Can Water Penetrate Through a Rivet Hole?
Table of Contents
Can water penetrate through a rivet hole? This is a question that engineers and users frequently raise in shipbuilding, car roof assembly, building curtain wall installation, and outdoor equipment design. Although rivets can provide a reliable mechanical connection, whether there is a risk of water seepage after installation has always been a concern in practical applications.
This blog will address this issue from three aspects: structural principles, potential water seepage risks, and waterproofing solutions. The aim is to assist designers and purchasing engineers in clearly understanding whether rivet connections pose any waterproofing risks, and how to avoid leakage by correctly selecting and installing.
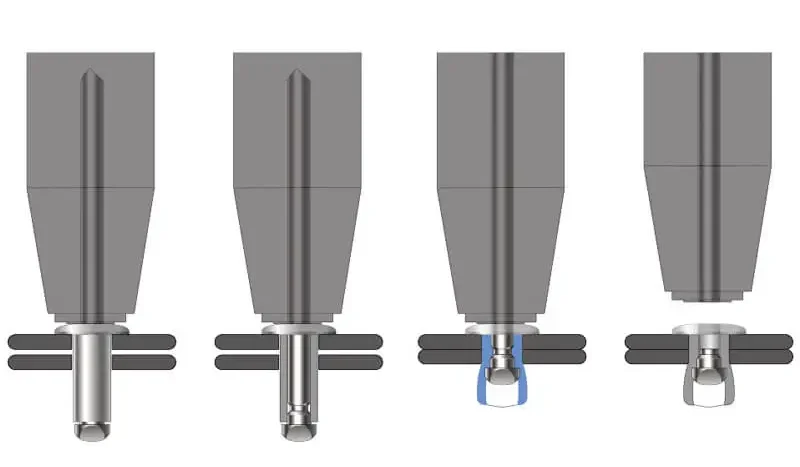
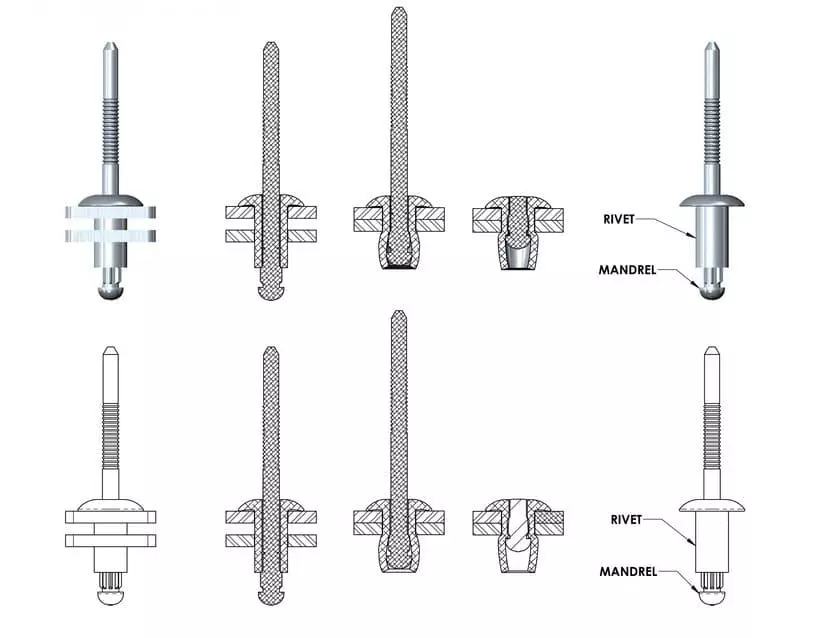
The working principle of a rivet is to firmly fix two or more layers of materials through mechanical deformation. During installation, the rivet shank is stretched or compressed, causing the tail to expand and lock the material, thereby forming a permanent connection.
However, even after the installation of ordinary rivets is completed, there may still be minor gaps at the connection points. These gaps provide a pathway for water to seep in, mainly including:
- Between the rivet rod and the hole wall: If the hole diameter is too large or the rivet is not fully filled, capillary infiltration channels are likely to form.
