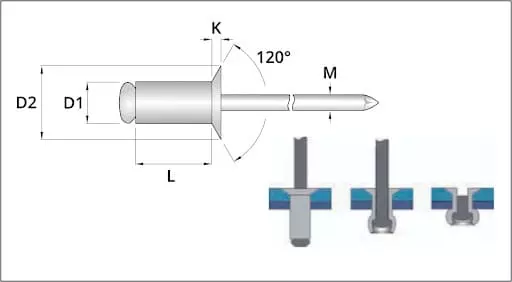
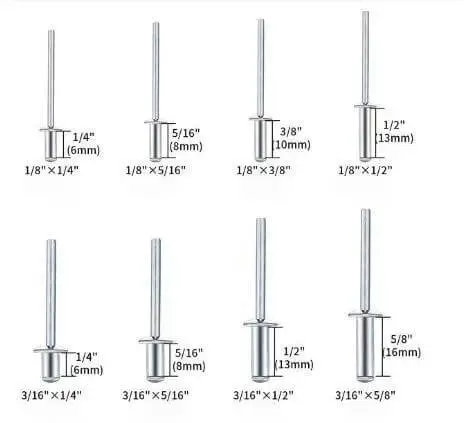
What Rivets to Use on Galvanized Steel?
Table of Contents
When dealing with galvanized steel, many people encounter a common problem: what rivets to use on galvanized steel. This is not a simple choice. If there is an electrochemical reaction between the rivets and the base material, it may lead to accelerated corrosion and affect the service life of the structure. Galvanized steel itself has good anti-rust performance, but if the rivet material does not match, it will destroy this layer of protection. Choosing the right rivets is not only about anti-corrosion, but also directly affects the strength and stability of the connection.
In engineering applications, the selection of rivets often requires a comprehensive consideration of corrosion resistance, structural strength, safety and cost. For instance, in outdoor or humid environments, if rivets undergo galvanic corrosion, the cost of maintenance and replacement far exceeds the initial material selection cost. The correct choice of rivets not only enhances the product’s lifespan but also reduces maintenance expenses over the long term.
Understanding Galvanized Steel and Its Challenges
Galvanized steel is a common structural and manufacturing material. Its surface is covered with a layer of zinc coating, which mainly serves to prevent the steel from direct contact with air or moisture, thereby delaying corrosion. Due to its durability and economy, galvanized steel is widely used in construction, transportation, energy, and outdoor facilities.

However, in the connection and fastening process, galvanized steel faces a particular challenge: galvanic corrosion. This is an electrochemical reaction that occurs when different metals come into contact and are exposed to an electrolyte, such as rainwater or moisture. The metal with a greater potential difference is preferentially corroded.
For example:
- If incompatible rivets (such as stainless steel or copper) are used on galvanized steel, it may accelerate the consumption of the zinc coating.
- Once the zinc coating is damaged, the steel substrate will oxidize rapidly, eventually leading to structural failure.
This risk is particularly prominent in outdoor applications, humid environments or industrial settings. According to data from the National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE), the global economic loss caused by corrosion accounts for approximately 3-4% of the GDP each year. Among them, electrochemical corrosion is one of the common causes.
Therefore, in the application of galvanized steel, choosing the appropriate material for rivets is of vital importance. This not only affects the firmness of the connection but also directly determines the overall service life and maintenance costs.
Why Rivet Material Matters: Galvanic Corrosion Explained
In fastening applications, electrochemical corrosion is the most common yet often overlooked issue. Its formation conditions are quite simple:
- Direct contact between different metals.
- Presence of an electrolyte environment, such as rainwater, moisture or salt fog.
- Existence of a potential difference between the metals.
When these three conditions are met, the metal with a lower potential will act as the “anode” and be corroded first. While the metal with a higher potential will serve as the “cathode” and remain relatively stable.
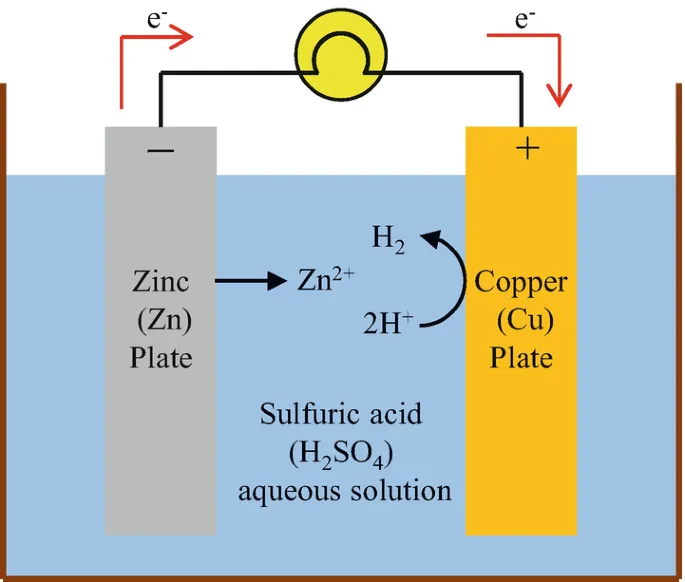
Illustrative Examples
- Use aluminum rivets on galvanized steel. Due to the significant potential difference between aluminum and zinc, in a humid environment, aluminum will accelerate oxidation, causing the strength of the rivets to rapidly decline.
- If stainless steel rivets are used, the situation will be reversed. At this time, the zinc coating will sacrifice first, resulting in the failure of the protection of the galvanized steel, exposing the steel substrate and causing rusting.
Table: Comparison of Electrode Potentials of Common Metals
(The values are the standard electrode potentials, in relative terms, with the unit: V)
| Metal / Coating | Electrode Potential (Approx. Value, V) | Corrosion Risk Relation |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Coating (Zn) | -0.76 V | Most likely to sacrifice, protects the steel substrate |
| Aluminum (Al) | -0.68 V | Close to zinc, but still carries corrosion risk |
| Carbon Steel (Fe) | -0.44 V | Relatively stable, but corrodes rapidly once zinc protection is lost |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | -0.10 ~ +0.05 V | Much higher potential, accelerates zinc corrosion |
As can be seen from the table, the potential difference between the galvanized layer and stainless steel is the greatest, and thus the risk is the highest. The galvanized layer is relatively close to aluminum, but there are still potential risks. Suggestion:
- On galvanized steel, it is preferable to use rivets of the same material or with similar potential. For example: galvanized steel rivets or special anti-corrosion coated rivets.
- If stainless steel rivets must be used, measures such as isolation gaskets and insulating coatings should be employed to reduce direct metal contact.
- In outdoor, marine or chemical environments, it is recommended to use rivet systems with higher anti-corrosion grades rather than relying on a single material.
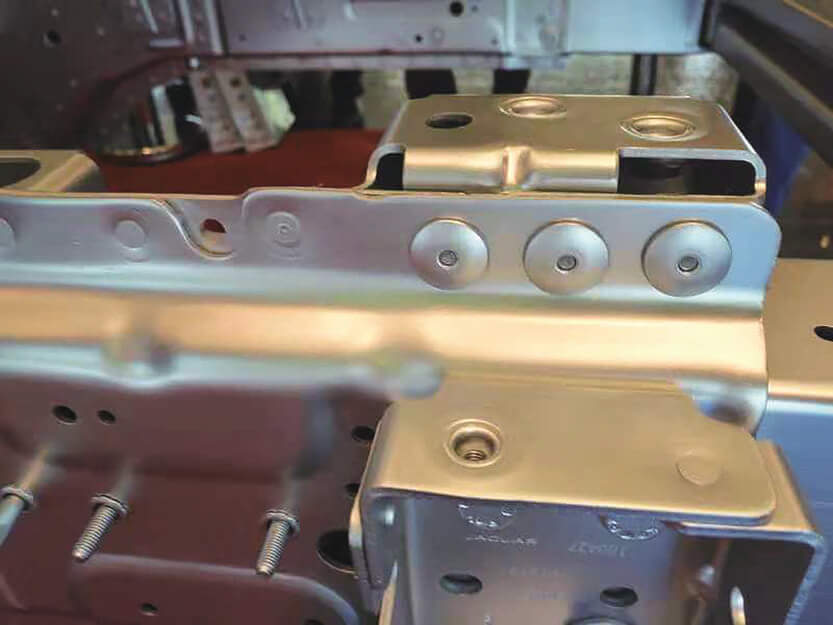
Best Rivet Materials for Galvanized Steel
When choosing galvanized steel rivets, material compatibility is crucial. The correct selection not only ensures a strong connection but also extends the service life and reduces maintenance costs. The following are the advantages and disadvantages of several common rivet materials:
- Advantages: Consistent with galvanized steel material, with the best electrochemical compatibility. Wide range of supply, low cost.