- Through the gap between the material layer and the rivet head: In the presence of external rain or pressure conditions, water may seep in through the gap.
Studies have shown that when exposed to rain, salt spray or humid conditions over a long period of time, these tiny channels will gradually expand, leading to water seepage, rusting and even structural failure. Therefore, in applications such as ships, automobiles and buildings, the waterproof riveting process is particularly important.
Can Water Penetrate Through a Rivet Hole?
Yes, water can indeed seep through the rivet holes. This situation is particularly common in the following scenarios:
- When using standard blind rivets → Ordinary blind rivets do not have a sealing design, and there is a tendency for tiny gaps to form between the material and the rivet.
- In outdoor, humid or high-pressure water environments → Under the long-term effects of rain, salt fog or water pressure, water is more likely to enter through the gaps.
- When the installation process is improper → If the hole diameter is too large or the rivet is not fully tightened, the risk of water seepage will significantly increase.
However, it is important to note that: By selecting the right type and optimizing the process, the risk of water seepage can be significantly reduced. For instance, using sealed rivets, combining with waterproof gaskets, and ensuring that the hole size precisely matches the rivets can all effectively prevent water from penetrating.
Industry experience shows that in shipbuilding and curtain wall projects, when using sealed rivets, the waterproof performance can be improved by 30% to 50%, significantly extending the service life of the structure.
Factors That Influence Water Penetration
Whether the rivet connection will leak water depends on the type of rivets, the installation process, and the usage environment. These factors interact with each other and directly determine the waterproof performance.
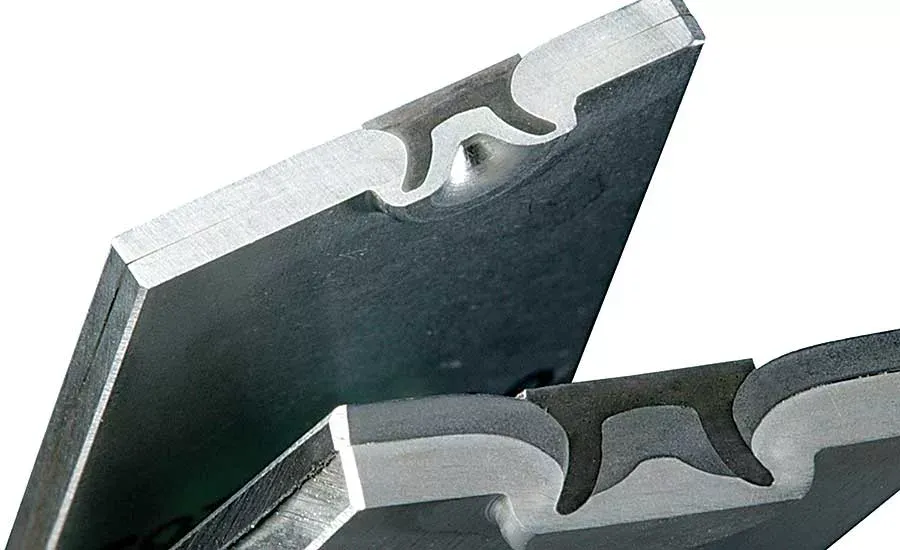
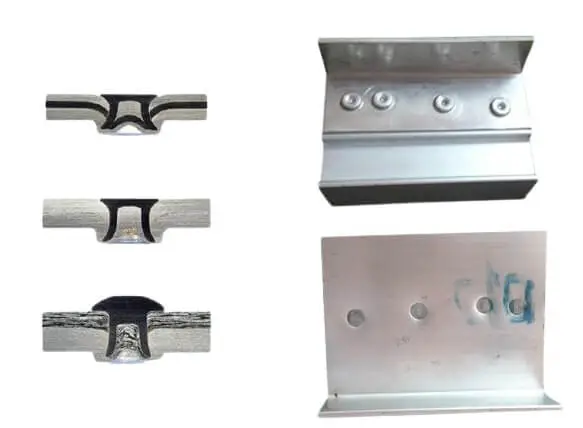
The core hole is completely through. It forms a “direct passage”. It is more prone to water seepage under rain pressure or wind pressure. If the hole diameter is slightly larger or if the molding is incomplete, the capillary effect will amplify the leakage. It is suitable for non-waterproof structures. When used outdoors, additional sealing is required.