- Disadvantages: The exposed parts are prone to rust. Usually, additional protection is required, such as anti-rust paint or sealant.
- Application scenarios: Construction, machinery, interior and general industrial use.
- Advantages: High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, particularly suitable for outdoor environments.
- Disadvantages: There is a significant potential difference with the galvanized layer, which may accelerate the corrosion of the zinc layer. Isolation measures are required, such as insulating gaskets, coatings or sealants.
- Application scenarios: Outdoor facilities, transportation, humid or highly corrosive environments.
- Advantages: Performs best in marine or extremely corrosive environments, resistant to salt fog and chemical corrosion.
- Disadvantages: Expensive, not suitable for large-scale use.
- Application scenarios: High-end applications such as ships, marine engineering, and chemical equipment.
d. Aluminum rivets (Not recommended)
- Disadvantage: It is prone to electrochemical corrosion when in contact with galvanized steel, resulting in a short service life.
- Application Limitations: It is only suitable for indoor use, low-strength applications, and temporary connections.
- Expert Recommendation: Try to avoid using aluminum rivets on galvanized steel.
Summary:
Economy option: Galvanized steel rivets.
Outdoor or industrial applications: Stainless steel rivets (with isolation measures required).
Extreme environments: Monel or specially anti-corrosion rivets.
Avoid using: Aluminum rivets.
Application-Based Recommendations
The selection of rivets is not only dependent on the material, but also closely related to the application environment. The corrosive media, load requirements and maintenance costs vary in different environments. The following table summarizes the best rivet choices for typical scenarios:
| Application Scenario | Recommended Rivet Material | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Construction | Stainless Steel Rivets + Sealant | Resistant to rain, moisture, and temperature variations. Sealant helps reduce galvanic corrosion risk. |
| Indoor Fixtures | Zinc-Plated Steel Rivets | Low cost, good compatibility. Suitable for low-humidity and low-corrosion environments. |
| Automotive / Rail / HVAC | Stainless Steel Rivets | High strength and vibration resistance. Suitable for automotive body, rail transport, and HVAC systems. |
| Marine / Coastal | Monel or Special Corrosion-Resistant Alloy Rivets | Excellent corrosion resistance. Ideal for ships, port facilities, and high-salinity environments. |
- In outdoor or high-humidity environments, stainless steel rivets should be used in conjunction with isolation measures.
- In extremely corrosive environments, although Monel is more expensive, its long-term maintenance cost is lower.
- Indoor low-risk environments, galvanized steel rivets are the most cost-effective choice.
Rivmate Expertise & Standards
As a professional supplier in the fastener industry, Rivmate has always emphasized the compatibility of its products with galvanized steel in the design and selection process. We are well aware that the matching of the rivet material and the base material directly determines the reliability and durability of the connection.
Material Compatibility Guarantee
- Rivmate offers a variety of material options, including galvanized steel, stainless steel, Monel, etc.
- Each batch of products undergoes electrochemical compatibility testing to ensure safe use in different environments.
- For the application of galvanized steel, Rivmate will preferentially recommend galvanized steel rivets or isolated stainless steel rivets to reduce the risk of electrochemical corrosion.
Adhered International Standards

Rivmate’s products comply with and implement multiple international standards, ensuring performance and quality:
- IFI (Industrial Fasteners Institute) — North American fastener standards.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization) — International unified standards.
- DIN (Deutsches Institut fur Normung) — German industrial standards, commonly used in mechanical manufacturing.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) — Involves tests on material properties, corrosion resistance, etc.
The strict implementation of these standards has enabled Rivmate’s rivets to meet the requirements of industrial applications in terms of strength, corrosion resistance and consistency.
Rivmate's Selection Chart
To facilitate customers’ quick selection, Rivmate offers an intuitive selection tool.