The end is sealed. The broken core is sealed inside the body. It blocks the water intake path through the central axis of the rivet. Suitable for nodes requiring air/water tightness such as roofs, curtain walls, and vehicle roofs. It is recommended to choose the “large flange” layout. It can increase the compression area and improve the sealing surface fit.
Sealed Ring Rivets (Gaskets / O-Rings)
Seal rings made of EPDM/fluororubber are installed at the brim. Fill the gaps and absorb assembly deviations. It is recommended to use EPDM with a Shore A hardness of 60-70. It is universal, resistant to weathering, and UV-resistant. When the medium is oil/coolant/chemicals, use fluororubber (FKM) instead. It has better resistance to the medium.
The sleeve expansion is more thorough. It has a greater tolerance for hole diameter. The full-hole rate is high, and the probability of water seepage is lower. It is suitable for parts with large vibrations (such as the vehicle roof’s wind vibration and equipment frame).

2. Installation Process
Aperture and Tolerance
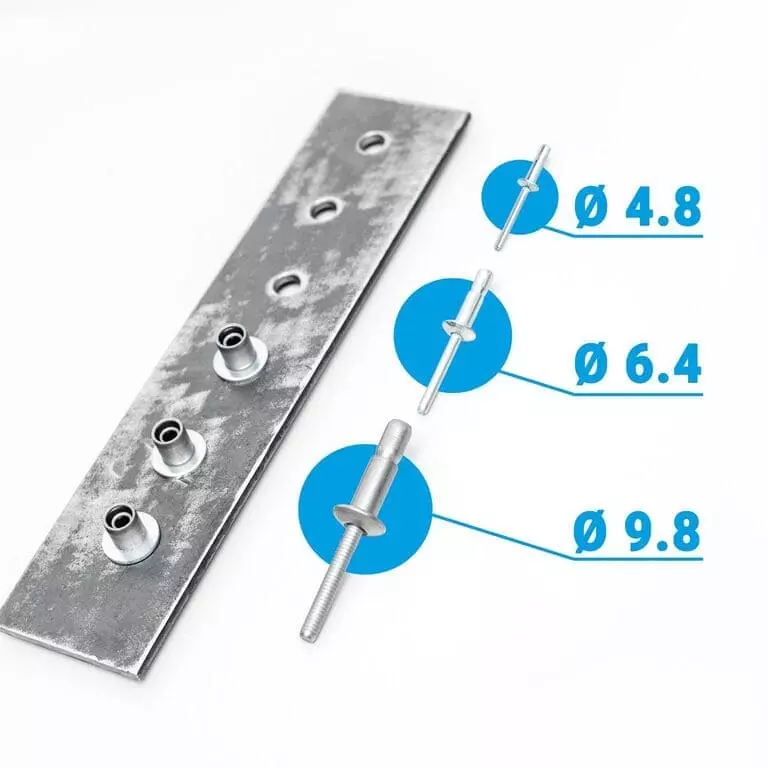
The hole size should be exactly matched with the diameter of the rivet body. Generally, it is recommended that D aperture = D rivet body + 0.10 to 0.20 mm (for small-sized thin plates). For steel substrates, the lower limit can be considered. To prevent the formation of “capillary waterways”, ensure that there is no excessive gap. The holes must be de-burred and chamfered. The burrs will widen the gap and damage the sealing rubber membrane.