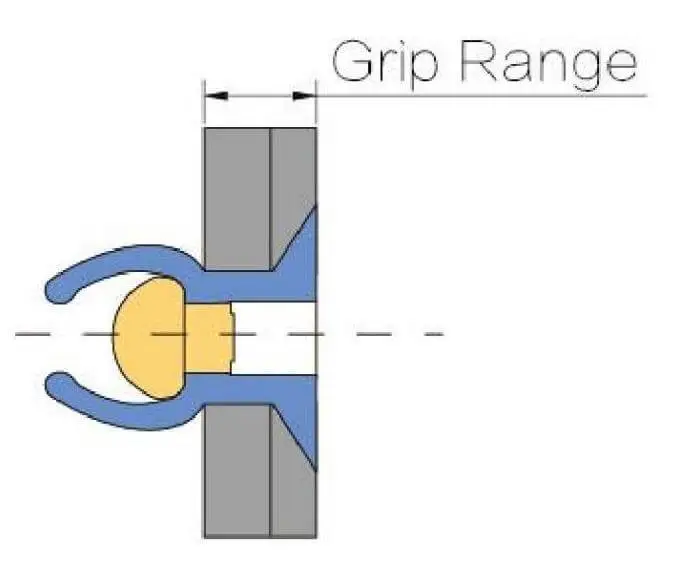
| Rivet Type | Recommended Material | Applicable Grip Range | Application Environment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Open Rivet | Zinc-Plated Steel | 1.5 – 6.0 mm | Indoor structures, light installations |
| Sealed Rivet | Stainless Steel | 2.0 – 8.0 mm | Outdoor facilities, humid environments |
| High-Strength Rivet | Stainless Steel / Monel | 3.0 – 12.0 mm | Transportation, heavy-duty equipment |
| Special Corrosion-Resistant Rivet | Monel / Alloy Coated | 2.5 – 10.0 mm | Marine, chemical, high-salt environments |
The advantages of Rivmate lie in compatibility testing + international standard implementation + application scenario selection table. This not only helps customers enhance the reliability of their projects, but also reduces the maintenance costs in the later stage.
FAQ
Can aluminum rivets be used on galvanized steel?
Answer: Not recommended. There is a potential difference between aluminum and zinc. In humid or salt spray environments, it will corrode rapidly, causing the rivets to fail. Only consider this option for indoor or temporary applications.
Will stainless steel and galvanized steel corrode?
Answer: There will be risks. The potential difference between stainless steel and the galvanized layer is significant, which may accelerate the consumption of the zinc layer. However, by using sealant, insulating gaskets or surface coatings, the risk of corrosion can be significantly reduced.
What is the most cost-effective choice of rivets for galvanized steel?
Answer: The galvanized steel rivets themselves. They have the best compatibility with the base material, are inexpensive, and are widely available. For most indoor and light structures, this is the most cost-effective solution.
Is it necessary to apply a coating or sealant during the installation process?
Answer: It is strongly recommended to use it in an outdoor environment. Sealants or coatings can prevent moisture and electrolytes from penetrating, thereby extending the service life. This step is particularly crucial for applications that are exposed to rain, salt fog, or chemical environments for an extended period.
Protect Against Corrosion — Choose Rivmate Rivets Today
In the application of galvanized steel, the correct selection of rivets is of utmost importance. It not only effectively prevents electrochemical corrosion but also significantly extends the service life of the structure and reduces the cost of later maintenance. Incorrect selection often leads to premature failure and additional expenses.
From a practical application perspective:
- Indoor environment → Choose galvanized steel rivets, which are economical and efficient.
- Outdoor or humid environment → Use stainless steel rivets and combine with sealing measures.
- Extremely corrosive environment → Use Monel or special anti-corrosion rivets.

Rivmate offers a complete range of galvanized steel special rivet solutions, covering various materials, specifications and application scenarios. Moreover, all products comply with international standards (IFI, ISO, DIN, ASTM) and have undergone rigorous testing to ensure reliability in different environments.
If you are looking for reliable galvanized steel rivets, please contact Rivmate. Our engineering team will provide you with professional selection suggestions and highly cost-effective products based on your project requirements.
Reference

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met