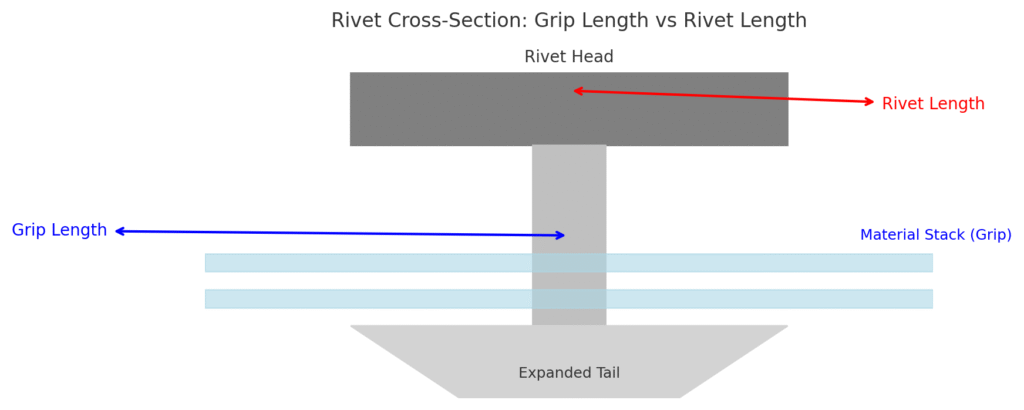
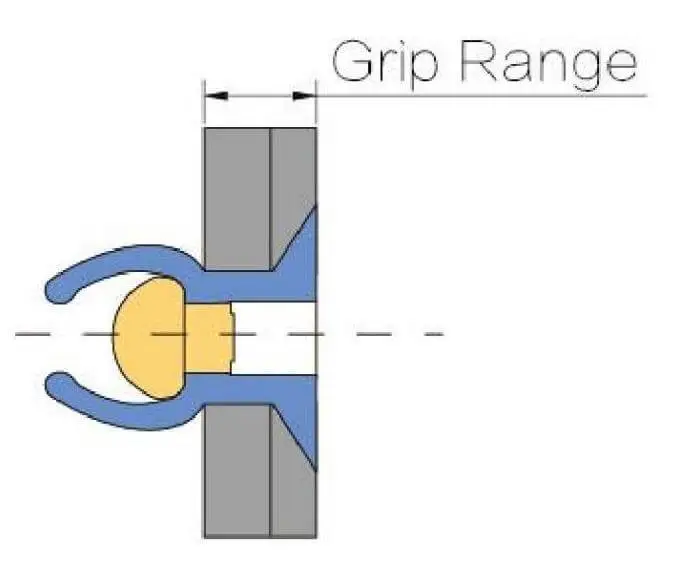
The selection should cover the actual layering thickness. If it is too short → not properly clamped, there will be gaps between the surfaces. If it is too long → the shape will be distorted, and the tail end may not bloom or be misaligned. Insufficient clamping is one of the main causes of water seepage.
3. Environmental Conditions
- Outdoor rain and wind pressure → Long-term exposure to rain and snow increases the risk of water seepage.
- Marine engineering and ship construction → High humidity and salt fog corrosion accelerate leakage and metal corrosion.
- HVAC systems and roof engineering → Condensation water and temperature difference cycles cause repeated expansion and contraction at joints, increasing the probability of water seepage.
How to Prevent Water Penetration Through Rivet Holes

Closed-End Blind Rivet
The end is sealed. It blocks the pull pin channel. It is naturally more waterproof. It is recommended to use large flange/flat head. This increases the compression area and reduces the gap between surfaces. For the wet side installation surface, use semi-round head instead of countersunk head. The countersunk head is more dependent on the adhesive and has lower tolerance.
With sealing ring or structural type (Sealed / Structural)
Choose the model with built-in O-ring/retainer ring. It can automatically compensate for minor assembly deviations.
Sealing material: EPDM (Shore A 60-70) – universal weather resistance; FKM – resistant to oil, refrigerants, and chemicals.
Structural/inserted-hole design, higher full-hole rate. More tolerant of hole tolerances, lower chance of water seepage.
Material and coating match the environment
Regular outdoor: Stainless steel or carbon steel + zinc nickel/ALMAC/dactro.
Marine and high salt spray environments: Stainless steel (A4) or Monel are preferred.
Avoid direct contact between aluminum and carbon steel. In case of necessity, add electrical isolation gaskets or coating isolation.
Model Selection Quick Reference
- For general outdoor applications, use closed-type blind rivets (with large cap).
- In case of heavy rain and wind pressure, use closed-type along with O-ring or washer.
- In vibration conditions, use structural-type blind rivets (with core retention/high clamping).
b. Add Sealing During Installation
Sealant
Select butyl/silicone/MS polymer/polyurethane. Requirements: UV resistance, water resistance, compatible with the substrate.
For sensitive materials such as polycarbonate, avoid acidic silicone. Use neutral curing type.
The sealing process should be continuous closed loop. Recommended 1-2 mm diameter sealing strips. No breaks are allowed.
Application and curing
Sequence: Clean → Apply adhesive → Insert pins → Pull pins → Make another ring of “Edge Sealant” on the outside.
Surface should be clean, dry and free of oil. Wipe with isopropyl alcohol and let it dry.
Avoid over-pressing at once. Excessive pressing can cause “air pockets”. It is advisable to have a slight amount of excess adhesive.
Gaskets/Washers
For the wet side, use a combination of metal pad and EPDM sealing pad. The metal pad bears the pressure, and the rubber provides the seal.
The compression amount should be controlled at 20-30% of the rubber thickness. If it is too loose, it won’t seal properly; if it is too tight, it will age easily.
Before re-tightening or applying additional glue, remove the old glue and the oxide layer first.
c. Process Optimization
Hole quality and tolerance
- Recommended hole diameter: D hole = D nail body + 0.10 – 0.20 mm (for small-sized thin plates).
- Deburr and chamfer. The burrs will widen the gap and disrupt the continuity of the adhesive film.
- The hole must be vertical. Inclined holes will cause the cap edge to not be properly pressed.
Clamping and Travel (Grip & Stroke)
- Grip Range covers the actual layer thickness. Too short → not clamped; too long → the tail does not open.
- Use a tool with controllable stroke or pulling force. Ensure consistency and repeatability of the broken core.
- The gun nozzle and the pull pin axis are perpendicular to the board surface. Avoid eccentric shaping.
Construction and Arrangement
- Use water flow reverse connection. Make the water flow away from the riveting line.
- Margin ≥ 1.5D – 2D, spacing ≥ 4D – 6D (D is the diameter of the rivet). Reduce edge leakage and stress concentration.
- If necessary, set up a second line of defense: main seal (rivet/ washer) + secondary seal (gluing along the joint).
| Industry | Water Leakage Risk | Recommended Rivet Type |
|---|---|---|
| Marine & Shipbuilding | High salt spray, high humidity, long-term seawater exposure | Stainless steel closed-end rivets + sealant |
| Automotive & RV Roofs | Continuous rain exposure, vehicle vibration | Closed-end blind rivets, optionally with sealing washers |
| Building Facades & HVAC | Wind pressure + rain infiltration, frequent temperature and humidity changes | Sealed rivets or structural rivets, applied with sealant |
Marine Engineering and Shipbuilding
It is necessary to use stainless steel closed rivets and combine them with waterproof sealant to resist corrosion from salt spray and seawater. Research shows that ordinary carbon steel rivets may experience rust and failure within six months in an ocean environment.
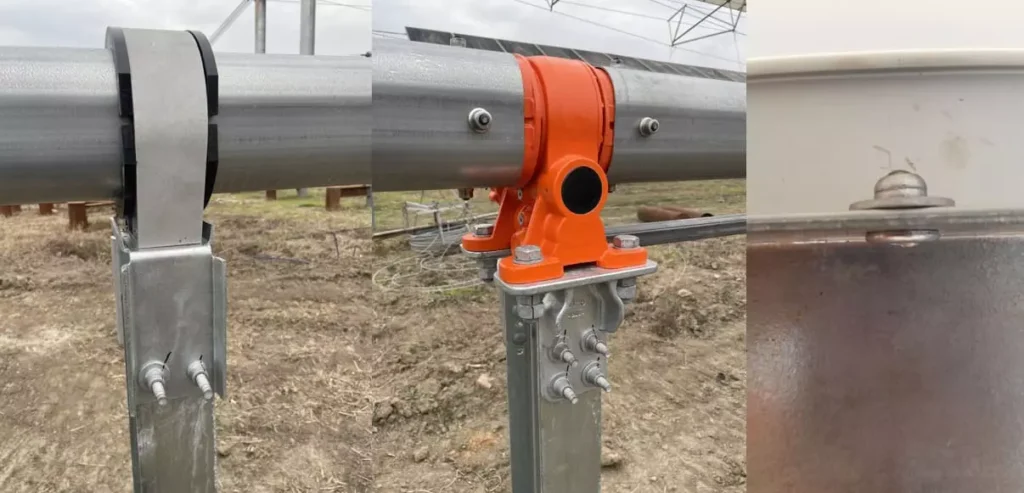
Car and RV Roof
The closed-type rivets can effectively prevent rainwater from seeping through the core holes. For the vehicle roofs that are exposed to rain and snow for a long time, it is also recommended to install rubber gaskets to enhance the sealing effect.
Building Curtain Wall and HVAC System
Changes in wind pressure and temperature as well as humidity can easily cause small gaps at the joints of curtain walls. For such applications, it is recommended to use sealing or structural rivets, and apply sealant during installation to ensure long-term waterproofing.
Rivmate Expertise & Solutions

Rivmate is well aware that different industries have varying requirements for waterproofing and corrosion prevention. Therefore, we offer a complete range of rivet products and technical support to help customers effectively manage the risk of water seepage.
Rivmate Product Coverage
- Closed-End Blind Rivets Designed specifically for waterproof and air-proof applications, it effectively prevents moisture and air from entering through the core hole.
- Rivets with sealing rings
Adding sealing rings at the head or tail of the rivets creates an additional barrier, suitable for use in curtain walls and vehicle roofs. - Multiple material options (aluminum, stainless steel, Monel)
Choose the optimal solution based on the application environment: Aluminum is suitable for lightweighting, stainless steel is suitable for outdoor use, and Monel is suitable for marine and extremely corrosive environments.
Rivmate Technical Support
- Waterproof Selection Guide
For different working conditions, detailed suggestions on bolt selection are provided to help customers avoid potential water seepage problems caused by incorrect selection. - Process Improvement Suggestions
Including aperture control, sealant application and installation force calibration, to ensure the best sealing effect. - Customized anti-corrosion and waterproof solutions
Special surface treatments and structural optimizations can be provided according to customer requirements, meeting the long-term durability standards.
FAQs
Q1: Will all the rivets leak water?
Answer: Not all rivets will leak. Standard blind rivets do have a risk of water leakage when there is no sealing design. However, closed-type rivets or the riveting process combined with sealant can effectively prevent water leakage.
Q2: Can the closed-type rivets completely prevent water from penetrating?
Answer: Closed-type rivets can significantly enhance the waterproofing performance. However, in environments with high-pressure water or prolonged exposure, it is still recommended to use sealants or waterproof gaskets in conjunction to ensure long-term reliability.
Q3: Is additional sealant required when installing on the roof?
Answer: It is recommended to use. The roof is constantly exposed to rain, snow and temperature fluctuations. The sealant can fill the tiny gaps between the materials and the rivets, thereby extending the lifespan of the waterproofing.
Q4: Can Rivmate provide waterproof rivets suitable for marine environments?
Answer: Yes. Rivmate offers stainless steel closed rivets and Monel material rivets, and they can be combined with high-performance anti-corrosion coatings, ensuring waterproofness and durability even in salt spray and high humidity environments.
Seal Your Projects with Confidence – Choose Rivmate Rivets

No matter whether you are dealing with marine environmental protection for ships, roof waterproofing for cars, or sealing for building curtain walls, Rivmate can offer you the most reliable waterproof riveting solutions.
Not only do we offer closed-type blind rivets, rivets with sealing rings, and multiple material options, but we also provide customers with waterproof selection guidelines, process optimization suggestions, and customized solutions.
Choose Rivmate and ensure that your project achieves higher durability and zero leakage protection.

How to Rivet Metal to Wood?
How to Rivet Metal to Woo

What Is Riveting in Metal Work?
What Is Riveting in Metal

What Metal Are Rivets Made Of
What Metal Are Rivets Mad

How to Rivet Metal to Metal
How to Rivet Metal to Met